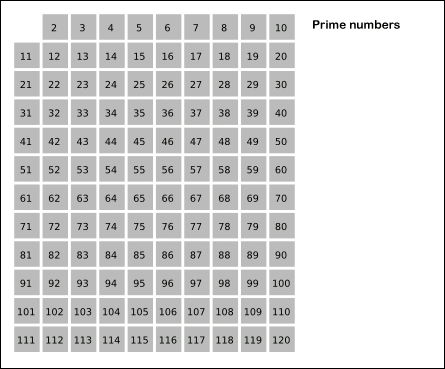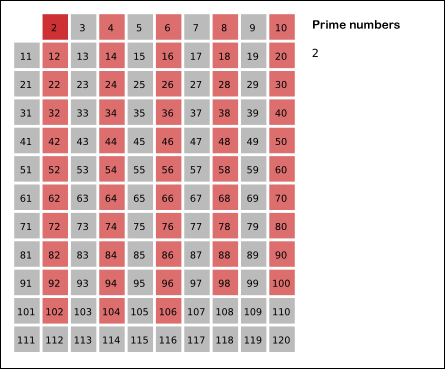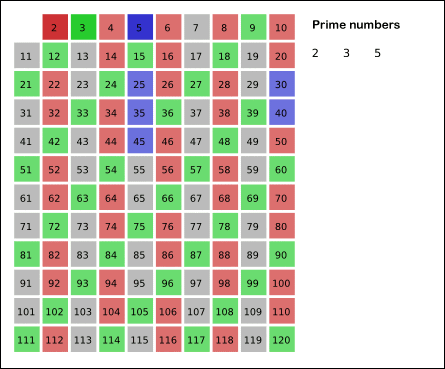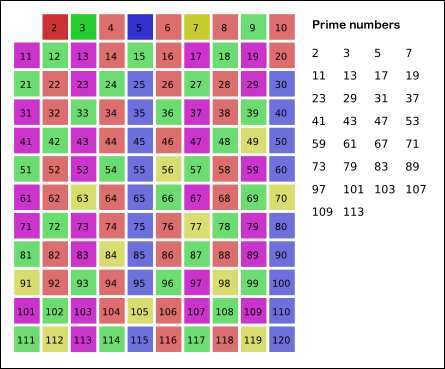
In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes is a simple, ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit.
It does so by iteratively marking as composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime, starting with the first prime number, 2. The multiples of a given prime are generated as a sequence of numbers starting from that prime, with constant difference between them that is equal to that prime.[1] This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime.
Add: Note that there are other prime sieves: ##Prime Sieves: A prime sieve or prime number sieve is a fast type of algorithm for finding primes. There are many prime sieves. The simple sieve of Eratosthenes (250s BCE), the sieve of Sundaram (1934), the still faster but more complicated sieve of Atkin[1] (2004), and various wheel sieves[2] are most common.
A prime sieve works by creating a list of all integers up to a desired limit and progressively removing composite numbers (which it directly generates) until only primes are left. This is the most efficient way to obtain a large range of primes; however, to find individual primes, direct primality tests are more efficient[citation needed]. Furthermore, based on the sieve formalisms, some integer sequences (sequence A240673 in the OEIS) are constructed which they also could be used for generating primes in certain intervals.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generating_primes#Prime_sieves