You signed in with another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You signed out in another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.You switched accounts on another tab or window. Reload to refresh your session.Dismiss alert
classComponent1extendsReact.Component<any>{handleClick(){this.props.history.push('/page2');}render(){return<divonClick={()=>this.handleClick()}>this is component1</div>;}}exportdefaultComponent1;
classComponent1extendsReact.Component<any>{handleClick(){this.props.history.push('/page2');}render(){return<divonClick={()=>this.handleClick()}>this is component1</div>;}}exportdefaultwithRouter(Component1);
render(){constroutes=this.props.routes||[];return(<div><divonClick={()=>this.handleClick()}>this is page2</div><Switch>{routes.map((route)=>(<Routepath={route.path}key={route.path}render={(props: any)=>(<route.component{...props}/>)}/>))}</Switch></div>);}
React Router 中的组件主要分为三类:
在 Web 应用程序中使用的所有组件建议都从 react-router-dom 导入
辛苦整理良久,还望手动点赞鼓励~
博客 github地址为:github.com/fengshi123/… ,汇总了作者的所有博客,欢迎关注及 star ~
1、安装路由包
2、路由组件
路由组件分为两种:BrowserRouter(history 模式) 和 HashRouter(hash 模式),用法一样,但是 url 展示不一样,其中 hash 模式带有 # 号符,如下所示:
2.1、BrowserRouter
2.2、HashRouter
3、Route 参数
3.1、path
string 类型,用来指定路由跳转路径,如下所示,根据 path 和 url 匹配到对应的页面
3.2、exact
boolean 类型,用来精确匹配路由,如果为 true 则精确匹配,否则为正常匹配;如下所示
3.3、sensitive
boolean 类型,用来设置是否区分路由大小写,如果为 true 则区分大小写,否则不区分;如下所示
3.4、strict
boolean 类型,对路径末尾斜杠的匹配。如果为 true,path 为 '/page1/' 将不能匹配 '/page1' 但可以匹配 '/page1/one'。;如下所示
3.5、component
设置路由对应渲染的组件,如下所示
3.6、render
(1)通过写 render 函数返回具体的 dom,如下所示
(2) 也可以通过写 render 函数返回组件,如下所示
这样写的好处是,不仅可以通过 render 方法传递 props 属性,并且可以传递自定义属性:
然后,就可在 Page1 组件中获取 props 和 name 属性:
4、Switch
如果路由 Route 外部包裹 Switch 时,路由匹配到对应的组件后,就不会继续渲染其他组件了。但是如果外部不包裹 Switch 时,所有路由组件会先渲染一遍,然后选择所有匹配的路由进行显示。
(1)当没有使用 Switch 时,如下所示
(2)当使用 Switch 时,如下所示
5、Link 和 NavLink
Link 和 NavLink 都可以用来指定路由跳转,NavLink 的可选参数更多。
5.1、Link
(1)通过字符串执行路由跳转
(2)通过对象指定路由跳转
**(3) replace **
如果设置 replace 为 true 时,表示路由重定向,即新地址替换掉上一次访问的地址;
5.2、NavLink
这是 的特殊版,顾名思义这就是为页面导航准备的。因为导航需要有 “激活状态”。
(1)activeClassName: string
导航选中激活时候应用的样式名,默认样式名为 active
(2)activeStyle: object
如果不想使用样式名就直接写 style,如下所示
(3)exact: bool
若为 true,只有当访问地址严格匹配时激活样式才会应用,跟 3.2 的 exact 一个道理;
(4)strict: bool
若为 true,只有当访问地址后缀斜杠严格匹配(有或无)时激活样式才会应用,跟 3.4 的 exact 一个道理;
(5)isActive: func
决定导航是否激活,或者在导航激活时候做点别的事情。不管怎样,它不能决定对应页面是否可以渲染。
6、Redirect
将导航到一个新的地址,即重定向;如下所示,当页面访问到 /page3 时,页面会直接重定向到 page3.
当然,也可以使用对象的形式,如下所示
7、History 对象 - 编程式导航
支持字符串作为参数跳转,如下所示
同样支持对象作为参数进行路由跳转,如下所示
跳转到对应的页面,我们打印出对应 history 对象,可以看到有以下属性
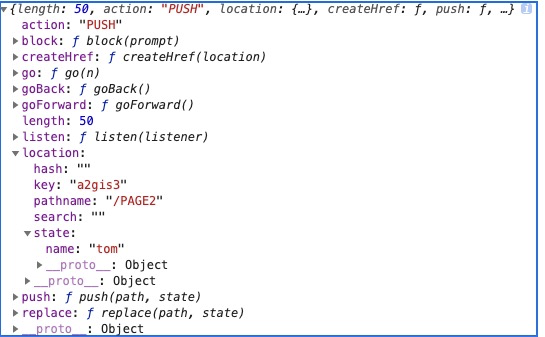
以上 history 对象的属性和方法解释如下:
8、withRouter
withRouter 可以将一个非路由组件包裹为路由组件,使这个非路由组件也能访问到当前路由的 match, location, history对象。使用场景:即如果想在路由页面的子组件中,进行路由的跳转,需要使用 withRouter 进行包裹,否则子组件是访问不到路由对象的。
(1)没有使用 withRouter 的场景
如下代码所示,我们没有使用 withRouter 对 Component1 组件进行包裹,当我们在 Component1 中调用 history 时会报错 TypeError: Cannot read property 'push' of undefined
(2)使用 withRouter 的场景
如下代码所示,我们使用 withRouter 对 Component1 组件进行包裹,当我们在 Component1 中调用 history 时能正常进行路由页面跳转
9、参数传递
9.1、params 传参
路由配置如下
路由跳转代码如下
参数获取代码如下
9.2、query 传参
query 方式可以传递任意类型的值,但是页面的 url 也是由 query 的值拼接的,url 很长且是明文传输。
路由传参如下
页面获取路由传过来的参数如下
9.3、隐式传参
路由跳转传参如下
参数获取代码如下
10、路由的综合应用
通过前面几节,介绍了路由的基本使用 api,本小节我们介绍下在正式项目中如何使用 react 路由。
(1)路由配置文件
我们一般在项目目录底下会新建路由配置文件 /router/index.ts,进行项目路由的相关配置
(2)react 入口代码中配置路由
我们通常会在 App.tsx 中进行项目的路由配置,相关代码如下
(3)嵌套路由
如果你的项目中有嵌套路由,则还需要在对应的页面中进行嵌套子路由的配置,如下所示
通过以上配置后,我们就完成整个 react 项目的路由配置,后续我们在功能需求迭代中,只需要尽情地编写业务代码以及使用 Link/NavLink 或者 this.props.history 进行路由的跳转即可。
11、路由原理
前端三大框架 Angular、React、Vue ,它们的路由解决方案 angular/router、react-router、vue-router 都是基于前端路由原理进行封装实现的 ,具体可以查看笔者之前写的一篇文章《深度剖析:前端路由原理》,这里不再赘述。
辛苦整理良久,还望手动点赞鼓励~
博客 github地址为:github.com/fengshi123/… ,汇总了作者的所有博客,欢迎关注及 star ~
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: