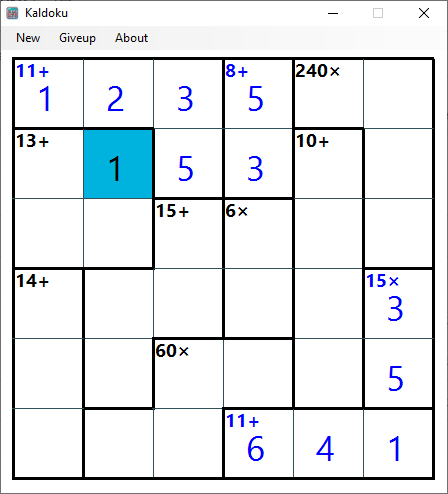
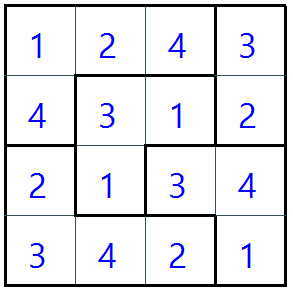
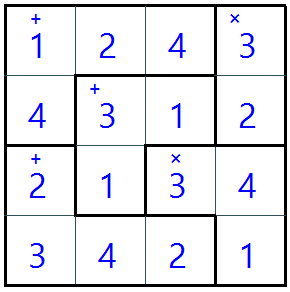
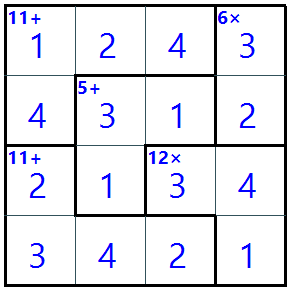
This is a puzzle game similar to sudoku. It can also be called Calcudoku, Mathdoku, or Kenken.
The size of the board you choose determines the numbers you use in the puzzle.
For example, a 4x4 board requires you to use numbers 1-4 while a 9x9 board requires numbers 1-9.
All the numbers must be entered into the cells and there must not be any duplicates in a row or column.
The target number must match the total of the values in the cells after they have been operated.
For example, if the block size is 4 AND the target number is 10 WITH the operator is + (10+)
These are examples of valid values
1,2,3,4
4,3,2,1
The block allows it to contain a duplicate number as long as it is not in the same row or the same column.
For example, if the block shape looks like this, and the target number is 14, it can consist of a duplicate value like this.
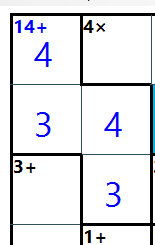
It cannot consist the values like this
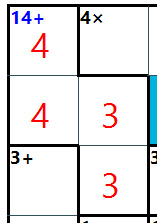
This is a class representative board information. It consists of attributes that represent the board size, the target numbers for each cell, and a list of pieces on the board
There are 2 variables the board used to store the value.
Cell[,] CellTable and public List lstPiece
We only need either 1 of them, but I use 2 variables to make it easier to track the board value.
CellTable is a 2D array of Cell objects.
lstPiece is the collection of piece objects.
public class Board
{
Cell[,] CellTable = new Cell[6, 6];
int[,] TargetCellValue = new int[6, 6];
private const int BlankCellValue = -1;
public int BoardSize { get; private set; } = 6;
public Board() => this.ClearBoard();
public Board(int pBoardSize)
{
this.BoardSize = pBoardSize;
this.ClearBoard();
}
public static Board Create(int boardSize,String piecesString, int[,] tarGetCellValue, Boolean IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber)
{
Board newBoard = new Board(boardSize);
/*
* Example of Parameter value
* boardSize:4
* pieceString:J3_Rotate270_0_0|J2_Rotate180_1_0|I2_Rotate360_0_3|J3_Rotate90_2_0|L2_Rotate180_2_2|
* int[,] targetNumber = new int[,]
{
{ 1,2,3,4 },
{ 2,3,4,1},
{ 3,4,1,2},
{ 4,1,2,3}
};
*/
string[] arrPieces = piecesString.Split(new char[] { '|' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
int i;
/*loop though arrPieces to create Piece object to put into a newBoard
* Example J3_Rotate270_0_1 means
* J3 piece type
* Rotate at 270
* Row in a board 0
* Column in a board 1
*/
for (i = 0; i < arrPieces.Length; i++)
{
string[] arrPieceType = arrPieces[i].Split(new char[] { '_' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
string pieceTypeString = arrPieceType[0] + "_" + arrPieceType[1];
int rowPut = int.Parse(arrPieceType[2]);
int colPut = int.Parse(arrPieceType[3]);
Piece piece = Piece.Create(pieceTypeString);
newBoard.Put(rowPut, colPut, piece);
}
newBoard.SetTargetNumber(tarGetCellValue);
newBoard.AssignOperationToPiece(IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber);
newBoard.CalTargetNumberForAllPieces();
return newBoard;
}
public List<Point> Dir = new List<Point>()
{
new Point(-1, 0) ,
new Point(0, 1) ,
new Point(1, 0) ,
new Point(0, -1) ,
};
public Boolean IsValidNumberInBoard()
{
int i;
int j;
int iMax = CellTable.GetLength(0);
for (i = 0; i < CellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if (CellTable[i, j].Value == BlankCellValue)
{
return false;
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < CellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
if (!IsValidNumberInRow(i))
{
return false;
}
if (!IsValidNumberInCol(i))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean IsValidNumberInRow(int iRow)
{
HashSet<int> hshRow = new HashSet<int>();
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if (CellTable[iRow, j].Value == 0)
{
continue;
}
if (hshRow.Contains(CellTable[iRow, j].Value ))
{
return false;
}
else
{
hshRow.Add(CellTable[iRow, j].Value );
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean IsValidNumberInCol(int iCol)
{
//List<HashSet<int>> lstRow = new List<HashSet<int>>();
HashSet<int> hshCol = new HashSet<int>();
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (j = 0; j < CellTable.GetLength(0); j++)
{
if (CellTable[j, iCol].Value == 0)
{
continue;
}
if (hshCol.Contains(CellTable[j, iCol].Value ))
{
return false;
}
else
{
hshCol.Add(CellTable[j, iCol].Value );
}
}
return true;
}
public Boolean HasIsolateCell(Cell[,] cellTable)
{
int i;
int j;
int k;
StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
List<Cell> lstCell = new List<Cell>();
for (i = 0; i < cellTable.GetLength(0); i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < cellTable.GetLength(1); j++)
{
if(cellTable[i,j].Value != BlankCellValue)
{
continue;
}
Boolean hasBlankNeighbor = false;
for (k = 0; k < Dir.Count; k++)
{
int neighborCellRow = i + Dir[k].X;
int neighborCellCol = j + Dir[k].Y;
if (!IsPositionInRange(neighborCellRow, neighborCellCol))
{
continue;
}
if (cellTable[neighborCellRow, neighborCellCol].Value == BlankCellValue)
{
hasBlankNeighbor = true;
continue;
}
}
if (!hasBlankNeighbor)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
public List<Piece> lstPiece = new List<Piece>();
public void PutNumber(Piece pPiece, List<int> lst)
{
int k = 0;
int iRow = pPiece.RowPut;
int iCol = pPiece.ColPut;
for (k = 0; k < pPiece.lstCell.Count; k++)
{
int iPieceRow = pPiece.lstCell[k].Row;
int iPieceCol = pPiece.lstCell[k].Col;
CellTable[iRow + iPieceRow, iCol + iPieceCol].Value = lst[k];
}
pPiece.HasPutNumber = true;
}
}Create()
The Create method creates a new Board object from a string representation of the board layout and target numbers.
These are the parameters
| Data Type | Parameter Name | Example Data | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| int | boardSize | 4 | The size of the board, the valid value is a number between 4-9 |
| String | piecesString | J3_Rotate270_0_0|J2_Rotate180_1_0 | The String that represents the list of pieces of information. It uses a pipe character as a separate character between each piece you need to look into the function comment for more detail |
| int[,] | tarGetCellValue | { 1,2,3,4 }, { 2,3,4,1}, { 3,4,1,2}, { 4,1,2,3} | The correct answer of the tables. |
| Boolean | IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber | True | If this value is true, The target number can be negative. |
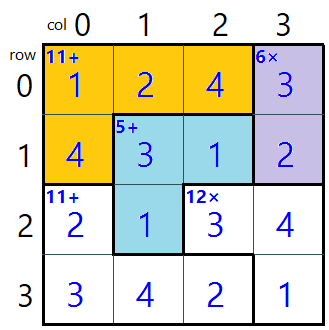
For example, if this is the board.
(I highlighted 3 blocks on the board to illustrate my explanation)
These will be the parameters.
| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| boardSize | 4 |
| piecesString | L3_Rotate90_0_0|L2_Rotate90_1_1|L2_Rotate180_2_2|I2_Rotate360_0_3|J3_Rotate90_2_0| |
| tarGetCellValue | {1,2,4,3},{4,3,1,2},{2,1,3,4},{3,4,2,1} |
This board size is 4, and it has 5 blocks
| Block Number | Value | Color highlighted | Describtion | Rotate degreee | Row | Column |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | L3_Rotate90_0_0 | orange | Block in L Shape that has 3 cells height | 90 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | L2_Rotate90_1_1 | blue | Block in L Shape that has 2 cells height | 90 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | L2_Rotate180_2_2 | - | Block in L Shape that has 2 cells height | 180 | 2 | 2 |
| 4 | I2_Rotate360_0_3 | purple | Block in I Shape that has 2 cells height | 360 | 0 | 3 |
| 5 | J3_Rotate90_2_0 | - | Block in J Shape that has 3 cells height | 90 | 2 | 0 |
For the target number and the operator
like 11+,5+,11+,6x,12x
We do not include the target number and operator when calling the create() function
those values will be calculated within the create () method.
IsValidNumberInBoard()
checks if the board contains all the required numbers and that there are no duplicates in each row and column.
HasIsolateCell()
This function returns true if there is no blank cell at the neighbor.
The board contains many pieces, and the piece contains many cells.
The piece store Operation, PieceType, Rotation,
This shows some of the code in the Piece class.
I omitted some of the code in the create method to reduce the duplicate code.
This is an example of the piece.
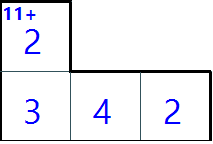
The piece in the picture is the piece in J Shape that has 3 cells high, being rotated at 90 degrees.
Its operation is Add, its target number is 11.
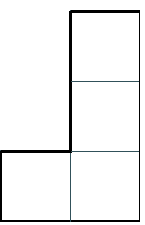
If this piece is not rotated it will look like this.
public class Piece
{
public enum PieceOperation
{
Add,
Subtract,
Multiply,
Divide
}
public enum PieceType // Shape of piece
{
I2,
I3,
I4,
L2,
L3,
J2,
J3,
S,
T,
Z,
O,
Dot,
}
public enum PieceRotation{
Rotate90,
Rotate180,
Rotate270,
Rotate360
}
private Board _Board;
public PieceOperation Operation { get; set; } = PieceOperation.Add;
private int _Number = -1;
public int TargetNumber { get; private set; } = -1;
public static Piece Create(String pieceTypeString)
{
string[] arrTemp= pieceTypeString.Split('_');
Piece.PieceType pieceType = dicPieceType[arrTemp[0]];
Piece.PieceRotation pieceRotation = dicRotation[arrTemp[1]];
return Create(pieceType, pieceRotation);
}
public static Piece Create(PieceType pType,PieceRotation pRotation){
Piece p=null;
List<Cell> lst = new List<Cell>();
Dictionary<PieceType, Dictionary<PieceRotation, List<System.Drawing.Point>>> Dic = new Dictionary<PieceType, Dictionary<PieceRotation, List<System.Drawing.Point>>>();
if(hshCannotRotate.Contains (pType ))
{
if(pRotation == PieceRotation.Rotate180 ||
pRotation== PieceRotation.Rotate270 )
{
pRotation = PieceRotation.Rotate360 ;
}
}
// Showing only 2 types of Piece to reduce the sample of the code
switch (pType)
{
case PieceType.Dot :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
break;
case PieceType.L2 :
switch (pRotation)
{
case PieceRotation.Rotate360:
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 1));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate90 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 1));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate180 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 1));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 1));
break;
case PieceRotation.Rotate270 :
lst.Add(new Cell(0, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, 0));
lst.Add(new Cell(1, -1));
break;
}
break;
}
//p=new Piece ();
p = new Piece(pType, pRotation, lst);
p.lstCell = lst;
return p;
}The Cell class is defined with properties to represent the cell's
row, column, value, target value, row on board, and column on board.
It has a property attribute _Piece to hold the reference to the piece object
that it belongs to.
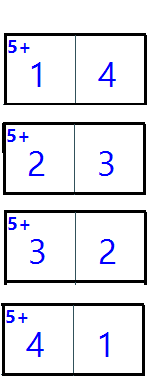
The Cell's target value is used to generate a target number of the piece, the user does not necessarily need to enter the value that matches the
cell target value.
For example, if the piece consists of 2 cells, the target number of the piece 5+,
and the target number of the cells is 4 and 1.
These 4 cases are valid values of Cell1 and Cell2 they don't need to be only 4 and 1.
The enum enCellStatus is to indicate the cell's status.
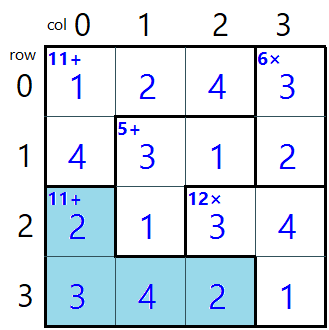
The difference between Row and RowOnBoard, Column and ColOnBoard is
Row and Column refer to the position on the block while RowOnBoard and ColOnBoard refer to the position on the board.
In this picture, the block that was highlighted consists of 4 cells.
| Cell Number | Target | Row | Column | RowOnBoard | ColOnBoard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 |
| 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 |
public class Cell
{
private Piece _Piece = null;
public enum enCellStatus
{
Blank,
Duplicate, //Duplicate with other cell in row/column
PieceIsNotComplete, //Contain blank cell
PieceIsNotCorrect, //No blank cell but contains duplicate or does not match with target value
PieceIsCorrect, // no match
PieceMatchbutContainDuplicate,
}
public enCellStatus CellStatus { get; set; } = enCellStatus.Blank;
public void SetPiece(Piece pPiece)
{
_Piece = pPiece;
_Piece.PieceBeingPutOnBoard += _Piece_PieceBeingPutOnBoard;
}
public void UnboundFromPiece()
{
_Piece = null;
}
private void _Piece_PieceBeingPutOnBoard(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.RowOnBoard = this.Row + _Piece.RowPut;
this.ColOnBoard = this.Col + _Piece.ColPut;
}
public int Row { get; private set; }
public int Col { get; private set; }
public int Value { get; set; }
public int TargetValue { get; set; }
public int RowOnBoard { get; private set; }
public int ColOnBoard { get; private set; }
public Cell(int pRow, int pCol)
{
this.InitializeProperty(pRow, pCol, 0);
}
private void InitializeProperty(int pRow, int pCol, int pValue)
{
Row = pRow;
Col = pCol;
Value = pValue;
}
public Cell(int pRow, int pCol, int pValue)
{
this.InitializeProperty(pRow, pCol, pValue );
}
}At this point you know how the board is built, the next step is to prepare the value for the board.
- First generate a list of blocks with blank cells.
We do not need to know what is the target number, we only need a valid list of the block like this.
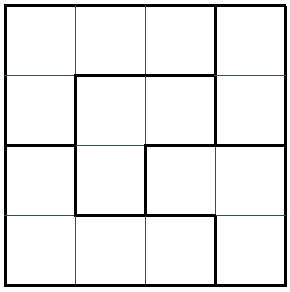
- Generete the number
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
At first, when I created a program, the program just needed to generate a list of blocks with blank cells on the fly.
The program works fine at the 4x4 until 7x7, at 8x8 or 9x9 board size sometimes it freezes because It cannot generate a valid block.
So I decided to generate a list of blocks in advance and then store them in the text files first when a program needs to use it
just read the value from the text files.
You can look into the PregeneratedBlankBlock folder you will see a list of text files for example 4x4.txt, and 5x5.txt.
Those files contain this kind of value.
Z_Rotate360_0_0|L3_Rotate90_2_1|J2_Rotate180_0_2|I3_Rotate360_1_0|I2_Rotate90_3_2|
J2_Rotate270_0_0|I3_Rotate90_2_1|I3_Rotate360_1_0|I2_Rotate90_0_2|I2_Rotate90_1_2|I3_Rotate90_3_1|
Each line is a valid value for the board.
If you would like to generate it by yourself self you can look into GenerateBlankBlocks() in FormGenerateBlankBlock.cs
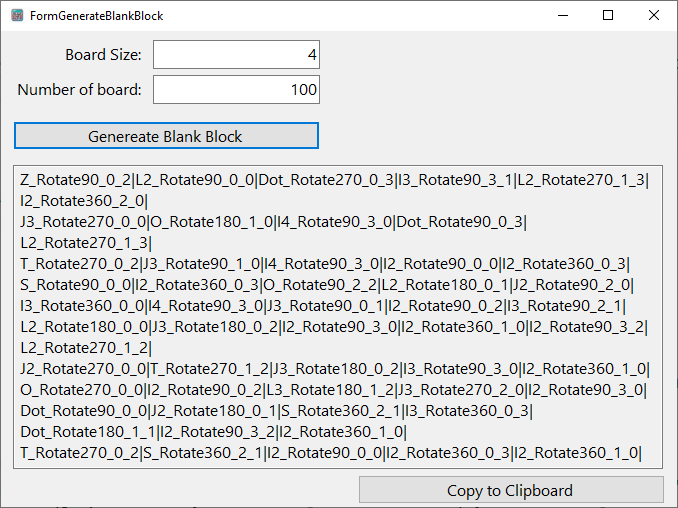
- Generate a random piece.
- Try to put the piece generated to the board
if the program can put, repeat #1 - If the program cannot put the piece
increase the value the number of times the program cannot put
Then we keep doing #1
if the number of times the program cannot put > numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece
removed the last piece - if #3 is still not good enough we call UnputLastNPiece to remove more than one piece.
private void GenerateBlankBlocks(Board board)
{
GeneratePiece generatePiece = new GeneratePiece(new BasicPieceGenerator());
int maximumAttemptLoopAllow = 50000000;
int numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece = 40;
int numberofTimesUnputLastPiece = 0;
int numberofTimeBeforeUnputLastNPiece = 30;
int countLoop = 0;
int countCannotPut = 0;
int numberofUnputLastNPiece = 3;
Boolean isSuccess = true;
while (!board.IsFullWithBlock() && countLoop < maximumAttemptLoopAllow)
{
Piece generatedPiece = generatePiece.GenPiece();
Boolean canPut = board.TryToPut(generatedPiece);
countLoop++;
if (canPut)
{
countCannotPut = 0;
continue;
}
countCannotPut++;
if (countCannotPut >= numberOfTryBeforeUnputLastPiece)
{
countCannotPut = 0;
board.UnputLastPiece();
numberofTimesUnputLastPiece++;
if (numberofTimesUnputLastPiece >= numberofTimeBeforeUnputLastNPiece)
{
board.UnputLastNPiece(numberofUnputLastNPiece);
numberofTimesUnputLastPiece = 0;
}
}
if (countLoop >= maximumAttemptLoopAllow)
{
isSuccess = false;
}
}
if (!isSuccess)
{
throw new Exception("Sorry I failed to generaete blank blocks, you can try again");
}
}
private void btnGenereateBlankBlock_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
int i;
try
{
/* Keep the existing generate block to make sure that the
* output will not duplicate
*/
HashSet<String> hshGenBlock = new HashSet<string>();
int boardSize = int.Parse(this.txtBoardSize.Text);
int numberOfBoardNeedToGenerate = int.Parse(this.txtNumberofBoard.Text);
StringBuilder strB = new StringBuilder();
for (i = 0; i < numberOfBoardNeedToGenerate; i++)
{
bool hasGenerate = false;
while (!hasGenerate)
{
var Board = new Board(boardSize);
GenerateBlankBlocks(Board);
string ListPiece = Board.GetListPieceString();
if (hshGenBlock.Contains(ListPiece))
{
continue;
}
hshGenBlock.Add(ListPiece);
hasGenerate = true;
strB.Append(ListPiece).Append(Environment.NewLine);
}
}
this.txtOutput.Text = strB.ToString();
} catch (Exception ex)
{
this.txtOutput.Text = ex.ToString();
}
}-
If you look into PrepareGenerateDigits folder you will see a list of file names like this 4_1.txt to 4_4.txt until 9_1.txt to 9_9.txt
-
Those files mean the boardsize_thefirstdig if the filename is 4_1.txt it means the file contains the data for board size 4 with the first digit as 1.
These are the data for board size 4.
| Line No | 4_1.txt | 4_2.txt | 4_3.txt | 4_4.txt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1234 | 2134 | 3124 | 4123 |
| 2 | 1243 | 2143 | 3142 | 4132 |
| 3 | 1324 | 2314 | 3214 | 4213 |
| 4 | 1342 | 2341 | 3241 | 4231 |
| 5 | 1423 | 2413 | 3412 | 4312 |
| 6 | 1432 | 2431 | 3421 | 4321 |
- To generate a number what we need to do is
Randomly select the value from each file
For example, We select
| Line No | From File | We get Value |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4_1.txt | 1 2 4 3 |
| 1 | 4_2.txt | 2 1 3 4 |
| 6 | 4_3.txt | 3 4 2 1 |
| 5 | 4_4.txt | 4 3 1 2 |
At this point, we have value like this
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
if the value is not valid for example this is not a valid value
In this case, column 2 at line numbers 2 and 3 has the duplicate value which is 4, program will continue
to get the new value from the file, until the board value is valid.
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
Now we already get the valid values. We are almost finished, it is just that the first value of the row is in order so We just need to randomly swap the row so we get this.
| 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 |
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 3 |
We call getTargetCellNumber() in ##PregenratedNumber.cs##
public static int[,] getTargetCellNumber(int boardSize)
{
int i;
int j;
var TargetCellValue = new int[boardSize, boardSize];
int[] arrRowTemp = new int[boardSize];
Dictionary<int, List<List<int>>> DicList = GetDicList(boardSize, FileUtil.PregeneratedDigitsPath);
for (i = 1; i <= boardSize; i++)
{
Boolean IsValid = false;
while (!IsValid)
{
int indexRandommed = 0;
indexRandommed = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, DicList[i].Count);
List<int> lst = DicList[i][indexRandommed];
IsValid = true;
for (j = 0; j < lst.Count && IsValid; j++)
{
int k;
for (k = 0; k <= boardSize - 1; k++)
{
if (TargetCellValue[k, j] == lst[j])
{
IsValid = false;
}
}
}
if (IsValid)
{
for (j = 0; j < lst.Count; j++)
{
TargetCellValue[i - 1, j] = lst[j];
}
}
}
}
//Swap Row;
for (i = 0; i <= 30; i++)
{
int iFirstRow = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, boardSize);
int iSecondRow = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, boardSize);
if (iFirstRow == iSecondRow)
{
continue;
}
for (j = 0; j <= boardSize - 1; j++)
{
arrRowTemp[j] = TargetCellValue[iSecondRow, j];
TargetCellValue[iSecondRow, j] = TargetCellValue[iFirstRow, j];
TargetCellValue[iFirstRow, j] = arrRowTemp[j];
}
}
return TargetCellValue;
}Next, we will do the rest of the process
In this step, we will do
Assign the number on each cell which the program just calls Board.SetTargetNumber()
Random Assign the operator to each block, by calling Board.AssignOperationToPiece()
Calculate the block target number and call Board.CalTargetNumberForAllPieces()
private void AssignOperationToPiece(Boolean IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber, Dictionary<Piece.PieceOperation, int> dicOpertorChance)
{
int i;
// Set some of them to use divided
for (i = 0; i < this.lstPiece.Count; i++)
{
var piece = lstPiece[i];
// Set default Operation to be Add for all of the pieces
Piece.PieceOperation DefaultOperator = Piece.PieceOperation.Add;
piece.Operation = DefaultOperator;
// Calculate the chance that it will be other value more than add
int iOperationChance = Baseclass.MyRandom.Random(0, 100);
foreach (Piece.PieceOperation Oper in dicOpertorChance.Keys)
{
int iSum = 0;
if(iOperationChance > dicOpertorChance[Oper])
{
continue;
}
var AssignOperator = Oper;
if (AssignOperator == Piece.PieceOperation.Subtract)
{
if (!IsAcceptNegativeTargetNumber)
{
/*Set AssignOperator to be Add if the result is a Negative
This is a process to prevent the result from being a negative number.
Supposing this is the value of the cell in piece
cell1:5
cell2:3
cell3:4
1. set iSum to be 5
2. iSum - 3 - 4;
3. if iSum < 0 we will not use Substract as Operator
we will ust use Add instead.
*/
//1. Assign iSum to be the first cell value
iSum = piece.lstCell[0].TargetValue;
int j;
//2. substrat iSum value from the rest of the cell in piece
for (j = 1; j < piece.lstCell.Count; j++)
{
iSum -= piece.lstCell[j].TargetValue;
}
//3. If iSum is less than 0 we will forece the operation to be Add instead.
if (iSum < 0)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
}
}
else if (AssignOperator == Piece.PieceOperation.Divide)
{
/*The condition that we will use Divide.
1. The number of cell must be 2
2. The result after from the division must be integer
For example
case 1
cell1:6
cell2:3
This case is valid because 2=6/3
case 2
cell1:5
cell2:2
This case is invalid because 2.5=5/2
*/
if (piece.lstCell.Count != 2)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
else
{
double doubleResult = (double)(piece.lstCell[0].TargetValue) /
(double)(piece.lstCell[1].TargetValue);
Boolean IsResultAfterDiviedInteger = (doubleResult % 1 == 0);
if (!IsResultAfterDiviedInteger)
{
AssignOperator = DefaultOperator;
}
}
}
if (piece.PType == Piece.PieceType.Dot)
{
//For Dot piece type, we don't allow other operators besides Add
piece.Operation = Piece.PieceOperation.Add;
}
else
{
piece.Operation = AssignOperator;
}
break;
}
}
}Piece.cs
CalculateTargetNumber is different than CalculateNumber that, in CalculateNumber
You have to calculate 2 values for the case of subtract and divide.
For example
The piece has 2 cells, and the piece target value is =1,
If the user enters 3,1 or the user enters 1,3 both cases will be considered it is correct.
The piece has 2 cells, and the piece target value is /2,
If the user enters 4,2 or the user enters 2,4 both cases will be considered it is correct.
public int CalculateTargetNumber()
{
int i;
int iSum = 0;
for(i=0;i<this.lstCell.Count;i++)
{
switch (this.Operation) {
case PieceOperation.Add:
iSum += lstCell[i].TargetValue ;
break;
case PieceOperation.Subtract:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum -= lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Multiply:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum *= lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Divide:
if (i == 0)
{
iSum = lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
else
{
iSum = iSum / lstCell[i].TargetValue;
}
break;
}
}
return iSum;
}
private const int InvalidValue = int.MinValue;
public void CalculateNumber(ref int Number1, ref int Number2)
{
int i;
Number1 = InvalidValue;
Number2 = InvalidValue;
int numberTemp = 0;
for (i = 0; i < this.lstCell.Count; i++)
{
switch (this.Operation)
{
case PieceOperation.Add:
if (i == 0)
{
Number1 = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 += lstCell[i].Value;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Subtract:
if (i == 0)
{
numberTemp = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 = numberTemp - lstCell[i].Value;
Number2 = lstCell[i].Value - numberTemp;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Multiply:
if (i == 0)
{
Number1 = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
Number1 *= lstCell[i].Value;
}
break;
case PieceOperation.Divide:
if (i == 0)
{
numberTemp = lstCell[i].Value;
}
else
{
int tempNumber1 = CalculateDivide(numberTemp, lstCell[i].Value);
int tempNumber2 = CalculateDivide(lstCell[i].Value, numberTemp);
if(tempNumber1 != InvalidValue)
{
Number1 = tempNumber1;
}
if(tempNumber2 != InvalidValue)
{
Number2 = tempNumber2;
}
}
break;
}
}
}UI/pictureBoxTable responsible for drawing the board.
I want to focus on drawing the border only because the other things just simply paint the background color.
The algorithm to draw the border is
-
Every cell has 4 borders, North, West, South, East
-
We draw all of the border if there is no other cell in the list next to the border. if there is we draw the line between cells.
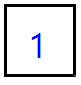
In this picture, the cell does not have any other cell within the same piece, so it draws all 4 borders.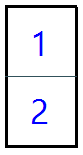
In this picture, the cell 1 does not need to draw the south border, the cell 2 does not need to draw the north border. -
We can determine if there is another cell in the same piece next to the border by using this algorithm.
loop through another cell
3.1 if the other cell has the same row as the checking cell, if the other cell column is less than the checking cell, no need to draw a west border.
3.2 is the same as #3.2 but if the other cell column is more than the checking cell, no need to draw an east border. 3.3 if the other cell has the same column as the checking cell if the other cell row is less than the checking cell, no need to draw a top border.
3.4 is the same as #3.3 but if the other cell row is more than the checking cell, no need to draw a south border.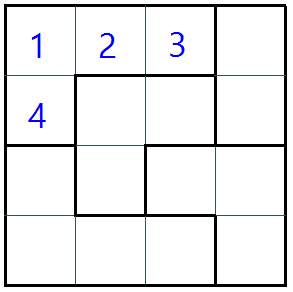
For example, in this picture, cell 1 does not need to draw the east border because it has the other cells (2,3) which have the same rows as its but the column is more than cell 1.cell 1 does not need to draw the south border because it has the other cell (4) which has the same column as it but the row is more than cell 1.
private void RenderBorder(Graphics g,Board pBoard)
{
int indexPiece = 0;
// loop for the list of pieces.
for (indexPiece = 0; indexPiece < pBoard.lstPiece.Count; indexPiece++)
{
Kaldoku.Piece Piece = pBoard.lstPiece[indexPiece];
int indexCell;
//loop all cell in piece.
for (indexCell = 0; indexCell < Piece.lstCell.Count; indexCell++)
{
Kaldoku.Cell Cell = Piece.lstCell[indexCell];
int indexOtherCell = 0;
Point p1 = new Point(0, 0);
Point p2 = new Point(0, 0);
int col = Piece.ColPut + Cell.Col;
int row = Piece.RowPut + Cell.Row;
int extrapixel = 2;
Point northBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset - extrapixel, row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point northEnd = new Point(northBegin.X + CellWidth + extrapixel, northBegin.Y);
Point westBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset, row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point westEnd = new Point(westBegin.X, westBegin.Y + CellWidth + 1);
Point eastBegin = new Point((col + 1) * CellWidth + xOffset, row * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point eastEnd = new Point(eastBegin.X, eastBegin.Y + CellWidth + 1);
Point southBegin = new Point(col * CellWidth + xOffset - extrapixel, (row + 1) * CellWidth + yOffset);
Point southEnd = new Point(southBegin.X + CellWidth + extrapixel, southBegin.Y);
Boolean isNeedToDrawNorthBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawWestBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawSouthBorder = true;
Boolean isNeedToDrawEastBorder = true;
PointF pointF = new PointF(col * CellWidth, row * CellWidth);
pointF = new PointF(col * CellWidth + (CellWidth / 4) + 3, row * CellWidth + (CellWidth / 4));
// Check other cell part.
for (indexOtherCell = 0; indexOtherCell < Piece.lstCell.Count; indexOtherCell++)
{
if (indexOtherCell == indexCell)
{
continue;
}
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Row == Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Row)
{
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Col > Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Col)
{
isNeedToDrawEastBorder = false;
}
else
{
isNeedToDrawWestBorder = false;
}
}
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Col == Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Col)
{
if (Piece.lstCell[indexOtherCell].Row > Piece.lstCell[indexCell].Row)
{
isNeedToDrawSouthBorder = false;
}
else
{
isNeedToDrawNorthBorder = false;
}
}
}
Pen pen = isNeedToDrawNorthBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, northBegin, northEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawWestBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, westBegin, westEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawSouthBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, southBegin, southEnd);
pen = isNeedToDrawEastBorder
? PenBorder
: PenLineBetweenCell;
g.DrawLine(pen, eastBegin, eastEnd);
}
}
}https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KenKen
This article also published at https://www.codeproject.com/Articles/5375124/Kaldoku-game