Face recognition is the process of detecting and identifying faces against a database of stored faces.The face recognition algorithm relies on the database of faces to train itself and try to learn about the facial structures of the people whose faces are stored in the database.
It basically consists of three sections
Training
Evaluation
Testing
In the training section, we pass in a particular image of a person such that it is easier for the algorithm to learn about the facial structure of the person.So at first the face is detected, certain features of the face is captured and then the face is stored against a label.
As we train our Face recognition algorithm with multiple faces of a person, we keep a certain portion of the faces seperate for testing the algorithm later.So at this stage, we pass in those images which the algorithm hasn't seen before and ensure it is successfully able to identify the person.If we meet success, we then move on to the next stage.
Now we pass in random images of a person and see if the algorithm can correctly identify the person.If the person's sample images are there in the database then it means the algorithm has seen the person before and has studied the facial structures of that person.So it should be able to correctly identify the person.
The basic idea of face recognition is based on the concept of Dimensionality Reduction.
Dimensionality Reduction reduces the data with high dimensional space (3D, 10D etc) to a lower dimensional space (2D, 1D etc).Why so? We don't higher dimension images to perform face recognition.For example a 10 * 10 image matrix will have 100 dimensions (10*10).So we don't need 100 dimensions to compare two faces.We reduce it down to 10D whcih contains enough features to compare two faces.
Suppose we have a 2*2 image matrix and we need to perform Dimensionality Reduction on that.So we need to convert the image to a 1D matrix.
To turn this 2D visualization to 1D, we can do projections where we project the points currently in 2D to 1D by projecting it to either X axis or Y axis.
X axis projection
Let us do a X axis projection
We can see above that here we have less or no overlapping of points which means this way of projection keeps most of the important feautures
Y axis projection
Now let us do a Y axis projection
We can see above that there are more and more points overlapping which means we could miss out some important features.
So it is important to choose an appropriate projection to retain important features.Futhermore higher the no of features, the harder it gets to visualize the training set and then work on it.Sometimes most of these features are corelated and hence redundant.So we reduce the features by dimensionality reduction.
There are multiple algorithms to perform face recognition.The ones I am gonna discuss and use in the application are
Principal Component Analysis
Linear Discriminant Analysis
Local Binary Patterns
Principal Component Analysis (PCA) works on unlabelled data (no classes or categories).It works on the condition that while the data in the higher dimension is mapped to the data in the lower dimension, the variance of the data in the lower dimension should be maximum.
We can see above that the variance (spread) along x axis is maximum so we choose the x axis where we get maximum variance.
Note- We are not limited to picking x axis or y axis.We pick an axis which gives us maximum variance.
As we can see above, x and y variance are almost the same but the variance along the tilted axis is way too high and hence we choose this as the variance.Algorithms like Eigen Faces uses PCA.
Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) works on labelled data.It works on the condition that while data in the higher dimensional space is mapped to data in the lower dimensional space, we look for axis that maximally seperate classes or categories.
For example we have two classes of data + and -
In the above figure, we try to mark the mid points of two extremes of each of the classes and measure the distance between the mid points.We observe that the distance between the mid points of two classes along the x axis is maximum.So this maximally seperates the classes and hence we choose X axis as the ideal axis.
Let us look at another example
In the above figure we choose the slanted axis as it maximally seperates the classes.Algorithms like Fisher Faces uses LDA.
Both the algorithms choose axis that best suits their needs.Below is an example where PCA and LDA choose two seperate axis to satisfy their requirements.
We can see in the above figure that the Y axis provides the best condition for maximum variance and hence PCA would choose this axis whereas the X axis provides the best condition for maximal seperation between two classes and hence LDA would choose this axis.
Local Binary Patterns (LBP) labels the pixels of an image by thresholding (comparing each pixel with its surrounding neighbourhood of pixels) the neighbourhood of each pixels and considers the result as a binary number.This is the most commonly used face recognition algorithm as it is more accurate than Eigen Faces or Fisher Faces algorithm.
Suppose we have a 3 * 3 matrix that represents an image.
The idea is to represent this matrix as a binary number.Here the central pixel is 50.So we replace pixels less than 50 as 0 and greater than 50 as 1.So we get the matrix represented in the below figure
Now we go either write the elements of the matrix clockwise or anticlockwise.Let me write the elements in clockwise direction.So we get the binary representation of 00011000.Converting the binary number to decimal yeilds us 24.So we replace the central element of the matrix with the decimal value 24 and all other pixels as none.
As we can see above, the resulting decimal number is stored in the 2D array.This process is repeated for each pixel in the image.
Now let us benchmark the training time for each of the algorithms discussed above.The figures represented below may vary.It is just to get a rough idea of the time taken to train the algorithm given a dataset.
LBP Training time: 0.389401912689209s
EigenFaces Training time: 1.8466179370880127s
FisherFaces Training time: 1.4000251293182373s
Judging by the above results, LBP takes the least time to train followed by FisherFaces and then EigenFaces.
Now before we start, we need to store our faces into the dataset.So I store faces of myself depicting different emotions and lighting conditions into the Yale dataset.You can pass either gif or jpeg images into the dataset.But ensure your images have plain or no background so that the background doesn't interfere with the face recognition algorithm.Below are the sample faces I stored in the Yale datset.
Now let us see the Face recognision algorithm in action.First I pass a picture of myself into the program.
So the Face recognition algorithm (in this case LBP algorithm) will work on it and give me the result below
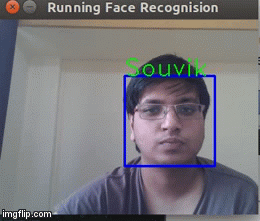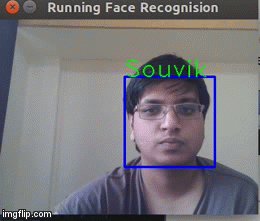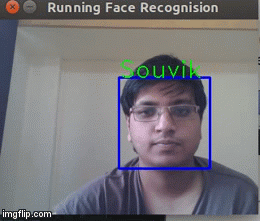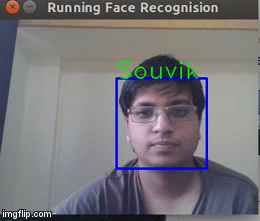
Now that we know the Face recognition algorithm works, why don't we try it on a realtime environment in this case a webcam?So we instruct the program to pick frames from a video and run the Face recognition on that.We get the result below
As you can see above, it is recognising my face in real time.Hurrah!The application works!But it is not perfect and it does tends to give wrong results quite often.Gotta look for a workaround for this.