##THIS TUTORIAL NEEDS TO BE UPDATED FOR 1.0.0
This tutorial will show how to connect your dart application, server and client side, to a PostgreSQL or MySQL database using Dartabase Migration and Dartabase Model
##Prerequisits
Though not needed, it might be usefull to bring some understanding of polymer elements and server/client communication into this tutorial.
If you want to know more about:
server/client communication, I can recommend you JSON WEB SERVICES by Chris Buckett
for more information on Polymer, please read POLYMER DART
and for nice Polymer examples, check out POLYMER DART EXAMPLES by Seth Ladd
##Getting Started
- Download Dartabase Tutorials from git and open it's root folder in the Dart Editor via Open Existing Folder
The example is a simple todo list webapp using polymer
The server is located inside the '/bin folder' and consists of
-a simple server
-an Item class
The client is inside the '/web folder' and consists of
-a start page index.html inside /web
-a Item polymer element inside /web/poly // Polymer version >=0.9.5 <0.10.0
-Item views for 'index', 'view', 'create', and 'edit' inside /web/Item
Additional the project uses helpers.
uses the params package. see (here)[http://pub.dartlang.org/packages/params]
**paths.dart** inside the /lib folder
a collection of all server and client urls to keep code clean
-
Download latest stand alone version of Dartabase Migration from pub, extract the zip somewhere to your drive and open the root folder (lets call it dartabase_migration) of the extracted content via 'Open Existing Folder'
-
Run 'Pub Get' on dartabase_migration/pubspec.yaml
#Dartabase Migration  ##Set Up
##Set Up
Migration is a tool to build version controlled database table and column structures for your MySQL or PostgreSQL database using json files.
Before we can use its features, we have to initiate migration once for each project we want to use it with.
- Execute 'dartabase_migration/bin/dbInit.dart'.
This process will establish a connection between dartabase_migration and your project.
Your output should look like this:
- Insert a project name.
Write 'todo' without '' and hit ENTER
- Insert the absolute path to your project root folder.
On my machine and for this example I use 'C:\Projects\Dart\DartabaseTutorials\examples\PreTutorialMixApp' without ''
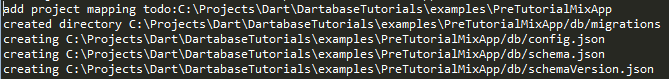
Once you hit enter, dartabase_migration should create the files and folders listed below
and the output dialog should look like this:
dartabase_migration/bin/projectsMapping.json
- maps project names to absolute project paths for interaction between tool and programm
PreTutorialMixApp/db/
- folder used by dartabase tools
PreTutorialMixApp/db/config.json
- the config file is used to set IP/PORT/DBType for DB connection
PreTutorialMixApp/db/schema.json
- schema is the current migrated version of the database structure as JSON used by dartabase tools
PreTutorialMixApp/db/schemaVersion.json
- safes name of latest migrated version file
PreTutorialMixApp/db/migrations
- you have to keep the migration files inside this folder!
- Open the PreTutorialMixApp/db/config.json file and adapt the file with your existing empty database config data
In this tutorial we use a PostgeSQL database called 'todoList'
with user 'postgres', password '1234' running on 'localhost:5432'.
The config file should look like this now:
--------config.json---------
{
"adapter": "PGSQL",
"database": "todolist",
"username": "postgres",
"password": "1234",
"host": "localhost",
"port": "5432"
}
**if you prefer to use MySQL use "MySQL" as the adapter instead**
We are ready to create our first database migration! Yeah!
##HOW TO CREATE MIGRATIONS
To create a database structure, we can now create mirgation files!
- Create a json file 'currentTimestamp_action.json' inside 'PreTutorialMixApp/db/migrations'
timestamp format is **YYYYMMDDHHMMSS**
eg. 'PreTutorialMixApp/db/migrations/20130623043400_create_item.json'
- Inside your migration file you, have to follow a fixed structure!
You can execute actions using JSON objects that work with an "UP" and "DOWN" key. each key takes each take a json object as a value.
DOWN is manly used to revert actions specified inside the UP
Some of the actions you can specify are
createTable
"createTable": {
"new_table_name_one": {
"new_column_name_one": "DATATYPE",
"new_column_name_last": "DATATYPE"
}
"new_table_name_two": {
...
}
}
createColumn
"createColumn": {
"existing_table_name_one": {
"new_column_name_one": "DATATYPE",
"new_column_name_last": "DATATYPE"
},
"existing_table_name_two": {
...
}
}
removeColumn
"removeColumn": {
"existing_table_name_one": ["existing_column_name_one"]
}
removeTable
"removeTable": ["existing_table_name_one"] (lower_case)
For our todoList, we want to create a list item with a text that stores the task and a done field, for once the task is done.
The migration file can look like this
----------20130623043400_create_item.json--------------
{
"UP": {
"createTable": {
"item": {
"text": "VARCHAR",
"done": {"type":"BOOLEAN","default":"0"}
}
}
},
"DOWN": {
"removeTable": [
"item"
]
}
}
We have a createTable action that creates a table named "item" with two columns. "text" as a string and "done" as a boolean with default value false.
Inside the DOWN action we simply add the reverse action. Later we can decide if we want to migrate UP or DOWN, making it possible to revert database changes.
removing columns or tables from the database will obviously delete the data! so be carefull
##HOW TO EXECUTE MIGRATIONS
- Execute dartabase_migration/bin/dbUp.dart
You should see a list of all projects that you initiated with Dartabase
The List includes the Project name, path and version
Your output should look like this
Currently version is empty.
- Now enter a project name.
Write 'todo' without '' and hit ENTER!
You should see a list of all migration files that you have inside your projects 'db/migration' folder and should look something like this.
- Now enter your goal migration version.
Write '0' without '' and hit ENTER!
The actions we specified inside the "UP" key and your output should look like this.
We can see that a table 'item' with columns 'text' and 'done' was created.
Additionally it should have updated
PreTutorialMixApp/db/schema.json with the current database structure as JSON
PreTutorialMixApp/db/schemaVersion.json with the name of latest migrated migration file
To revert a migration (execute actions in DOWN key) Execute dartabase_migration/bin/dbDown.dart and follow the instuctions.
NOTE:
Additionally to the two columns, dartabase_migration creates for each table an
"id", "created_at" and "updated_at" column, that will be filled automatically!
Now that we have the structure, why not lets use it.
#Dartabase Model ##Set Up
After you have sucessfully finished setting up 'Dartabase Migration'
-
Install Dartabase Model inside your project the usual pubspec way
-
Inside 'bin/simpleServer.dart', insert 'Model.initiate("path-to-your-project");' at the beginning of the main method like below:
-----simpleServer.dart--START--
library dataServer; import 'package:dartabase_model/dartabase_model.dart'; main(){ Model.initiate("C:\\Projects\\Dart\\dartabase\\examples\\PostTutorialMixApp"); ... your code }-----simpleServer.dart--END--
Since we created a table inside our database named 'item', we have make small changes to the object server files.
-
Open the file '/bin/item.dart' and extend the class with 'Model' to connect the server model class with our database model like below
-----item.dart--START--
part of example.server; class Item extends Model{ num id; String text; bool done; DateTime created_at; DateTime updated_at; String toString() => "Item id=$id:text=$text:done=$done:created_at:$created_at:updated_at:$updated_at"; ...-----item.dart--END--
##HOW TO USE MODEL
Dartabase Model provides functions to load and save data from and to the database. To use them we have to replace the dummy code inside the '/bin/item.dart' file.
-
To load all items, replace
print("implement loadItems"); res.write(JSON.encode([{'text':'implement loadItems'}])); res.close();
with
new Item().findAll().then((List items){
if(!items.isEmpty){
List jsonList=[];
items.forEach((Item item){
Map itemMap = item.toJson();
print(itemMap);
jsonList.add(itemMap);
});
print("found ${items.length} items");
res.write(JSON.encode(jsonList));
}else{
print("no items found");
res.write("no items found");
}
res.close();
});
We call findAll() on Item
If at leat one exists in the table it returns a List of them
Else it returns an empty list
So if we find at least one item, we have to convert the list into a standart JSON format via the toJson() function provided by Model to be able to send the JSON string back to the client.
Else we responde with 'no items found'.
-
To load a single item, replace
print("implement loadItem"); res.write(JSON.encode({'text':'implement loadItem'})); res.close();
with
new Item().findById(int.parse(id)).then((item){
if(item != null){
Map itemMap = item.toJson();
print("found item $itemMap");
res.write(JSON.encode(itemMap));
}else{
print("no item found with id $id");
res.write("no item found with id $id");
}
res.close();
});
Here we call findById() on Item
If one exists in the table it returns an Item.
Else it returns null.
If we find an item, we have to convert it into again and send it to the client.
Else we responde with 'no item found with id'.
-
To save an item, replace
print("implement saveItem"); res.write(JSON.encode({'text':'implement saveItem'})); res.close();
with
if(postDataMap['id'] == null){
print("creating item with data $postDataMap");
fill(new Item(),postDataMap,res);
}else{
new Item().findById(postDataMap['id']).then((item){
print("updating item ${item.id} with data $postDataMap");
fill(item,postDataMap,res);
});
}
and add this to the end of the class.
static fill(Item item,Map dataMap, HttpResponse res){
item.done = dataMap['done'];
item.text = dataMap['text'];
item.save().then((process){
if(process == "created" || process == "updated"){
new Item().findById(item.id).then((Item reloadedItem){
print("$process item $reloadedItem");
print("$process item ${reloadedItem.toJson()}");
res.write(JSON.encode(reloadedItem.toJson()));
res.close();
});
}else{
print("object not saved during 'process': $process");
res.write("object not saved during 'process': $process");
res.close();
}
});
}
here we call save() on Item
If save is successful, we reload the item via its 'id' to see if the change happened inside the database.
Else we return 'object not saved'.
-
Last point! To delete an item, replace
print("implement deleteItem"); res.write(JSON.encode({'text':'implement deleteItem'})); res.close();
with
Map postDataMap = JSON.decode(new String.fromCharCodes(buffer));
if(postDataMap['id'] == null){
print("no item id provided");
res.write("no item id provided");
}else{
var id = postDataMap['id'];
new Item().findById(id).then((item){
if(item != null){
print("found item with id $id for deletion");
item.delete().then((result){
print("$result");
res.write("$result");
});
}else{
print("no item with id $id found for deletion");
res.write("no item with id $id found for deletion");
}
res.close();
});
}
If we find an item via an id, we call delete() on the item. If successful the item should be deleted.
Now your PreTutorialmixApp/bin/item.dart file should look like PostTutorialmixApp/bin/item.dart!
#You are done, congratulations!
**Now simply run
the 'bin/simpleServer.dart' server
the 'web/index.html' client
and make sure your database server is running!**
##ENJOY!
I am Happy about feedback and input thank you! :)