GTTtg uses data from aperTO for a simple Telegram bot that can show the real time arrivals of public transport of the city of Turin.
The two dataset used can be found at GTFS and GTFS-RealTime.
Repositories used are:
- Google transit: For analyzing the GTFS RealTime. Actually the module used is already present in this repository compiled with the latest version of Protobuf (Otherwise the one fetched by npm won't run).
- python-telegram-bot: Version 13.15
The bot, which code is in file tg.py, it is just a simple showcase of the capabilities of GTTtg.
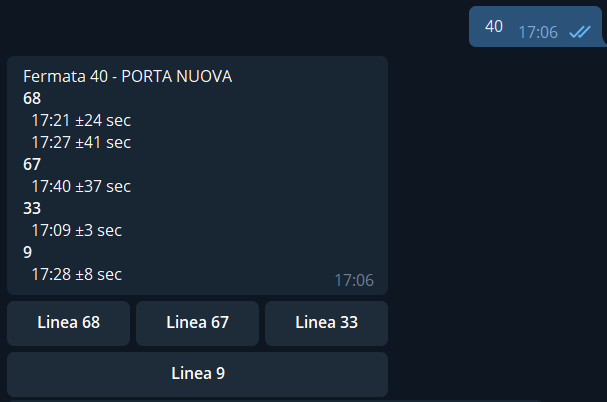
It can send all the forecasted arrivals to a specific stop, by giving the stop code as shown below:
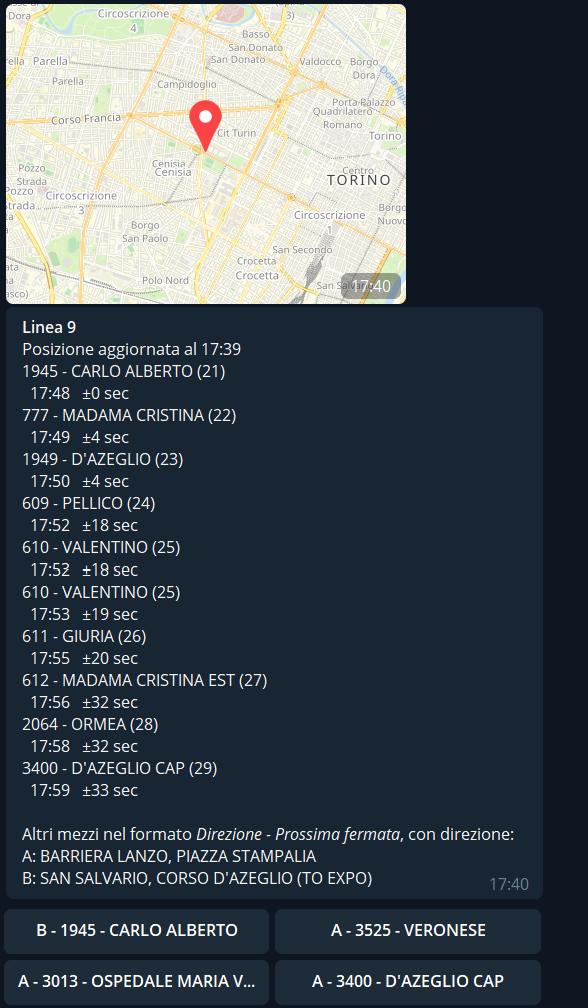
At the end of the message users can find buttons for all the routes that are expected to arrive at the stop, by clicking on them the user will receive the position and the list of stops (with estimated times) of the first trip of that specific route, example by clicking on Linea 9:
All the structures are implemented with standard Python structure, usually dicts of dicts.
The function getGTFS() loads all the static part, indicated with a grey background in the picture shown below. The function getRT() is called every 15 seconds and updates the times of arrival at the stops (stop_times) and the position of every trip.
- routes: a dictionary of all the routes, every route is a dict with its info, related trips and timetable
- version and timetable: every route has a few different paths (2 for the 2 ways and some other with a partially different stopsequence) so there's a version for every path with his own timetable which contains all the combination of stop_sequence and stop_id and the extimated time delta between the stop and the previous one. This time is loaded initialy by getGTFS with the timetable one (found in stoptimes.txt) and it is updated every time the GTFS-RT gives an arrival (identified by a timestamp prior to now), by this way the system has an extimated time delta between two stop based always on the last 30 registered arrivals (stored in times[ ], outliers are removed every 5 minutes) and can follow the traffic flow. Also the variance and the standard devation of this time is calculated and shown to the user.
- trips: a dictionary of all the trips (singular istance of a route), every element contains general info plus the last position and a list of stop_times
- stops: a dict with info about every stop with its stop_times
- stopcodes: a simple translation table implemented by a dict for passing from stop_codes (the numbers you see at the bus stops) to stop_id (the one used in the GTFS system)
- stop_times: the core of the realtime part, stop_time are referenced both by trips and stops: the former is a ordered dict which indicates for that specific trip which are its next stops and the estimated time of arrival, the latter is a dict containing every routes that has an extimated time of arrival at that stop and for that route a dict with the extimated times
- recent_arrivals: a dictionary holding the last arrivals of every trip, this is implemented to calculate the time delta between every arrival for updating the timetable mean. Every once a new time is inserted if there's the one referred to the previous stop the time delta is calculated and the previous time deleted.

GTTtg use python-telegram-bot (v13.15 is in use) and google transit (this repository is no more supported by google, therefore I included the file needed compiled with the last version of Protobuf, I suggest to use that for not having compabilities issues). To run it you just need the tg.py, main.py and a file named tg.txt with the Token of your telegram bot, this file should be inserted in an exterior folder, you can also hardcode your token in the variable TOKEN at the start of tg.py.
$ python3 tg.py
--- retrieveGTFS: 3.5385632514953613 seconds ---
--- 46952 trips reduced to 1440 timetable versions (33:1) ---
--- getGTFS: 12.71294093132019 seconds ---
23/02/23 11:58:33
--- retrieveRT (472 items): 1.55149 seconds ---
--- getRT (9185 items): 0.10671 seconds ---
--- retrievePos (433 items): 2.46884 seconds ---
--- getPos (433 items): 0.00214 seconds ---
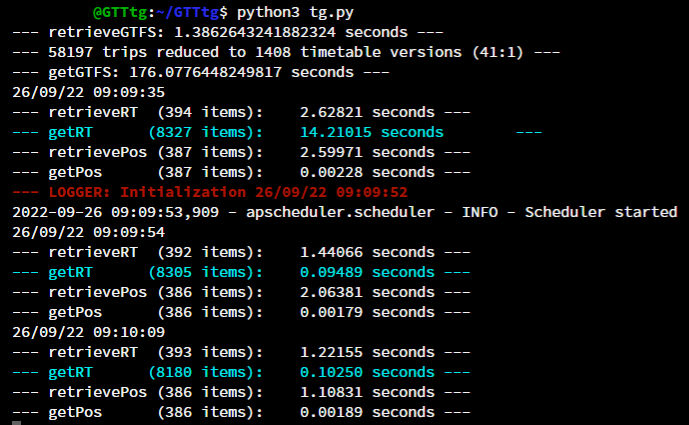
With the new version performance was a goal for me, especially regarding memory consumption because the project is running on a student free tier vps with only 1GB of RAM. For this reason I left out gtfs-kit and pandas to reduce the memory overhead and have full control over the datastructure, unfortunately there's still a peak usage (around 760MB) while loading stop-times.txt with his nearly 2 millions lines, therefore the server must use a swap memory to survive the getGTFS function that is called about once a week. Beside that while operating normally the memory consumption is under 600MB, you can find an analysis line by line done by memory_profiler here.
For treating the stop_times calculations I've chosen to group the trips of the same route in versions, every version has the same sequence of stops, in this way different trips can share their data and have a richier dataset from which calculate the mean times and there's also less data consumption (every version refers to 33 different trips on average).
Performance on my server, even at peak hour, is good as you can se below, the getGTFS part is really slow for the memory issues, on another machine it takes around 10 seconds. Also getRT is slow at the first run, but after that is always around 0.1 sec.