https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/837/
维护一个字符串集合,支持两种操作:
- “I x”向集合中插入一个字符串x;
- “Q x”询问一个字符串在集合中出现了多少次。
共有N个操作,输入的字符串总长度不超过 105105,字符串仅包含小写英文字母。
第一行包含整数N,表示操作数。
接下来N行,每行包含一个操作指令,指令为”I x”或”Q x”中的一种。
对于每个询问指令”Q x”,都要输出一个整数作为结果,表示x在集合中出现的次数。
每个结果占一行。
1≤N≤2∗104
5
I abc
Q abc
Q ab
I ab
Q ab
1
0
1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx;
char str[N];
void insert(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++)
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++ ;
}
int query(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; str[i]; i++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if (!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n --)
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);
if (op[0] == 'I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/
mplement a trie with insert, search, and startsWith methods.
Example:
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // returns true
trie.search("app"); // returns false
trie.startsWith("app"); // returns true
trie.insert("app");
trie.search("app"); // returns true
Note:
- You may assume that all inputs are consist of lowercase letters
a-z. - All inputs are guaranteed to be non-empty strings.
class Trie {
int N = 100010;
int[][] son;
int[] cnt;
int idx;
String str;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
son = new int[N][26];
cnt = new int[N];
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int u = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (son[p][u] == 0) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
cnt[p] ++;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
int u = word.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (son[p][u] == 0) return false;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p] > 0;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
int u = prefix.charAt(i) - 'a';
if (son[p][u] == 0) return false;
p = son[p][u];
}
return true;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
* boolean param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/https://leetcode.com/problems/design-add-and-search-words-data-structure/
Design a data structure that supports adding new words and finding if a string matches any previously added string.
Implement the WordDictionary class:
WordDictionary()Initializes the object.void addWord(word)Addswordto the data structure, it can be matched later.bool search(word)Returnstrueif there is any string in the data structure that matcheswordorfalseotherwise.wordmay contain dots'.'where dots can be matched with any letter.
Example:
Input
["WordDictionary","addWord","addWord","addWord","search","search","search","search"]
[[],["bad"],["dad"],["mad"],["pad"],["bad"],[".ad"],["b.."]]
Output
[null,null,null,null,false,true,true,true]
Explanation
WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();
wordDictionary.addWord("bad");
wordDictionary.addWord("dad");
wordDictionary.addWord("mad");
wordDictionary.search("pad"); // return False
wordDictionary.search("bad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search(".ad"); // return True
wordDictionary.search("b.."); // return True
Constraints:
1 <= word.length <= 500wordinaddWordconsists lower-case English letters.wordinsearchconsist of'.'or lower-case English letters.- At most
50000calls will be made toaddWordandsearch.
class WordDictionary {
public class Node {
boolean is_end;
Node[] next;
Node() {
is_end = false;
next = new Node[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) next[i] = null;
}
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Node root;
public WordDictionary() {
root = new Node();
}
/** Adds a word into the data structure. */
public void addWord(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (p.next[u] == null) p.next[u] = new Node();
p = p.next[u];
}
p.is_end = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter. */
public boolean search(String word) {
return dfs(word, 0, root);
}
public boolean dfs(String word, int k, Node node) {
if (k == word.length()) return node.is_end;
char cur = word.charAt(k);
if (cur != '.') {
if (node.next[cur - 'a'] != null)
return dfs(word, k + 1, node.next[cur - 'a']);
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (node.next[i] != null)
if (dfs(word, k + 1, node.next[i]))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your WordDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
* WordDictionary obj = new WordDictionary();
* obj.addWord(word);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(word);
*/https://leetcode.com/problems/word-search-ii/
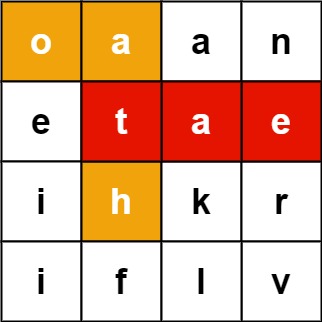
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Example 1:
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
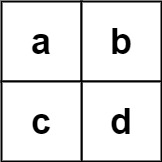
Example 2:
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output: []
Constraints:
m == board.lengthn == board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 12board[i][j]is a lowercase English letter.1 <= words.length <= 3 * 10^41 <= words[i].length <= 10words[i]consists of lowercase English letters.- All the strings of
wordsare unique.
class Solution {
public class TrieNode {
int id;
TrieNode[] son;
TrieNode() {
id = -1;
son = new TrieNode[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) son[i] = null;
}
}
public TrieNode root;
public Set<Integer> ids;
public char[][] g;
public int[] dirs = {-1, 0, 1, 0, -1};
void insert(String word, int id) {
// insert ith word into trie.
TrieNode p = root;
for (char c : word.toCharArray()) {
int u = c - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) p.son[u] = new TrieNode();
p = p.son[u];
}
p.id = id;
}
void dfs(int x, int y, TrieNode p) {
if (p.id != -1) ids.add(p.id);
// backtrack
char ch = g[x][y];
g[x][y] = '.';
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int xx = x + dirs[d], yy = y + dirs[d + 1];
if (xx >= 0 &&
xx < g.length &&
yy >= 0 &&
yy < g[0].length
&& g[xx][yy] != '.') {
int u = g[xx][yy] - 'a';
if (p.son[u] != null)
dfs(xx, yy, p.son[u]);
}
}
// recover
g[x][y] = ch;
}
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
g = board;
root = new TrieNode();
ids = new HashSet<>();
// insert all words into trie
int k = 0;
for (String w : words) insert(w, k++);
// traverse the board.
int n, m;
n = g.length; m = g[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int u = g[i][j] - 'a';
if (root.son[u] != null)
dfs(i, j, root.son[u]);
}
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer id : ids) res.add(words[id]);
return res;
}
}https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-magic-dictionary/
Design a data structure that is initialized with a list of different words. Provided a string, you should determine if you can change exactly one character in this string to match any word in the data structure.
Implement the MagicDictionary class:
MagicDictionary()Initializes the object.void buildDict(String[] dictionary)Sets the data structure with an array of distinct stringsdictionary.bool search(String searchWord)Returnstrueif you can change exactly one character insearchWordto match any string in the data structure, otherwise returnsfalse.
Example 1:
Input
["MagicDictionary", "buildDict", "search", "search", "search", "search"]
[[], [["hello", "leetcode"]], ["hello"], ["hhllo"], ["hell"], ["leetcoded"]]
Output
[null, null, false, true, false, false]
Explanation
MagicDictionary magicDictionary = new MagicDictionary();
magicDictionary.buildDict(["hello", "leetcode"]);
magicDictionary.search("hello"); // return False
magicDictionary.search("hhllo"); // We can change the second 'h' to 'e' to match "hello" so we return True
magicDictionary.search("hell"); // return False
magicDictionary.search("leetcoded"); // return False
Constraints:
1 <= dictionary.length <= 1001 <= dictionary[i].length <= 100dictionary[i]consists of only lower-case English letters.- All the strings in
dictionaryare distinct. 1 <= searchWord.length <= 100searchWordconsists of only lower-case English letters.buildDictwill be called only once beforesearch.- At most
100calls will be made tosearch.
- 为了找到只有一个不匹配的word,这里需要在dfs的时候加上参数判断。
class MagicDictionary {
static final int N = 10010;
int[][] son;
int idx;
boolean[] is_end;
public void insert(String s) {
int p = 0;
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (son[p][u] == 0) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
is_end[p] = true;
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MagicDictionary() {
son = new int[N][26];
is_end = new boolean[N];
}
public void buildDict(String[] dictionary) {
for (String s : dictionary) insert(s);
}
public boolean search(String searchWord) {
return dfs(searchWord, 0, 0, 0);
}
public boolean dfs(String s, int p, int pos, int c) {
if (is_end[p] && c == 1 && pos == s.length()) return true;
if (c > 1 || pos == s.length()) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (son[p][i] == 0) continue;
int miss = s.charAt(pos) - 'a' == i ? 0 : 1;
if (dfs(s, son[p][i], pos + 1, c + miss))
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
/**
* Your MagicDictionary object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MagicDictionary obj = new MagicDictionary();
* obj.buildDict(dictionary);
* boolean param_2 = obj.search(searchWord);
*/https://leetcode.com/problems/map-sum-pairs/
Implement the MapSum class:
MapSum()Initializes theMapSumobject.void insert(String key, int val)Inserts thekey-valpair into the map. If thekeyalready existed, the originalkey-valuepair will be overridden to the new one.int sum(string prefix)Returns the sum of all the pairs' value whosekeystarts with theprefix.
Example 1:
Input
["MapSum", "insert", "sum", "insert", "sum"]
[[], ["apple", 3], ["ap"], ["app", 2], ["ap"]]
Output
[null, null, 3, null, 5]
Explanation
MapSum mapSum = new MapSum();
mapSum.insert("apple", 3);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 3 (apple = 3)
mapSum.insert("app", 2);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 5 (apple + app = 3 + 2 = 5)
Constraints:
1 <= key.length, prefix.length <= 50keyandprefixconsist of only lowercase English letters.1 <= val <= 1000- At most
50calls will be made toinsertandsum.
-
Trie + HashMap 首先默写一遍 Trie 的模板
-
然后 HashMap 存放的是之前 insert 字符串时的值,目的是为了后续如果发现有相同的string,需要被覆盖,便于减去对应节点上的值。
class MapSum {
class TrieNode {
int v;
TrieNode[] son;
TrieNode() {
v = 0;
son = new TrieNode[26];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) son[i] = null;
}
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public TrieNode root;
public Map<String, Integer> hash;
public MapSum() {
root = new TrieNode();
hash = new HashMap<>();
}
public void insert(String key, int val) {
if (hash.containsKey(key)) {
int prev = hash.get(key);
TrieNode p = root;
for (char ch : key.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
p.son[u].v = p.son[u].v - prev + val;
p = p.son[u];
}
}
else {
TrieNode p = root;
for (char ch : key.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) p.son[u] = new TrieNode();
p.son[u].v += val;
p = p.son[u];
}
}
hash.put(key, val);
}
public int sum(String prefix) {
TrieNode p = root;
int tot = 0;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) return 0;
p = p.son[u];
}
return p.v;
}
}
作者:acw_林少
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/942408/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。https://leetcode.com/problems/index-pairs-of-a-string/
Given a text string and words (a list of strings), return all index pairs [i, j] so that the substring text[i]...text[j] is in the list of words.
Example 1:
Input: text = "thestoryofleetcodeandme", words = ["story","fleet","leetcode"]
Output: [[3,7],[9,13],[10,17]]
Example 2:
Input: text = "ababa", words = ["aba","ab"]
Output: [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4]]
Explanation:
Notice that matches can overlap, see "aba" is found in [0,2] and [2,4].
Note:
- All strings contains only lowercase English letters.
- It's guaranteed that all strings in
wordsare different. 1 <= text.length <= 1001 <= words.length <= 201 <= words[i].length <= 50- Return the pairs
[i,j]in sorted order (i.e. sort them by their first coordinate in case of ties sort them by their second coordinate).
class Solution {
class Node {
boolean isWord = false;
Node[] son = new Node[26];
}
public Node root;
public void insert(String s) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch: s.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) p.son[u] = new Node();
p = p.son[u];
}
p.isWord = true;
}
public boolean search(String s) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) return false;
p = p.son[u];
}
return p.isWord;
}
public int[][] indexPairs(String text, String[] words) {
List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
root = new Node();
for (String w : words) insert(w);
for (int i = 0; i < text.length(); i++ ) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= text.length(); j++) {
String t = text.substring(i, j);
if (search(t)) res.add(new int[]{i, j - 1});
}
}
int[][] res1 = new int[res.size()][2];
for (int i = 0; i < res.size() ; i++) {
res1[i] = res.get(i);
}
return res1;
}
}https://leetcode.com/problems/prefix-and-suffix-search/
Design a special dictionary which has some words and allows you to search the words in it by a prefix and a suffix.
Implement the WordFilter class:
WordFilter(string[] words)Initializes the object with thewordsin the dictionary.f(string prefix, string suffix)Returns the index of the word in the dictionary which has the prefixprefixand the suffixsuffix. If there is more than one valid index, return the largest of them. If there is no such word in the dictionary, return-1.
Example 1:
Input
["WordFilter", "f"]
[[["apple"]], ["a", "e"]]
Output
[null, 0]
Explanation
WordFilter wordFilter = new WordFilter(["apple"]);
wordFilter.f("a", "e"); // return 0, because the word at index 0 has prefix = "a" and suffix = 'e".
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 150001 <= words[i].length <= 101 <= prefix.length, suffix.length <= 10words[i],prefixandsuffixconsist of lower-case English letters only.- At most
15000calls will be made to the functionf.
class WordFilter {
class Node {
int id;
Node[] son = new Node[27]; // 加上'{'作为分隔符,ASCII码为'a' + 27
}
Node root;
public void insert(String s, int pos) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) {
p.son[u] = new Node();
}
p.son[u].id = pos;
p = p.son[u];
}
}
public WordFilter(String[] words) {
root = new Node();
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
String w = "{" + words[i];
for (int j = words[i].length(); j >= 0; j--) {
String pw = words[i].substring(j).concat(w);
insert(pw, i);
}
}
}
public int f(String prefix, String suffix) {
Node p = root;
String s = suffix + "{" + prefix;
for (char ch : s.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) return -1;
p = p.son[u];
}
return p.id;
}
}
/**
* Your WordFilter object will be instantiated and called as such:
* WordFilter obj = new WordFilter(words);
* int param_1 = obj.f(prefix,suffix);
*/https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-trie-ii-prefix-tree/
A trie (pronounced as "try") or prefix tree is a tree data structure used to efficiently store and retrieve keys in a dataset of strings. There are various applications of this data structure, such as autocomplete and spellchecker.
Implement the Trie class:
Trie()Initializes the trie object.void insert(String word)Inserts the stringwordinto the trie.int countWordsEqualTo(String word)Returns the number of instances of the stringwordin the trie.int countWordsStartingWith(String prefix)Returns the number of strings in the trie that have the stringprefixas a prefix.void erase(String word)Erases the stringwordfrom the trie.
Example 1:
Input
["Trie", "insert", "insert", "countWordsEqualTo", "countWordsStartingWith", "erase", "countWordsEqualTo", "countWordsStartingWith", "erase", "countWordsStartingWith"]
[[], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["apple"], ["apple"], ["app"], ["apple"], ["app"]]
Output
[null, null, null, 2, 2, null, 1, 1, null, 0]
Explanation
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple"); // Inserts "apple".
trie.insert("apple"); // Inserts another "apple".
trie.countWordsEqualTo("apple"); // There are two instances of "apple" so return 2.
trie.countWordsStartingWith("app"); // "app" is a prefix of "apple" so return 2.
trie.erase("apple"); // Erases one "apple".
trie.countWordsEqualTo("apple"); // Now there is only one instance of "apple" so return 1.
trie.countWordsStartingWith("app"); // return 1
trie.erase("apple"); // Erases "apple". Now the trie is empty.
trie.countWordsStartingWith("app"); // return 0
Constraints:
1 <= word.length, prefix.length <= 2000wordandprefixconsist only of lowercase English letters.- At most
3 * 104calls in total will be made toinsert,countWordsEqualTo,countWordsStartingWith, anderase. - It is guaranteed that for any function call to
erase, the stringwordwill exist in the trie.
class Trie {
class Node {
int end = 0; // isEnd
Node[] son = new Node[26];
int v = 0; //
}
Node root;
public Trie() {
root = new Node();
}
public void insert(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) p.son[u] = new Node();
p.son[u].v ++;
p = p.son[u];
}
p.end ++;
}
public int countWordsEqualTo(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) return 0;
p = p.son[u];
}
return p.end;
}
public int countWordsStartingWith(String prefix) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
if (p.son[u] == null) return 0;
p = p.son[u];
}
return p.v;
}
public void erase(String word) {
Node p = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
int u = ch - 'a';
p.son[u].v--;
p = p.son[u];
}
p.end --;
}
}
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* int param_2 = obj.countWordsEqualTo(word);
* int param_3 = obj.countWordsStartingWith(prefix);
* obj.erase(word);
*/