#Composite Pattern
Intent
Compose objects into tree structures to represent part- whole or parent-child hierarchies. Composite lets clients treat individual objects and compositions of objects uniformly.
Motivation
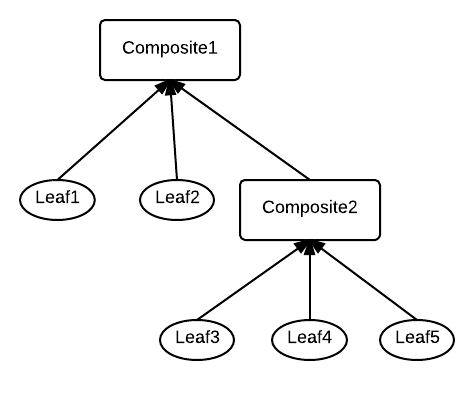
Many times you need to model a system that deals with relationships between objects that are of the same type but on different levels (for example in whole-part, parent-child, or supervisor-employee, relationships.) and in your system the number of levels is unknown until runtime.
Participants
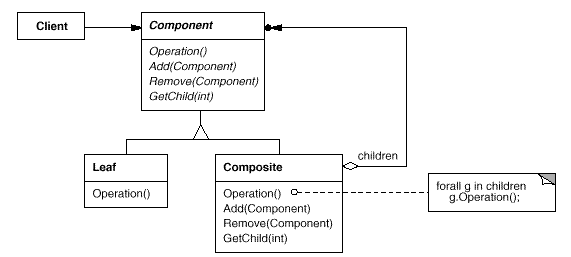
Component
- declares the interface for objects in the composition.
- implements default behavior for the interface common to all classes, as appropriate.
- declares an interface for accessing and managing its child components.
- (optional) defines an interface for accessing a component's parent in the recursive structure, and implements it if that's appropriate.
`Leaf` - represents leaf objects in the composition. A leaf has no children. - defines behavior for primitive objects in the composition.
`Composite` - defines behavior for components having children. - storeschildcomponents. - implements child-related operations in the Component interface.
`Client` - manipulates objects in the composition through the Component interface.
Applicability.
Use the Composite pattern when:
- You want to represent part-whole or parent-child hierarchies of objects
- You want clients to be able to ignore the difference between compositions of objects and individual objects. Clients will treat all objects in the composite structure uniformly.
Task
Below is a high-level view of the browser architecture. We are going to implement a “render tree” for the rendering engine. A render tree is basically a data structure that stores all visual elements in an html document with the original relations, dimensions, stylings information kept (for example, parent- child/sibling relations, height, width, color, styles, etc.).


<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>Your Title Here</TITLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<CENTER><IMG SRC="clouds.jpg" > </CENTER>
<a href="http://somegreatsite.com">Link Name</a>
<H1>This is a Header</H1>
<H2>This is a Medium Header</H2>
<B>This is a new paragraph!</B>
<B><I>This is a new sentence without a paragraph break, in bold italics.</I></B> </BODY>
</BODY>
</HTML>
So you will create a tree-structure that stores all the elements in the html file. No need for logic to really render it. Look at the example code which should be similar to your solution. Then put the tree-building logic inside the client.