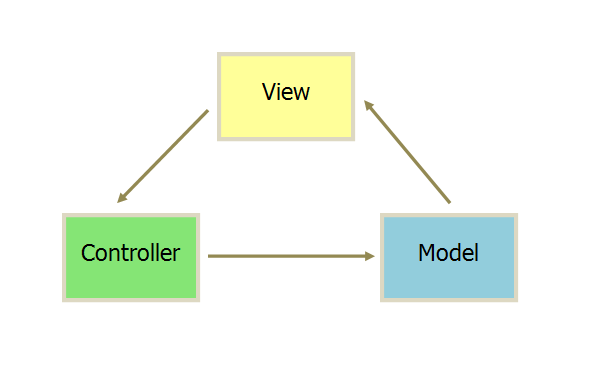
MVC 模式下,软件被划分为视图(View:用户界面)、控制器(Controller:业务逻辑)、模型(Model:数据保存)
- 用户操作 View,在 View 上面的事件都将被传递到 Controller 处理
- Controller 处理事件、请求网络,操作 Model 更新状态
- Model 将更新后的数据发送到 View,用户得到反馈
所有的通信都是单向的。
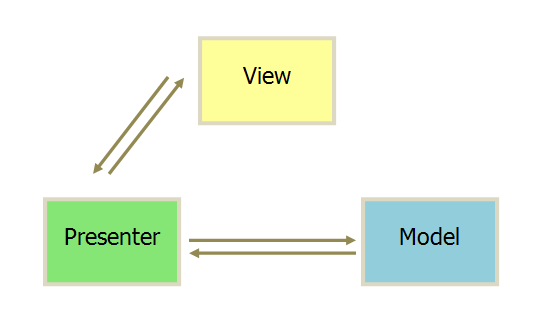
MVP 模式将 Controller 改名为 Presenter,通信改变了通信方向
- 各部分之间的通信都是双向的
- Model 与 View 不发生联系,都通过 Presenter 传递
- View 层非常薄。不部署任何业务逻辑,称为“被动视图(Passive View)”,即没有任何主动性,而 Presenter 非常厚,所有的逻辑都部署在这层
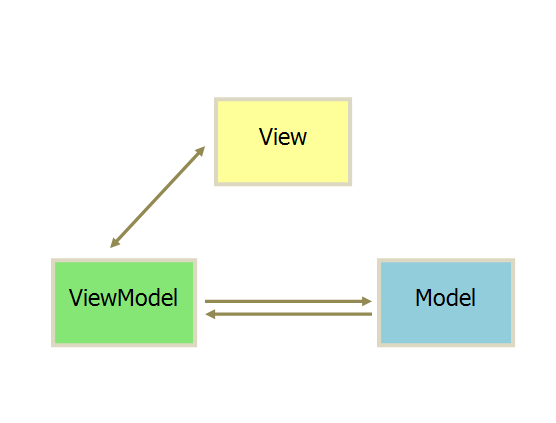
MVVM 模式将 Presenter 改名为 ViewModel,基本上与 MVP 模式完全一致。
区别在于:采用双向绑定的模式。View 的改变,自动反应在 ViewModel 上。 ViewModel 的改变会发应在 View 上。
MVC 等到业务逻辑很复杂的时候�被称为 �Massive View Controller (重量级视图控制器)。这样的 Controller 后期维护看着阅读成本很高、不易于测试、维护。当时写这个代码的人离职后,几千行规模的代码在后期添加新功能或者修改 Bug 都是一件折磨人的事情。
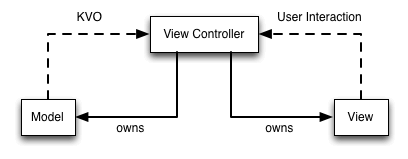
�看到 View 和 ViewController 是不同的技术组件,但是日常开发中它们总是成对的存在,为什么不考虑将他们的连接正规化呢?
典型的 MVC 存在弊端就是 Controller 层非常复杂,很多逻辑都在里面,包括一些不是逻辑的“表示逻辑”(presentation logic)。用 MVVM 术语来说就是将那些 Model 数据转换为 View 可以呈现的东西。例如将一个 NSDate 格式化为一个“2018-11-17” 这样的 NSString。
上图中缺少一个环节,一个专门�用来处理所有的表示逻辑。称为 “ViewModel”。位于 ViewController 与 Model 之间。
MVVM 就是 MVC 的增强版,将展示层逻辑单独拎出来,即 ViewModel。iOS 使用 MVVM 可以降低 ViewController 的复杂性并使得�表示逻辑易于测试。
- MVVM 兼容当下的 MVC 机构
- MVVM 增加应用的可测试性
- MVVM �配合一个绑定机制效果最好
PersonModel
@interface Person : NSObject
- (instancetype)initwithSalutation:(NSString *)salutation firstName:(NSString *)firstName lastName:(NSString *)lastName birthdate:(NSDate *)birthdate;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *salutation;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *firstName;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *lastName;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSDate *birthdate;
@end
PersonViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
if (self.model.salutation.length > 0) {
self.nameLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@ %@", self.model.salutation, self.model.firstName, self.model.lastName];
} else {
self.nameLabel.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", self.model.firstName, self.model.lastName];
}
NSDateFormatter *dateFormatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init];
[dateFormatter setDateFormat:@"EEEE MMMM d, yyyy"];
self.birthdateLabel.text = [dateFormatter stringFromDate:model.birthdate];
}
上面是标准的 �MVC。现在我们考虑用 ViewModel 增加改进下
PersonViewModel
@interface PersonViewModel : NSObject
- (instancetype)initWithPerson:(Person *)person;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) Person *person;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *nameText;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) NSString *birthdateText;
- (instancetype)initWithPerson:(Person *)person;
@end
@implementation PersonViewModel
- (instancetype)initWithPerson:(Person *)person {
self = [super init];
if (!self) return nil;
_person = person;
if (person.salutation.length > 0) {
_nameText = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@ %@", self.person.salutation, self.person.firstName, self.person.lastName];
} else {
_nameText = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@ %@", self.person.firstName, self.person.lastName];
}
NSDateFormatter *dateFormatter = [[NSDateFormatter alloc] init];
[dateFormatter setDateFormat:@"EEEE MMMM d, yyyy"];
_birthdateText = [dateFormatter stringFromDate:person.birthdate];
return self;
}
@end
此时,我们的 ViewController 会很轻量
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.nameLabel.text = self.viewModel.nameText;
self.birthdateLabel.text = self.viewModel.birthdateText;
}
�
可测试?View Controller 是出了名的难测试。因为传动的 VC �很重,在 MVVM 的世界里,代码各司其职,测试 View Controller 变得较为容易
SpecBegin(Person)
NSString *salutation = @"Dr.";
NSString *firstName = @"first";
NSString *lastName = @"last";
NSDate *birthdate = [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSince1970:0];
it (@"should use the salutation available. ", ^{
Person *person = [[Person alloc] initWithSalutation:salutation firstName:firstName lastName:lastName birthdate:birthdate];
PersonViewModel *viewModel = [[PersonViewModel alloc] initWithPerson:person];
expect(viewModel.nameText).to.equal(@"Dr. first last");
});
it (@"should not use an unavailable salutation. ", ^{
Person *person = [[Person alloc] initWithSalutation:nil firstName:firstName lastName:lastName birthdate:birthdate];
PersonViewModel *viewModel = [[PersonViewModel alloc] initWithPerson:person];
expect(viewModel.nameText).to.equal(@"first last");
});
it (@"should use the correct date format. ", ^{
Person *person = [[Person alloc] initWithSalutation:nil firstName:firstName lastName:lastName birthdate:birthdate];
PersonViewModel *viewModel = [[PersonViewModel alloc] initWithPerson:person];
expect(viewModel.birthdateText).to.equal(@"Thursday January 1, 1970");
});
SpecEnd