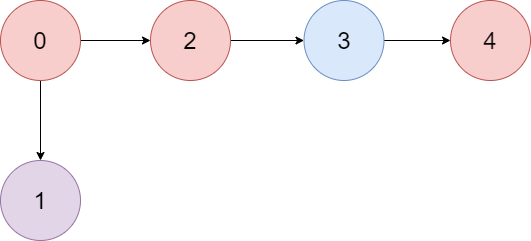
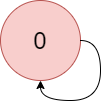
There is a directed graph of n colored nodes and m edges. The nodes are numbered from 0 to n - 1.
You are given a string colors where colors[i] is a lowercase English letter representing the color of the ith node in this graph (0-indexed). You are also given a 2D array edges where edges[j] = [aj, bj] indicates that there is a directed edge from node aj to node bj.
A valid path in the graph is a sequence of nodes x1 -> x2 -> x3 -> ... -> xk such that there is a directed edge from xi to xi+1 for every 1 <= i < k. The color value of the path is the number of nodes that are colored the most frequently occurring color along that path.
Return the largest color value of any valid path in the given graph, or -1 if the graph contains a cycle.
Example 1:
Input: colors = "abaca", edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[3,4]]
Output: 3
Explanation: The path 0 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 contains 3 nodes that are colored "a" (red in the above image).
Example 2:
Input: colors = "a", edges = [[0,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: There is a cycle from 0 to 0.
Constraints:
n == colors.lengthm == edges.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= m <= 105colorsconsists of lowercase English letters.0 <= aj, bj < n
Companies:
Google
Related Topics:
Dynamic Programming, Topological Sort
Intuition: We can use BFS Topological Sort to visit the nodes. When visiting the next node, we can forward the color information to the next node. Also Topo-sort can help detect circle.
Algorithm:
Just do normal topo sort. One modification is that, for each node, we need to store a int cnt[26] array where cnt[i] is the maximum count of color i in all paths to the current node.
For example, assume there are two paths reaching the current node, aba, bba. Then cnt['a'] = 2 and cnt['b'] = 2 because both color a and b can be 2 in different paths.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/contest/weekly-contest-240/problems/largest-color-value-in-a-directed-graph/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(V + E)
// Space: O(V + E)
class Solution {
typedef array<int, 26> T;
public:
int largestPathValue(string C, vector<vector<int>>& E) {
unordered_map<int, vector<int>> G;
vector<int> indegree(C.size());
for (auto &e : E) {
G[e[0]].push_back(e[1]); // build graph
indegree[e[1]]++; // count indegrees
}
vector<T> cnt(C.size(), T{}); // cnt[i][j] is the maximum count of j-th color from the ancester nodes to node i.
queue<int> q;
for (int i = 0; i < C.size(); ++i) {
if (indegree[i] == 0) { // if this node has 0 indegree, we can use it as a source node
q.push(i);
cnt[i][C[i] - 'a'] = 1; // the count of the current color should be 1
}
}
int ans = 0, seen = 0;
while (q.size()) {
auto u = q.front();
q.pop();
int val = *max_element(begin(cnt[u]), end(cnt[u])); // we use the maximum of all the maximum color counts as the color value.
ans = max(ans, val);
++seen;
for (int v : G[u]) {
for (int i = 0; i < 26; ++i) {
cnt[v][i] = max(cnt[v][i], cnt[u][i] + (i == C[v] - 'a')); // try to use node `u` to update all the color counts of node `v`.
}
if (--indegree[v] == 0) {
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return seen < C.size() ? -1 : ans;
}
};