ServiceStack.OrmLite library has support for use with an Aurora database via the ServiceStack.OrmLite.MySql NuGet package. This can be used in conjunction with Amazon's RDS service using Aurora.
To get started, first you will need to create your Aurora database via the AWS RDS service.
- Login to the AWS Web console.
- Select RDS from the Services from the top menu.
- Select Instances from the RDS Dashboard and click Launch DB Instance.
The above steps will start the RDS Wizard to launch a new DB instance. To setup a new Aurora instance, follow the wizard selecting the appropriate options for your application. As an example, we can create a Customers database for a non-production environment.
- Select Engine - Select Amazon Aurora
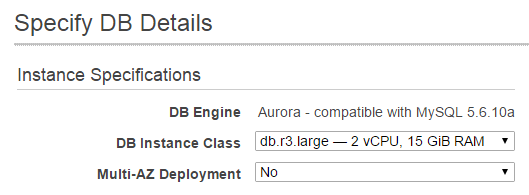
- Specify DB Details
- Create a
db.r3.largeinstance with default settings - Specify Multi-AZ Deployment as
No
- Create a
-
Specify DB Instance Identifier, eg
servicestack-example-customers. -
Specify Master Username, eg
admin. -
Create and confirm master user password.
-
Configure Advanced Settings - Leave the suggested settings and specify a Database Name, eg
customers. This will be used in your connection string.
Note: Problems can occure if your default VPC is not setup to DNS Resolution and/or DNS Hostname. Navigate to Services, VPC and enable these two options on your default VPC. Default settings are to create a new VPC security group that will allow remote access to your DB instance based on your IP address. If your IP address changes, you will lose remote access and this security group will need to be updated.
Click Launch DB Instance at the bottom right to launch your new instance. If all is successful, you should see the following.
Now that you're Aurora instance is running, connecting with OrmLite will require the ServiceStack.OrmLite.MySql NuGet package as well as connection string to your new Aurora instance.
<appSettings>
<add key="ConnectionString" value="Uid={User};Password={Password};Server={EndpointUrl};Port={EndpointPort};Database=customers" />
</appSettings>Once this dependency is installed, the OrmLiteConnectionFactory can be used with the MySqlDialect.Provider can be configured in the AppHost Configure method. For example.
public class AppHost : AppSelfHostBase
{
public AppHost() : base("AWS Aurora Customers", typeof(AppHost).Assembly) {}
public override void Configure(Container container)
{
container.Register<IDbConnectionFactory>(c => new OrmLiteConnectionFactory(
AppSettings.GetString("ConnectionString"), MySqlDialect.Provider));
using (var db = container.Resolve<IDbConnectionFactory>().Open())
{
if (db.CreateTableIfNotExists<Customer>())
{
//Add seed data
}
}
}
}Using our connection from a ServiceStack Service, we can use the Db property to access our Customer table. Eg, Below is an example of a CRUD service using OrmLite.
public class CustomerService : Service
{
public object Get(GetCustomers request)
{
return new GetCustomersResponse { Results = Db.Select<Customer>() };
}
public object Get(GetCustomer request)
{
return Db.SingleById<Customer>(request.Id);
}
public object Post(CreateCustomer request)
{
var customer = new Customer { Name = request.Name };
Db.Save(customer);
return customer;
}
public object Put(UpdateCustomer request)
{
var customer = Db.SingleById<Customer>(request.Id);
if (customer == null)
throw HttpError.NotFound("Customer '{0}' does not exist".Fmt(request.Id));
customer.Name = request.Name;
Db.Update(customer);
return customer;
}
public void Delete(DeleteCustomer request)
{
Db.DeleteById<Customer>(request.Id);
}
}See the OrmLite GitHub page for more info on working with OrmLite API.