-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 20
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
[ARMv8] C语言的一些有趣的特性 #203
Comments
关于ARM大小端模式和CPU有关还是编译器有关结论,ARM大小端模式和CPU有关也和编译器有关系。 ARM默认状态配置为小端模式,编译器不指定编译模式也默认是小端模式。但有些ARM是可以配置为大端模式的。例如:
如果在ARM上面配置了大端模式,gcc编译器则需要增加参数 与CPU配置保持一致。 参考文献:https://gcc.gnu.org/onlinedocs/gcc-4.3.2/gcc/ARM-Options.html |
Volatile关键字面试的时候,很多面试官,en,会问,volatile有啥用啊?今天我们就来了基于ARM架构,聊聊在ARMv7/v8架构上,volatile到底是什么东西。 在编译器配置较高优化级别的时候,可能程序中会出现一些问题,这些问题在较低的优化不太明显,volatile易失性限定符可以告诉编译器,不要对该变量做过多的优化。这种优化可以通过以下场景复现:
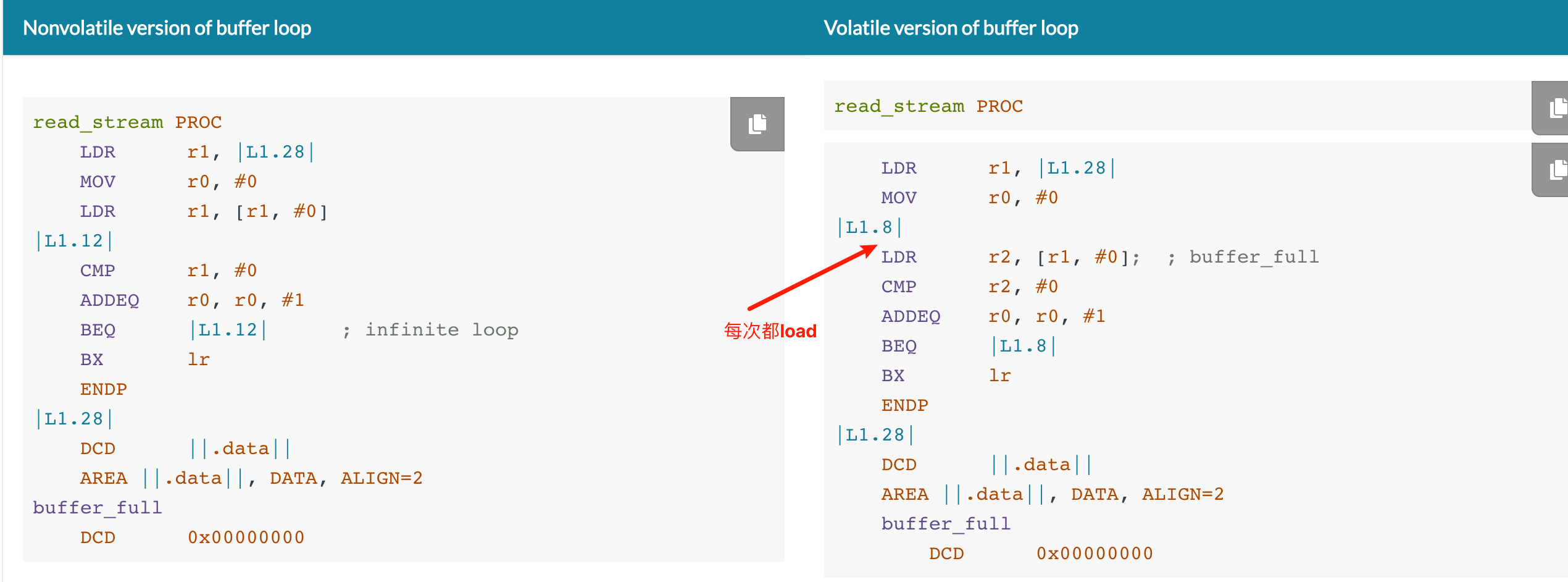
volatile标记会被编译器识别,可以在实现外部随时修改变量,例如操作系统、其他执行线程(中断、信号处理)或硬件,这样就间接给这个变量增加了一个保护,外部随时修改的变量是可能被外面更改的,因此每次在代码中引用该值的时候,需要从内存中去读取,而不是缓存到寄存器中。(将某个变量缓存到寄存器里面是ARM处理器的一种优化手段)。在实现睡眠和计时延迟的上下文,需要将变量声明为volatile告诉编译器需要特定类型的行为。 The two versions of the routine differ only in the way that
Table 13 shows the corresponding disassembly of the machine code produced by the compiler for each of the sample versions in Table 8, where the C code for each implementation has been compiled using the option 如果采用-O2的优化等级,还是看出差异了,左边的r1寄存器被load了r1的值,之后就没有再load了,然后就在L1.12的分支里面无限循环。而在加了volatile的版本,每次都要LDR这个值。 要注意以下情况需要volatile:
Ref |


变量定义的位置
在C语言中,变量的定义位置取决于编码风格和标准。在C89(ANSI C)标准中,要求在函数的开始部分声明所有变量。但在C99及之后的标准中,允许在需要时在函数内任何位置声明变量。
C89标准
在C89标凈中,所有变量必须在函数的任何执行语句之前定义。这意味着所有的变量声明都应该在函数的开始部分,通常是在任何逻辑或计算操作之前。
C99及后续标准
C99标准引入了在需要时声明变量的概念。这意味着你可以在函数中的任何位置声明变量,通常是在第一次使用该变量之前。
最佳实践
关于性能的一些讨论
我们对上面的两个代码的进行objdump输出汇编信息:
可以看到在汇编上,提前定义变量的C89风格会多让处理器执行指令,其他的部分几乎一模一样。因此,最好是使用变量的最小生命周期。
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: