What is Minimum Spanning Tree? Given a connected and undirected graph, a spanning tree of that graph is a subgraph that is a tree and connects all the vertices together. A single graph can have many different spanning trees. A minimum spanning tree (MST) or minimum weight spanning tree for a weighted, connected and undirected graph is a spanning tree with weight less than or equal to the weight of every other spanning tree. The weight of a spanning tree is the sum of weights given to each edge of the spanning tree.
How many edges does a minimum spanning tree has? A minimum spanning tree has (V – 1) edges where V is the number of vertices in the given graph.
What are the applications of Minimum Spanning Tree? See this for applications of MST.
Below are the steps for finding MST using Kruskal’s algorithm
- Sort all the edges in non-decreasing order of their weight.
- Pick the smallest edge. Check if it forms a cycle with the spanning tree formed so far. If cycle is not formed, include this edge. Else, discard it.
- Repeat step#2 until there are (V-1) edges in the spanning tree.
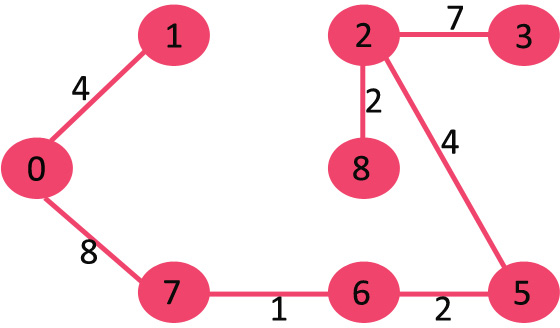
The algorithm is a Greedy Algorithm. The Greedy Choice is to pick the smallest weight edge that does not cause a cycle in the MST constructed so far. Let us understand it with an example: Consider the below input graph.
The graph contains 9 vertices and 14 edges. So, the minimum spanning tree formed will be having (9 – 1) = 8 edges.
After sorting:
Weight Src Dest
1 7 6
2 8 2
2 6 5
4 0 1
4 2 5
6 8 6
7 2 3
7 7 8
8 0 7
8 1 2
9 3 4
10 5 4
11 1 7
14 3 5
Now pick all edges one by one from sorted list of edges
-
Pick edge 8-2: No cycle is formed, include it.
-
Pick edge 6-5: No cycle is formed, include it
-
Pick edge 0-1: No cycle is formed, include it.
-
Pick edge 2-5: No cycle is formed, include it.
-
Pick edge 8-6: Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
-
Pick edge 2-3: No cycle is formed, include it.
-
Pick edge 7-8: Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
-
Pick edge 0-7: No cycle is formed, include it.
-
Pick edge 1-2: Since including this edge results in cycle, discard it.
-
Pick edge 3-4: No cycle is formed, include it.
- Since the number of edges included equals (V – 1), the algorithm stops here.