A Distributed Microservice RPC Framework | Chinese Documentation | SpringBoot conformity RPC
- Solutions based on
SocketandNettyasynchronous non-blocking communication. - Cross-language protocol communication is supported, including other languages such as
GoLang. - Support
JdkandJavassisttwo dynamic proxy. - is suitable for 'IO' intensive scenario applications based on' Netty'. Although the performance is not as good as the' CPU' intensive scenario applications, concurrency is the best.
- support distributed timeout retry mechanism, idempotent historical result elimination strategy, asynchronous caching for efficient communication.
- Implementation of
idgenerator usingJedis/Lettucetwo snowflake-based algorithms; - Support 'JDK' built-in 'SPI' mechanism, in the extension of dynamic configuration, registry, service discovery and service provision, to achieve non-intrusive programming.
- registry high availability, providing clustered registries that can continue to serve users through caching even after all registered nodes are down.
- Providing personalized services, introducing personalized service
name, servicegroup, suitable in test, experimental and formal environments, as well as providing better services for compatibility, maintenance and upgrading of later versions. - Provide cluster registry downtime restart service.
- Providing unlimited horizontal scaling of the service.
- provide two load balancing policies for the service, such as random and polled load.
- provide request timeout retry and guarantee the idempotency of business execution, timeout retry can reduce the delay of thread pool tasks, thread pool guarantees the stability of the number of threads created under high concurrency scenarios, but thus brings delay problems, deal with the problem can be enabled retry requests, and retry reaches the threshold will abandon the request, consider the service temporarily unavailable, resulting in business loss, please use with caution.
- provide custom annotated extensions to the service, using proxy extensions that can non-intrusively extend personalized services.
- provide scalable serialization services, currently providing
KryoandJacksontwo serialization methods . - provide a logging framework
Logback. - provides Netty extensible communication protocol, the communication protocol header uses the same 16-bit magic number
0xCAFEBABEas Class, packet identification id to identify request and response packets,reslength to prevent sticky packets, and finallyres, which internally adds a check digit and a unique identification id to allow the server to efficiently handle multiple different request packets or resend request packets at the same time, and packet validation. - Support second-level clock callback server to take the initiative to block the client request strategy, more than minutes-level clock callback server to take the initiative offline strategy.
- In conjunction with the timeout retry mechanism, silence and retransmission of hijacked packets are adopted to enhance the security of communication.
- Supports one-way delay shutdown processing requests on the server side.
- supports extension' Bean' custom instantiation to meet third-party frameworks such as' Spring' dependency injection and tangent execution.
Architecture Diagram
- Retry mechanism architecture diagram
- Service Discovery and Registration Architecture Diagram
- Load Balancing Policy
- Serialization policy
- Auto-discovery and logout services
- Registration Center
- Standalone and Cluster
- Heartbeat mechanism
- Message digest
- Timeout retry mechanism
- Idempotency
- Robustness
- Singleton Pattern
- Dynamic Proxy
- Static Factory
- Builder
- Strategy Mode
- Future (Observer)
The use of the information digest algorithm is actually not difficult. It can be achieved by adding a member variable checkCode of type String to the data packet for anti-counterfeiting.
- Principle
The sender encrypts the original message into a digest with the HASH function, and then sends the digital digest together with the original message to the receiver. The receiver also uses the HASH function to encrypt the original message into a digest to see if the two digests are the same. Indicates that the information is complete. Otherwise, it is incomplete.
- accomplish
When the client sends a request packet, the server will use MD5 one-way encryption to become a unique information digest (128 bits, 16 bytes) after the content of the request execution result is converted into bytecode and stored in the response packet. The corresponding member variable checkCode, so after the client gets the response packet, the most valuable place (the result of the request to be executed is changed), then the checkCode will not guarantee consistency, which is the principle of the information summary application.
Security Enhancements
Considering that this is only for the consistency of results returned by customer requirements, and does not ensure that the same request content exists between request packets, the request id is introduced.
Each packet will generate a unique requestId. After the request packet is sent, the packet can only be accepted by the client that sent the request. Even if one of the two places is maliciously changed by the other party, the client will report an error and discard the received The response packet will not be unpacked and returned to the user.
If not only the returned result is changed, but both the result and the message digest are modified, it is difficult for the other party to ensure that the modified content is the same as the modified message digest after encryption, because it is necessary to ensure the consistent data transmission protocol and data encoding and decoding.
The RPC of the heartbeat mechanism is widely used. The implementation of the heartbeat mechanism in this project is very simple, and the countermeasure is to force the server to disconnect. Of course, some RPC frameworks implement the server to actively try to reconnect.
- Principle
For the application of the heartbeat mechanism, a handler processor in the Netty framework is actually used. Through the handler, the heartbeat packet is sent regularly to let the server know that the client remains active.
- Accomplish
Utilize the IdleStateEvent event listener in the Netty framework, rewrite the userEventTriggered() method, listen for read operations on the server side, read client write operations, monitor write operations on the client side, and monitor whether it is still there Activity, that is, whether there is a request sent to the server.
If the client does not actively disconnect the connection with the server, but continues to maintain the connection, then after the client's write operation times out, that is, the client's listener listens to the client to make a write operation event within the specified time, then at this time The client processor actively sends a heartbeat packet to the server to ensure that the client allows the server to ensure that it remains active.
Resource directory META-INF/services under the new interface fully qualified name as a file name, the contents of the implementation class fully qualified name, support JDK built-in SPI.
The essence to create instances through reflection to create instances without parameters, if the constructor involves the injection of members through parameters, then the interface can be converted to an abstract class, the abstract class exposes the set method to allow subclasses to override, thus indirectly achieve injection.
This mechanism separates the implementation of the interface when the registry logic layer handles service discovery and registration to the configuration file META-INF/services, thus better supporting other plugins such as Zookeeper, Eureka extensions.
Configuration files applied to.
cn.fyupeng.discovery.ServiceDiscovery
cn.fyupeng.discovery.NacosServiceDiscoverycn.fyupeng.provider.ServiceProvider
cn.fyupeng.provider.DefaultServiceProvidercn.fyupeng.registry.ServiceRegistry
cn.fyupeng.registry.NacosServiceRegistryIO asynchronous non-blocking allows the client to be in a blocking state when requesting data, and can process things of interest during the time period when the requested data is returned.
- Principle
Using the CompletableFuture concurrency tool class born in java8, it can process data asynchronously and obtain it when needed in the future.
- accomplish
The data is transmitted in the channel channel between the server and the client. The client sends a request packet to the channel and needs to wait for the server to return. In this case, you can use CompletableFuture as the return result, just let the client read the After the data, the result is put in the value through the complete() method, and the result is obtained through the get() method in the future.
- define
/**
* custom object header protocol 16 bytes
* 2 bytes magic number
* 1 bytes protocol packet type
* 1 bytes serialized type
* 4 bytes data length
*
* The transmission protocol is as follows :
* +---------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+
* | Magic Number | Package Type | Serializer Type | Data Length |
* | 2 bytes | 1 bytes | 1 bytes | 4 bytes |
* +---------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+
* | Data Bytes |
* | Length: ${Data Length} |
* +---------------+---------------+-----------------+-------------+
*/The RNF protocol is the upper application protocol and is in the application layer, the TCP protocol is the transport protocol, that is, the upper layer transport has TCP unpacked into RNF packets, and the lower layer transport is RNF packets encapsulated into TCP packets.
- Unpacking analysis
Frame 30759: 368 bytes on wire (2944 bits), 368 bytes captured (2944 bits) on interface \Device\NPF_Loopback, id 0
Null/Loopback
Internet Protocol Version 4, Src: 192.168.2.185, Dst: 192.168.2.185
Transmission Control Protocol, Src Port: 53479, Dst Port: 8085, Seq: 4861, Ack: 4486, Len: 324
RNF Protocol
Identifier: 0xcafebabe
PackType: 726571
SerializerCode: 2
Length: 308
Data [truncated]: C\036cn.fyupeng.protocol.RpcRequest�\trequestId\rinterfaceName\nmethodName\nreturnType\005group\theartBeat\nparameters\nparamTypes`\025230113199152359542784\fhelloService\bsayHelloC\017java.lang.Class�\004namea\036cn
Identifier (0xcafebabe): indicates the identifier, while 0xCAFEBABE is the object header representation of the java object.
PackType (726571, 726573): 726571 is converted from the ASCCI code of the character res (\u0072\u0065\u0073), req is the same.
SerializerCode (0,1,2): currently provides three (json,kryo,hesian2) serialization methods, corresponding to (0,1,2).
Length (308): indicates the length of Data.
Data [truncated] (C\036cn.fyupeng.protocol.RpcRequest... ): Indicates a ${PackType} package of length ${Length} using the ${SerializerCode} serialization method.
Use Wireshare local connection to capture and write RNF protocol decoder in lua language to understand the packet hierarchy more intuitively.
If you want to understand the decoder, you can download it directly from the root directory, put it in the lua plugin plugins of Wireshark, and reload the plugin.
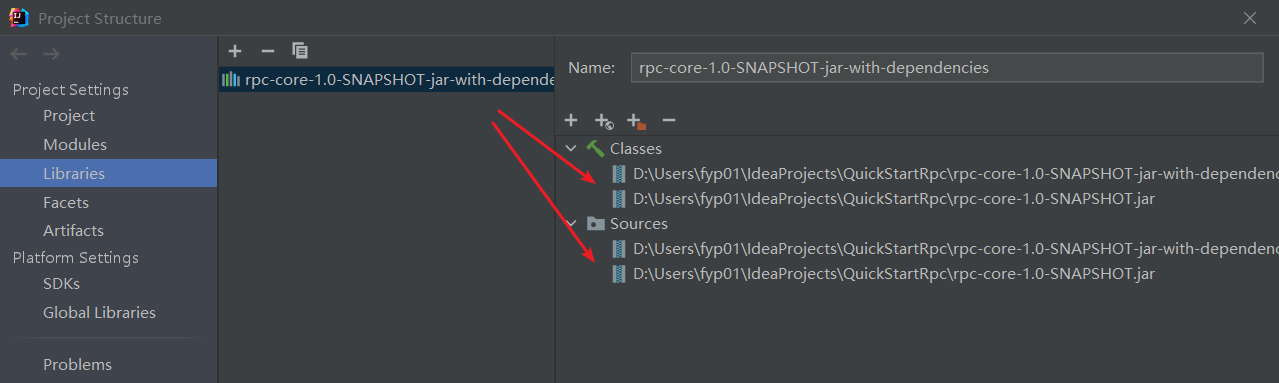
First import two jar package files rpc-core-1.0.0.jar and rpc-core-1.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar
The jar package includes bytecode files and java source code. After introduction, class and sources will be automatically imported together. The source code can be used as a reference
Import the following maven will also import the dependencies of rpc-common and the default registry center framework nacos-client
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.fyupeng</groupId
<artifactId>rpc-core</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5</version>
</dependency>Only configuration is supported before 2.1.0 version
# Standalone mode
cn.fyupeng.nacos.register-addr=192.168.10.1:8848
# Cluster mode
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.use=false
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.load-balancer=round
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.nodes=192.168.43.33:8847|192.168.43.33.1:8848;192.168.43.33.1:8849Version 1.0 only supports @Service and @ServiceScan annotations
Version 2.0.5 is a standalone version, supports @Reference annotation, uses local cache to solve single node timeout retry, can't handle multi-node timeout retry.
Note
Use the annotation @Reference to get the proxy must pass the class where the annotation is located to the proxy, otherwise the annotation will be invalid
public class Client {
private static RandomLoadBalancer randomLoadBalancer = new RandomLoadBalancer();
private static NettyClient nettyClient = new NettyClient(randomLoadBalancer, CommonSerializer.HESSIAN_SERIALIZER);
private static RpcClientProxy rpcClientProxy = new RpcClientProxy(nettyClient);
/**
* Pass Client.class to the proxy so that the proxy can capture the annotation @Reference
*/
@Reference(name = "helloService", group = "1.0.0", retries = 2, timeout = 2000, asyncTime = 18000, giveTime = 1)
private static HelloWorldService service = rpcClientProxy.getProxy(HelloWorldService.class, Client.class);
}2.1.0 and later introduced
# Standalone mode
cn.fyupeng.nacos.register-addr=192.168.10.1:8848
# Cluster mode
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.use=false
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.load-balancer=round
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.nodes=192.168.43.33:8847|192.168.43.33.1:8848;192.168.43.33.1:8849
# Implement distributed caching (necessary, not to do default on or off)
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-addr=localhost:6379
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-auth=true
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-pwd=yupengRedis
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-way=lettuce
cn.fyupeng.redis.client-way=jedis
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-async=trueThe annotation @Reference is supported for solving timeout retry scenarios.
Recommend using the latest version 2.1.7, 2.0 version introduces distributed caching, which solves some problems arising from distributed scenarios.
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.fyupeng</groupId
<artifactId>rpc-core</artifactId>
<version>2.1.10</version>
</dependency>Recommend another maven official repository
<mirror>
<id>repo1maven</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<name>maven public repository</name
<url>https://repo1.maven.org/maven2</url
</mirror>-m:模式,standalone:单机
命令使用:
startup -m standaloneNote: Open source RPC uses the local port number 8848 specified by nacos by default
Official Documentation:https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html
Advantage:
Nacos was chosen as the registry because of the high availability for long-term service reliability
- A list of registry services is kept locally
- Services remain available during automatic restart recovery of down nodes
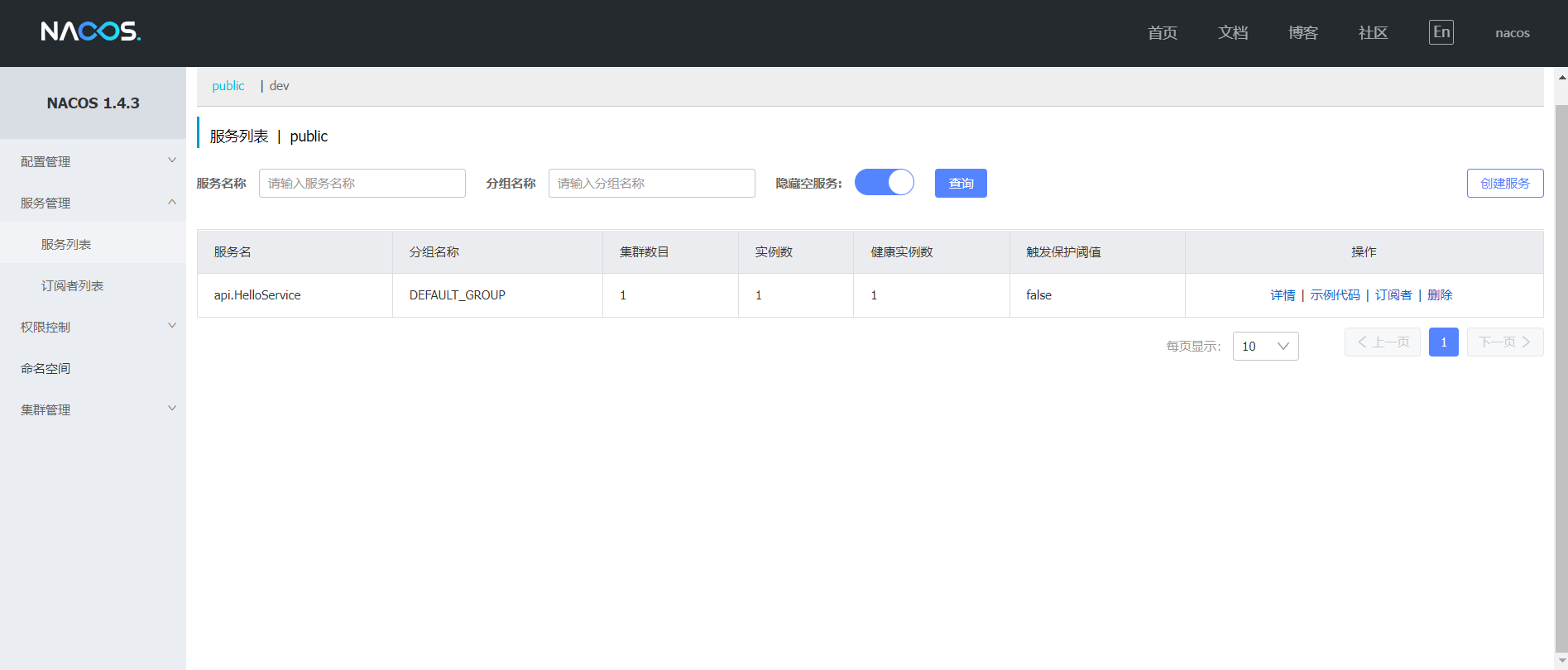
Nacos start effect:
public interface HelloService {
String sayHello(String message);
}- Real Service
@Service
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String sayHello(String message) {
return "hello, here is service!";
}
}- Service Launcher
@ServiceScan
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
NettyServer nettyServer = new NettyServer("127.0.0.1", 5000, SerializerCode.KRYO.getCode());
nettyServer.start();
} catch (RpcException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}Note:
- add annotations' cn.fyupeng.annotation.Service' and' cn.fyupeng.annotation.ServiceScan' to be scanned by the automatic discovery service and registered to nacos.
- the self-management container uses reflection creation by default, which will cause Spring annotation dependency injection and tangent failure. for the solution, please move to [SpringBoot integration RPC](/document/springboot integration rpc-netty-framework.md)
There are two ways to connect to the server when initializing the client:
-
Direct connection
-
use load balancing
public class MyClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
RoundRobinLoadBalancer roundRobinLoadBalancer = new RoundRobinLoadBalancer();
NettyClient nettyClient = new NettyClient(roundRobinLoadBalancer, CommonSerializer.KRYO_SERIALIZER);
// Jdk dynamic proxy
HelloService helloService = rpcClientProxy.getProxy(HelloService.class);
// Javassist dynamic proxy
//HelloService helloService = rpcClientProxy.getJavassistProxy(HelloService.class);
HelloService helloService = rpcClientProxy.getProxy(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.sayHello("hello");
System.out.println(result);
}
}- Project mode start
Add resource.properties to resources
The hostname is specified using localhost or 127.0.0.1
cn.fyupeng.nacos.register-addr=localhost:8848
Jarway to start
, Compatible with springboot external startup configuration file injection, you need to create a config folder in the same directory as the Jar package, and inject the configuration file in config like springboot, but the configuration injected by springboot The file default constraint name is application.properties, and the rpc-netty-framework default constraint name is resource.properties.
Add logback.xml to resources
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<appender name="console" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<!--%date{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %c -->
<pattern>%date{HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%level] %c [%t] - %m%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="info">
<appender-ref ref="console"/>
</root>
</configuration>In addition, the framework also provides Rpc services in Socket mode
- Support springBoot integration
In order to support springBoot to integrate logback logs, inherit rpc-netty-framework to use the same set of logs, abandon the built-in slf4j-api of nacos-client and the original Jar package of commons-loging, Because this framework will lead to repeated log binding and log printing method parameter compatibility problems when integrating springboot, this problem can be solved by using jcl-over-slf4j-api;
In springboot1.0 and 2.0 versions, instead of using its default version of spring-boot-starter-log4j, it is recommended to use 1.3.8.RELEASE;
The simple configuration of springboot is as follows
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!-- Exclude springboot's default logback logging framework -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
<!-- Exclude the default commons-logging implementation of springboot (the version is low, and there is a problem that the method cannot be found) -->
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jcl</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- Integration with logback (available via @Slf4j annotation) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- import log4j log dependency, the purpose is to use jcl-over-slf4j to rewrite the implementation of commons logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.3.8.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.use=true
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.load-balancer=random
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.nodes=192.168.10.1:8847,192.168.10.1:8848,192.168.10.1:8849-
Usage and Points to Note
By default,
cn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.useobeys the convention better than the configuration setting, and the default value isfalse, indicating that the cluster is not opened by defaultcn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.load-balancerandcn.fyupeng.nacos.cluster.nodesmust be turned on in cluster mode before they can be used. -
Cluster node load policy
random: random policyround: polling policy
-
Cluster node fault-tolerant switching
- Node downtime: When a node is down, it will re-elect a new normal node from the node configuration list, otherwise it will retry infinitely
Cluster nodes are theoretically infinitely scalable and can be extended using the separator [;,|].
The retry mechanism is not used by default, in order to ensure the correctness of the service, because there is no guarantee of idempotency.
The reason is that the client cannot detect whether there is a problem in the client's network transmission or a problem in the server's network transmission on the way back after receiving correctly, because if the former is the case, then retrying can guarantee idempotency, but if the latter is the case, it may lead to multiple executions of the same service, which is a non-consistent result for the client.
The timeout retry mechanism can cause idempotence problems, so adding a reissue flag bit to the client request packet indicates a reissue, and using 'HashSet' to add the request 'id' in the server for timeout cache processing.
- timeout retry: 'cn.fyupeng.annotation.Reference' annotation provides multiple configuration parameters for retry times, timeout time, asynchronous time, and retry, where:
- Number of retries: the number of times the server fails to respond within the timeout period and is allowed to trigger a timeout
- Timeout time: the maximum time allowed for the client to wait for the server, and the timeout triggers the retry mechanism
- Asynchronous time: the time to wait for the asynchronous response from the server, and can only be used in the timeout retry mechanism, the default use of non-timeout retry blocking wait mode
- Retry surrender time: the default is 1 second, which reduces the competition of thread scheduling cpu resources and can solve the problem of low throughput of 'cpu'
For Example:
private static RandomLoadBalancer randomLoadBalancer = new RandomLoadBalancer();
private static NettyClient nettyClient = new NettyClient(randomLoadBalancer, CommonSerializer.KRYO_SERIALIZER);
private static RpcClientProxy rpcClientProxy = new RpcClientProxy(nettyClient);
@Reference(retries = 2, timeout = 1000, asyncTime = 3000, giveTime = 1)
private static HelloWorldService service = rpcClientProxy.getProxy(HelloWorldService.class, Client.class);- Idempotency
The retry mechanism server side should guarantee the principle of executing the retry packet once, i.e., to achieve idempotency.
Implementation idea: with the help of distributed cache for the first request packet asynchronous cache request id, distributed cache selection Redis, client selection Jedis and Lettuce, given a key expiration time to meet the retry mechanism to reduce the steps to clean up the cache again.
The idempotency acts on the expiration time, which also affects the number of retries of the timeout mechanism as well as the high concurrency scenario. There is the advantage of the snowflake algorithm, which does not generate duplicate ids at different times, so you can boldly set the expiration time larger, depending on how much memory you can afford and turn to the memory bottleneck.
/**
* Custom distributed id number only
* 1-bit Symbol bit
* 41-bit Timestamp
* 10-bit Worker id
* 12-bit Concurrent Sequence Number
*
* The distribute unique id is as follows :
* +---------------++---------------+---------------+-----------------+
* | Sign | epoch | workerId | sequence |
* | 1 bits | 41 bits | 10 bits | 12 bits |
* +---------------++---------------+---------------+-----------------+
*/- Introduction
Snowflake algorithm: It mainly consists of three parts: timestamp, machine code and sequence code, and each part has a representative meaning.
Sign Bit
Represents the sign bit, with a fixed value of 0, indicating a positive number.
Timestamp
The timestamp represents the running time, it consists of 41 bits and can be used up to 69 years, expressed by the difference between the current system timestamp and the early morning timestamp of the day the service starts.
Machine Code
Machine code represents distributed nodes, it consists of 10 bits and can represent up to 1024 machine codes, which are generated by default using the current service host number hashCode, high-low dissimilarity and distributed caching algorithm, machine code generation exceptions are generated by SecureRandom using random seeds, AtomicLong and CAS locks, when machine code maximum number will throw an exception WorkerIdCantApplyException.
Sequence Number
Sequence number code concurrency, which occurs in the same millisecond, i.e. millisecond concurrency as part of a unique value, it consists of 12 bits and can represent up to 4096 sequence numbers.
- Application Scenarios
(1) Multi-service node load to achieve business persistence primary key unique
(2) The maximum number of concurrent requests within milliseconds can reach 4095, and the sequence number can be changed appropriately to meet different scenarios
(3) Meet the basic ordered unique number id, conducive to efficient index query and maintenance
(4) id number before the 6 bit attached to the current time year month day log query, can be used as a log record
And in RPC mainly used the snowflake algorithm to achieve the unique identification number of the request packet, because UUUID generation uniqueness and time continuity than the snowflake algorithm is better, but it id value is non-increasing sequence, in the index establishment and maintenance of higher cost.
The 'id' generated by the snowflake algorithm is basically orderly increasing, distributed and unique, and has low maintenance cost. It can be used as a primary key or other index value at the cost of relying on the machine clock. The server must manually set the system time synchronization when restarting.
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-addr=127.0.0.1:6379
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-auth=true
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-pwd=123456In addition to this, the timeout retry mechanism, in the distributed scenario, the second retry will be loaded to other service nodes through the load balancing policy, using the snowflake algorithm to make up for the problem of the inability to solve the idempotency in the distributed scenario.
Timeout retry uses Jedis/Lettuce two ways to implement caching, and the corresponding caching connection client ways can be configured on the server side and client side respectively.
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-way=lettuce
cn.fyupeng.redis.client-way=jedis
cn.fyupeng.redis.server-async=trueHow do I choose between JRedisHelper and LRedisHelper?
JRedisHelper
- Thread safety
- Pessimistic locking mechanism for
synchronizedandlock - No thread pooling
- Connection count of
1 - Synchronized operations
- Cache and get machine
idby host number - Cache and fetch request results based on request
id
LRedisHelper
- Thread safety
- Provides thread pooling
- Connection count is stable and provided by the thread pool
- Asynchronous/synchronous operations
- Provides caching and fetching machine
idby host number - Provide caching and fetching of request results based on request
id
Special Reminder
Highly concurrent requests do not have duplicate request numbers, the current maximum millisecond concurrency 4096, and the timeout mechanism, LRedisHelper thread pool on the connection timeout control and other configuration parameters are not mature, specific application scenarios can download the source code to modify the parameters.
With the support of Netty high-performance framework, there are single Reactor single-threaded, single Reactor multi-threaded and master-slave Reactor multi-threaded, using the best performance master-slave Reactor multi-threaded, the advantage is that when concurrent processing of multiple service nodes (in the case of multiple channel), from the workGroup in each However, in the case of a single channel carrying high concurrency, multiple threads cannot process events simultaneously because a channel can only bind one thread.
If multiple threads handle a channel at the same time, there will be a security problem similar to the one that occurs with Redis multi-threaded operation with Jedis, where multiple threads responding to a channel will make the situation extremely complicated. As long as the channel is distributed again to the thread pool, the thread that gets the channel can read the message and write the return message to the server itself.
This way, the single thread responsible for reading the channel bindings only needs to submit the task to the thread pool, without blocking, to handle the highly concurrent requests.
In terms of code details, reading the channel event means that the cache buffer has been read and will not affect other threads to continue reading the channel, but of course there will be a short blocking here because reading also takes some time, so there will not be multiple tasks submitted to perform crossover behavior.
The fast read here also involves zero copy, the data in the user state is not copied, directly transparent use.
Of course, there is still a problem to be considered under high concurrency. When the task processing is too slow, the client cannot be blocked and waited all the time. Timeout can be set to avoid giving up to other threads in need because a task on the server affects the execution of other requests. Therefore, the timeout mechanism introduced is combined with distributed cache. Under the timeout mechanism, either the result cached on the server after the first request is directly returned or directly failed, to ensure a high concurrency stability.
- ServiceNotFoundException
Throws exception ServiceNotFoundException
Stack information: service instances size is zero, can't provide service! please start server first!
Under normal circumstances, general errors can be resolved from the error report.
Solve the situation that the real service does not exist, resulting in an abnormal situation in the strategy used in the load balancing. After the repair, a ServiceNotFoundException will be forced to be thrown. Perhaps the service is not started in most cases.
Of course, it is recommended that the real service should be in the inner package of the service launcher, the same layer may not work.
Unless an annotation is used to indicate the package name @ServiceScan("com.fyupeng")
In other cases, if there is no response from the server, and the service has been successfully registered in the registry, then you have to check whether the package names of the interface named in the server and the client are consistent. If they are inconsistent, the service cannot be automatically discovered. The registry found that the most common error is service instances size is zero.
- ReceiveResponseException
Throws exception data in package is modified Exception
The implementation of the information digest algorithm uses the equals method of the String type, so when the client writes the Service interface, if the return type is not the eight basic types + String type, that is, the complex object type, then the Write the toString method.
Do not use the default toString method of Object, because it prints the information as a 16-bit memory address by default. During verification, the sent packet and the requested packet need to be re-instantiated. To put it bluntly, it is Deep clone, must override the original toString method of Object.
In order to avoid this situation, it is recommended that all PoJo and VO classes must rewrite the toString method. In fact, all entities of the return type of the real business methods must rewrite the toString method.
If the return body has nested complex objects, all complex objects must rewrite toString. As long as the toString method of different objects but the same content prints the same information, the data integrity detection will not be false.
- RegisterFailedException
Throws an exception Failed to register service Exception
The reason is that the registry is not started or the address and port of the registry are not specified, or the port access of the server where Nacos is located fails due to a firewall problem.
When using the framework, the following two points should be noted.
(1) support the registration of local addresses, such as localhost or 127.0.0.1, then the registered address will be resolved into a public address.
(2) support the registration of intranet addresses and extranet addresses, then the address is the corresponding intranet address or extranet address, and will not resolve them.
- NotSuchMethodException
Throws exception java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.slf4j.spi.LocationAwareLogger.log
The reason for this exception is that the dependency package depends on the jar package of jcl-over-slf4j, which is the same as the jcl-over-slf4j provided in springboot-starter-log4j. It is recommended to manually delete rpc-core -1.0.0-jar-with-dependenceies.jar in the org.apache.commons package
- DecoderException
Throws exception: com.esotericsoftware.kryo.KryoException: Class cannot be created (missing no-arg constructor): java.lang.StackTraceElement
Mainly because Kryo serialization and deserialization are created by reflection with no parameter construction, so when using the Pojo class, you must first create a parameterless constructor for it, otherwise the exception will be thrown and cannot be executed normally .
- InvocationTargetException
Throws exception: Serialization trace:stackTrace (java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException)
The main reason is that the reflection call fails. The main reason is that the reflection execution target function fails, and the related functions are missing. It may be a problem with the constructor or other method parameters.
- AnnotationMissingException
Throwing exception: cn.fyupeng.exception.AnnotationMissingException
As can be seen from the printing information, trace the printing of the AbstractRpcServer class information
cn.fyupeng.net.AbstractRpcServer [main] - mainClassName: jdk.internal.reflect.DirectMethodHandleAccessorIf mainClassName is not the class name of the @ServiceScan annotation mark, you need to modify or rewrite the getStackTrace method under the package cn.fyupeng.util.ReflectUtil, and add the unfiltered package name to the filter list. Yes, it may be related to the version of JDK.
- OutOfMemoryError
Throws exception java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
It is basically impossible to throw this error. Considering concurrent requests, it may cause many problems if the request package is subpackaged, so only one request package is sent per request. For example, in application scenarios, large data needs to be sent, such as publishing Articles, etc., need to manually override the serialize method of the serialization class used.
For example: KryoSerializer can override the size of the write cache in the serialize method. The default value is 4096. Exceeding this size will easily report an array out-of-bounds exception.
/**
* bufferSize: buffer size
*/
Output output = new Output(byteArrayOutputStream,100000))- RetryTimeoutExcepton
Throw exception cn.fyupeng.exception.AnnotationMissingException
After the retry mechanism is enabled, if the client fails to invoke the service after the number of retries, the service is considered unavailable and a timeout retry exception is thrown.
After the exception is thrown, the thread will be interrupted and the tasks not yet executed by the thread will be terminated, and if the retry mechanism is not enabled by default, the exception will not be thrown.
- InvalidSystemClockException
Throw exception cn.fyupeng.idworker.exception.InvalidSystemClockException
Snowflake algorithm generation is a small probability of clock redirection, time redirection needs to solve the problem of id value duplication, so it is possible to throw InvalidSystemClockException interrupt exception, logic can not handle the exception.
- WorkerIdCantApplyException
Throw exception cn.fyupeng.idworker.exception.WorkerIdCantApplyException
Snowflake algorithm generation, with the help of IdWorker generator to generate a distributed unique id, is with the help of machine code, when the number of machine code generated to reach the maximum will no longer apply, then will throw an interrupt exception WorkerIdCantApplyException.
- NoSuchMethodError
Exception thrown io.netty.resolver.dns.DnsNameResolverBuilder.socketChannelType(Ljava/lang/Class;)Lio/netty/resolver/dns/ DnsNameResolverBuilder
Integration of SpringBoot will override the netty dependency and lettuce dependency, SpringBoot2.1.2 before the included netty version is low, and RPC framework support is compatible with netty-all:4.1.52.Final and above, it is recommended to use SpringBoot2.3.4.RELEASE that is, above can solve the problem .
- AsyncTimeUnreasonableException
Throw exception cn.fyupeng.exception.AsyncTimeUnreasonableException
AsyncTimeUnreasonableException, when using the @Reference annotation, the field asyncTimemust be greater thantimeoutto ensure that the timeout will not report an exceptionjava.util.concurrent.TimeoutException, otherwise the maximum timeout will probably be unreachable and will print warnlog, causing the next retry to be triggered, which in2.0.6and2.1.8` will force an exception to be thrown to terminate the thread.
Similarly used are RetryTimeoutExcepton and RpcTransmissionException, both of which will terminate task execution.
- RpcTransmissionException
Throw exception cn.fyupeng.exception.RpcTransmissionException
Data transmission exception, thrown in the protocol layer decoding, usually because the implementation class before parsing and the receiving intern class toString() method protocol after parsing are different, or the package may be hijacked and the content is tampered.
Internal design using toSring () method to, rather than a certain fixed way to verify, which allows greater uncertainty in the verification, as a way to obtain a higher transmission security, of course, this design allows developers to design their own security toString method to achieve, such as not to achieve, will inherit Object memory address toString print, because it is transmitted through the network serialization, that is, the deep cloning method to create the class, the original checksum and the server side to be checked is generally different, it will throw the exception, generally need to re-toString () method.
The delayed shutdown aftermath on the server side ensures that the connection is closed properly.
- TCP shutdown (four waves)
8191 80.172711 192.168.2.185 192.168.2.185 TCP 44 8085 → 52700 [FIN, ACK] Seq=3290 Ack=3566 Win=2616320 Len=0
8190 80.172110 192.168.2.185 192.168.2.185 TCP 44 8085 → 52700 [ACK] Seq=3290 Ack=3566 Win=2616320 Len=0
8191 80.172711 192.168.2.185 192.168.2.185 TCP 44 8085 → 52700 [FIN, ACK] Seq=3290 Ack=3566 Win=2616320 Len=0
8192 80.172751 192.168.2.185 192.168.2.185 TCP 44 52700 → 8085 [ACK] Seq=3566 Ack=3291 Win=2616320 Len=0And there is no longer the problem of sending RST, that is, there is still data in the receive buffer that has not been received, the reason for this is that Netty has a problem with its own aftercare, that is, after future.channel().closeFuture().sync() the operation is executed, the thread termination will not be executed down the line, instantly there is finally still So, the close hook is called automatically to complete the normal closure of the connection.
- Closing hooks
public class ServerShutdownHook {
private static final ServerShutdownHook shutdownHook = new ServerShutdownHook();
private ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry;
private RpcServer rpcServer;
public ServerShutdownHook addRegistry(ServiceRegistry serviceRegistry) {
this.serviceRegistry = serviceRegistry;
return this;
}
public ServerShutdownHook addServer(RpcServer rpcServer) {
this.rpcServer = rpcServer;
return this;
}
public static ServerShutdownHook getShutdownHook() {
return shutdownHook;
}
/**
* Add shutdown hooks
* Client-side hooks are added separately from server-side hooks, do not put them together
*/
public void addClearAllHook() {
log.info("All services will be cancel after shutdown");
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(()->{
JRedisHelper.remWorkerId(IpUtils.getPubIpAddr());
log.info("the cache for workId has bean cleared successfully");
//NacosUtils.clearRegistry();
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
serviceRegistry.clearRegistry();
}
//NettyServer.shutdownAll();
// 开启子线程(非守护线程) 的方式能够 避免因服务器 关闭导致 关闭钩子 未能正常执行完毕(守护线程)
if(rpcServer != null) {
rpcServer.shutdown();
}
}));
}
}- Usage
Called when the server-side or client-side agent is started
public class NettyServer extends AbstractRpcServer {
@Override
public void start() {
/**
* Encapsulates the previously used thread eaters and task queues
* implements the ExecutorService interface
*/
ServerShutdownHook.getShutdownHook()
.addServer(this)
.addRegistry(serviceRegistry)
.addClearAllHook();
}
}Netty already provides a graceful shutdown, bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().sync(), which can be wrapped in a static method and just handed over to the hook to call.
-
[ #1.0.1 ]: Solve the problem that the registration service cannot be found in real distributed scenarios logical problem;
-
[ #1.0.2 ]: Decoupled registry address binding, available to the launcher Configure the
resource.propertiesfile under the resources of the project where you are located; -
[ #1.0.4.RELEASE ]: Fixing the problem that services registered to the registry are not discovered after deploying the project in the
Jarway, decoupling the injection of theJarpackage startup configuration file, where the same constraint name will overwrite the original configuration information of the project. -
[ #1.0.5 ]: The default level of the heartbeat mechanism printing configuration is
trace, and the default log level isinfo, which needs to be enabled inlogback.xml. -
[ #1.0.6 ]: The default request packet size is
4096Bytes, and the expansion is100000Bytes, meet the daily100000word data packets, it is not recommended to send large data packets, if necessary, see the exceptionOutOfMemoryErrordescription. -
[ #1.0.10 ]: Repair the problem of
selectfailure in load balancing, provide configuration center highly available cluster node injection configuration, load balancing configuration, fault-tolerant automatic switching
-
[ #2.0.0 ]: Optimized version
1.0version, version2.0introduced timeout retry mechanism, using to idempotency to solve the business loss problem and improve business reliability. -
[ #2.0.1 ]: Version maintenance
-
[ #2.0.2 ]: Repair the problems of downtime retry and load in the cluster configuration center
-
[ #2.0.3 ]: Provide personalized service version number to support various scenarios, such as test and formal scenarios, allowing better compatibility of services and supporting version maintenance and upgrades.
-
[ #2.0.4 ]: Support
SPImechanism, interface and implementation decoupling. -
[ #2.0.5 ]:
2.0will be maintained for a long time, and the issues to be solved by inheriting2.0in2.1version are solved simultaneously. -
[ #2.0.6 ]: Overall improvement and performance optimization.
-
[ #2.0.8 ]: Code logic optimization and preload optimization.
-
[ #2.0.9 ]: Repair the client/server failed to normally closed questions, lead to end connection abort.
-
[ #2.1.0 ]: introduce snowflake algorithm and distributed cache,
2.0.0version only supports single machine idempotency, fix the distributed scenario failure problem, usepolling load + timeout mechanism, can efficiently solve the service timeout problem. -
[ #2.1.1 ]: Change the configuration information
cn.fyupeng.client-asynctocn.fyupeng.server-async. -
[ #2.1.3 ]: Fix public network get 403 exception.
-
[ #2.1.5 ]: Fix the default default error reporting exception of
groupin the registration center. -
[ #2.1.7 ]: Repair the problem of saving articles normally but reading articles beyond the boundary, solve the problem that
nettycannot listen to the local public network address of Aliyun and Tencent Cloud under the firewall, repair the problem of serialization logic abnormality when the query is empty/no return value, and repair the serialization abnormality in the case of distributed cache special. -
[ #2.1.8 ]: Overall improvement and performance optimization.
-
[ #2.1.9 ]: Code logic optimization and preload optimization.
-
[ #2.1.10 ]: Repair the client/server failed to normally closed questions, lead to end connection abort, Consolidate a unified pool of business threads for later cleanup.
-
[ #2.2.0 ]: supports the extension of 'Bean' custom instantiation, meets the requirements of 'Spring' annotation dependency injection and annotation section execution, corrects the annotation package name 'annotation', solves the failure to manually clear the memory of the service instance when the service is logged out, improves the performance slightly, and maintains the instability of the polling policy under concurrency.
-
[ #2.2.1 ]: Code optimization, performance optimization, improved clock callback policy, SPI extension to support third-party service registration and discovery, and load balancing to obtain generic services.
-
[ #2.2.2 ]: Solve singleton factory failure problem, optimize thread pool factory, optimize redundancy configuration.
-
[ #2.2.3 ]: Change the custom protocol 16 bytes to 8 bytes, optimize the timeout retry mechanism, fix the thread safety problem under high concurrency, and greatly improve the performance.
-
[ #2.2.4 ]:Support javassist dynamic proxy phase (trial), the client proxy provides javassist mode API method, the default choice JDK dynamic proxies, performance is higher than the javassist.
-
[ #2.2.5 ]:Repair the empty results abnormal response to a question.
RNF open source RPC framework has followed Apache License Version 2.0 protocol. Please follow the above protocol before using it. If you have copyright disputes or inconvenience, please contact the author!