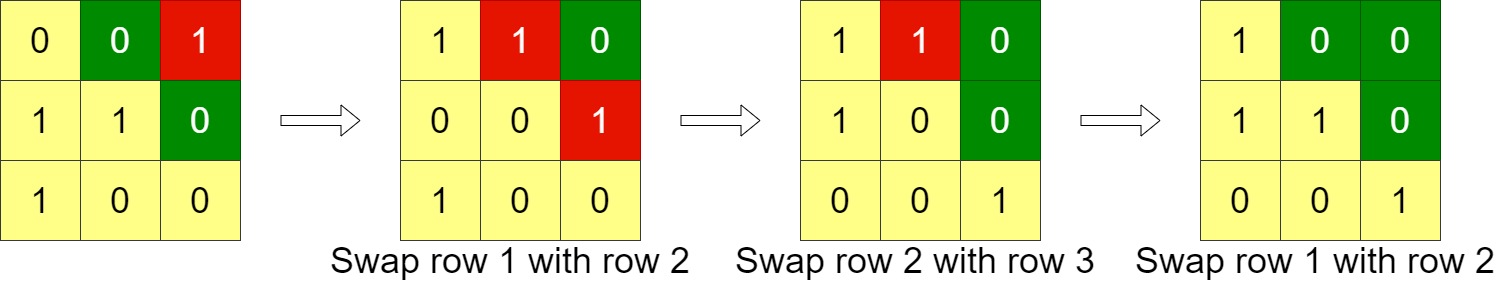
Given an n x n binary grid, in one step you can choose two adjacent rows of the grid and swap them.
A grid is said to be valid if all the cells above the main diagonal are zeros.
Return the minimum number of steps needed to make the grid valid, or -1 if the grid cannot be valid.
The main diagonal of a grid is the diagonal that starts at cell (1, 1) and ends at cell (n, n).
Example 1:
Input: grid = [[0,0,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,0]] Output: 3
Example 2:
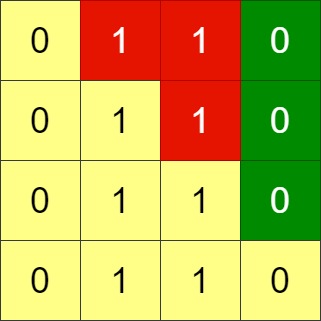
Input: grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0]] Output: -1 Explanation: All rows are similar, swaps have no effect on the grid.
Example 3:
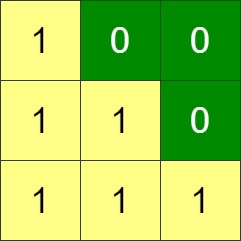
Input: grid = [[1,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,1]] Output: 0
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 200grid[i][j]is0or1
[Greedy]