Today, we are going to talk a particular type of ZKP, which does not require interaction between a verifier and a prover, is a Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Proof (NIZK).
NIZK are very suitable for Ethereum blockchain applications because they allow a smart contract to act as a verifier. This way, anyone can generate a proof and send it as part of a transaction to the smart contract, which can perform some action depending on whether the proof is valid or not. Also, this protocol can verify one’s statement to a larger group of people.
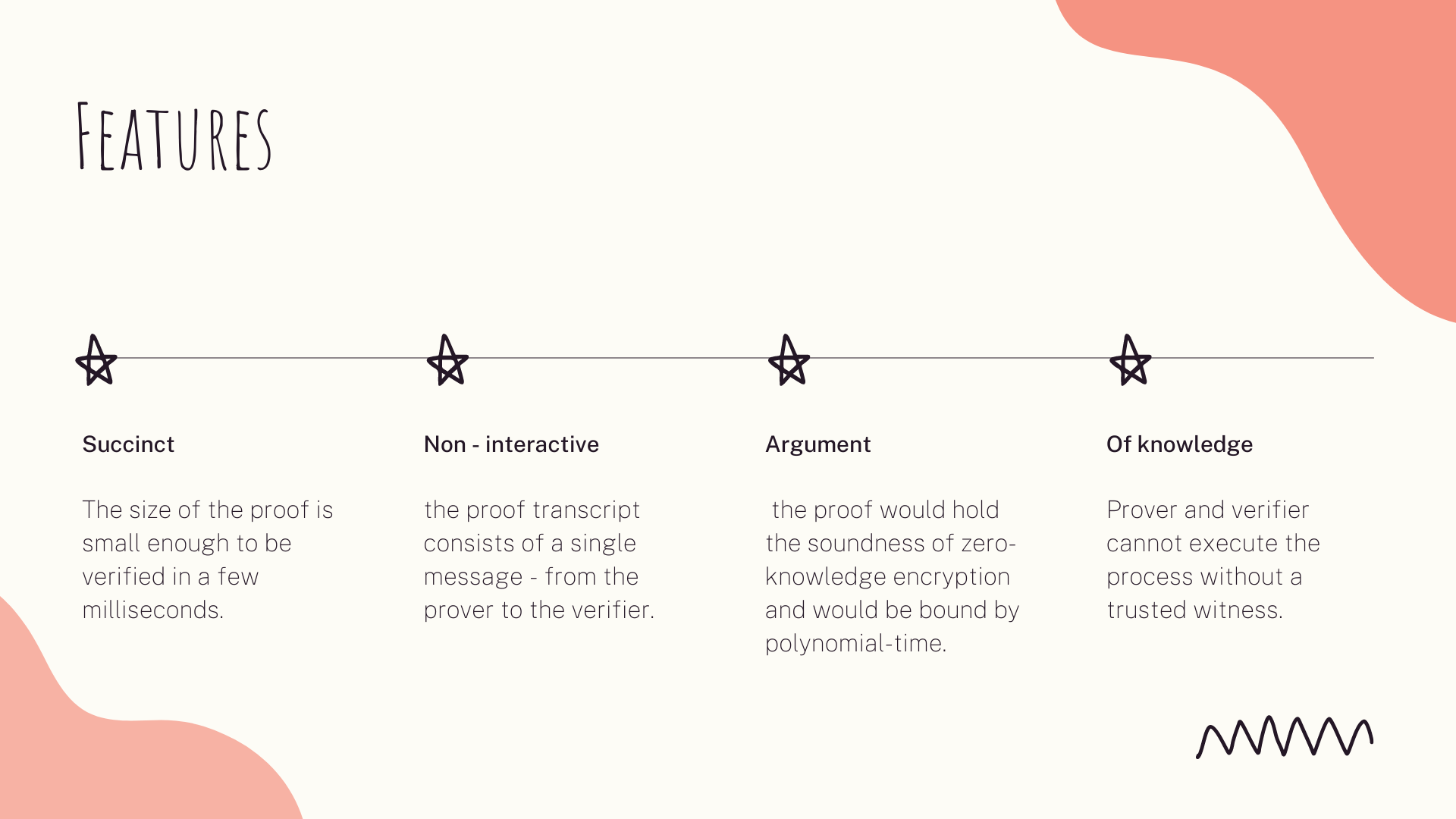
The most preferable NIZK is Zero-knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge (zk-SNARK) proof.
This protocol adds the following:
These properties make zk-SNARK especially suitable for blockchains, where on-chain storage and computation can be expensive and senders often go offline after sending a transaction.
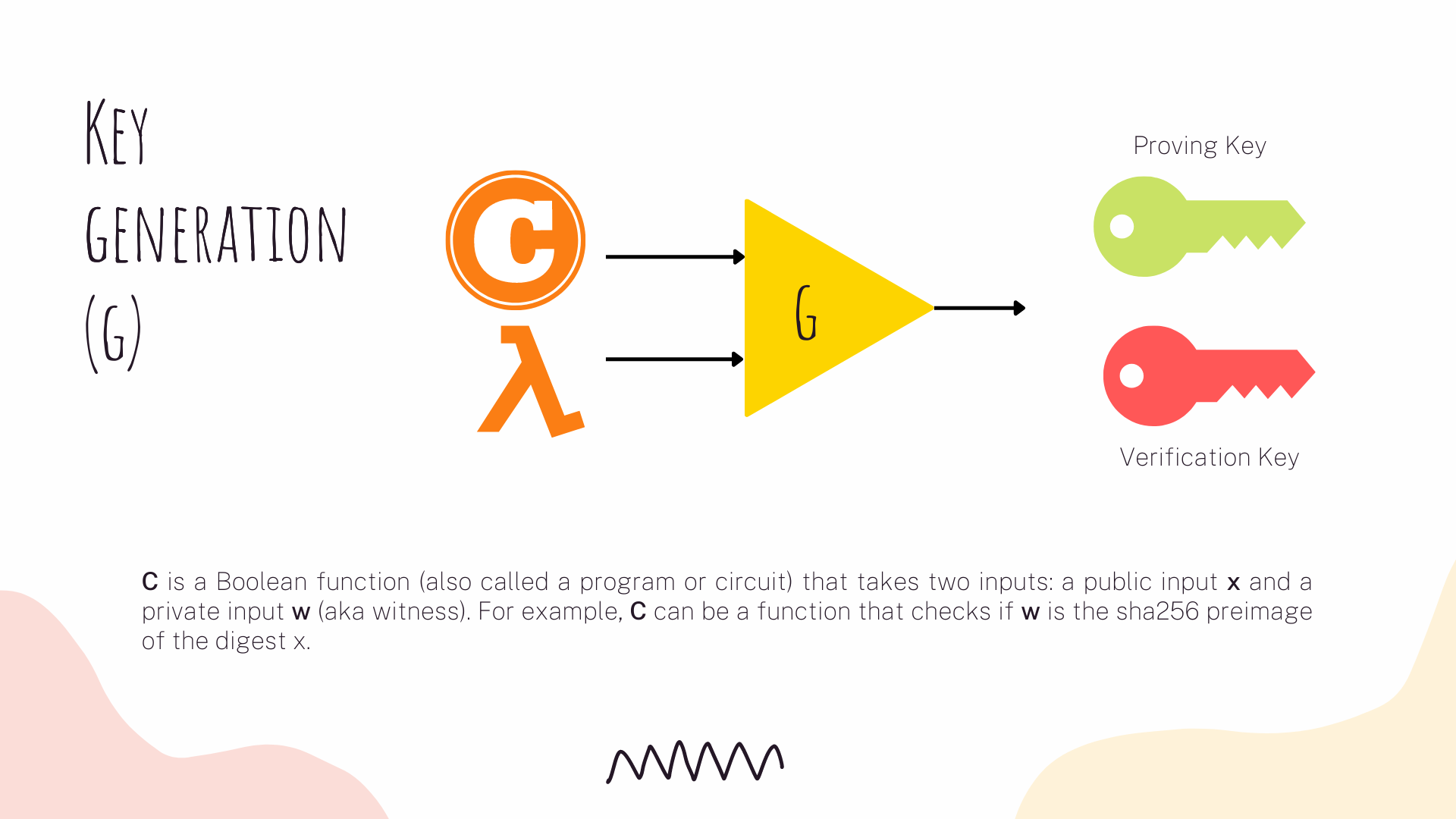
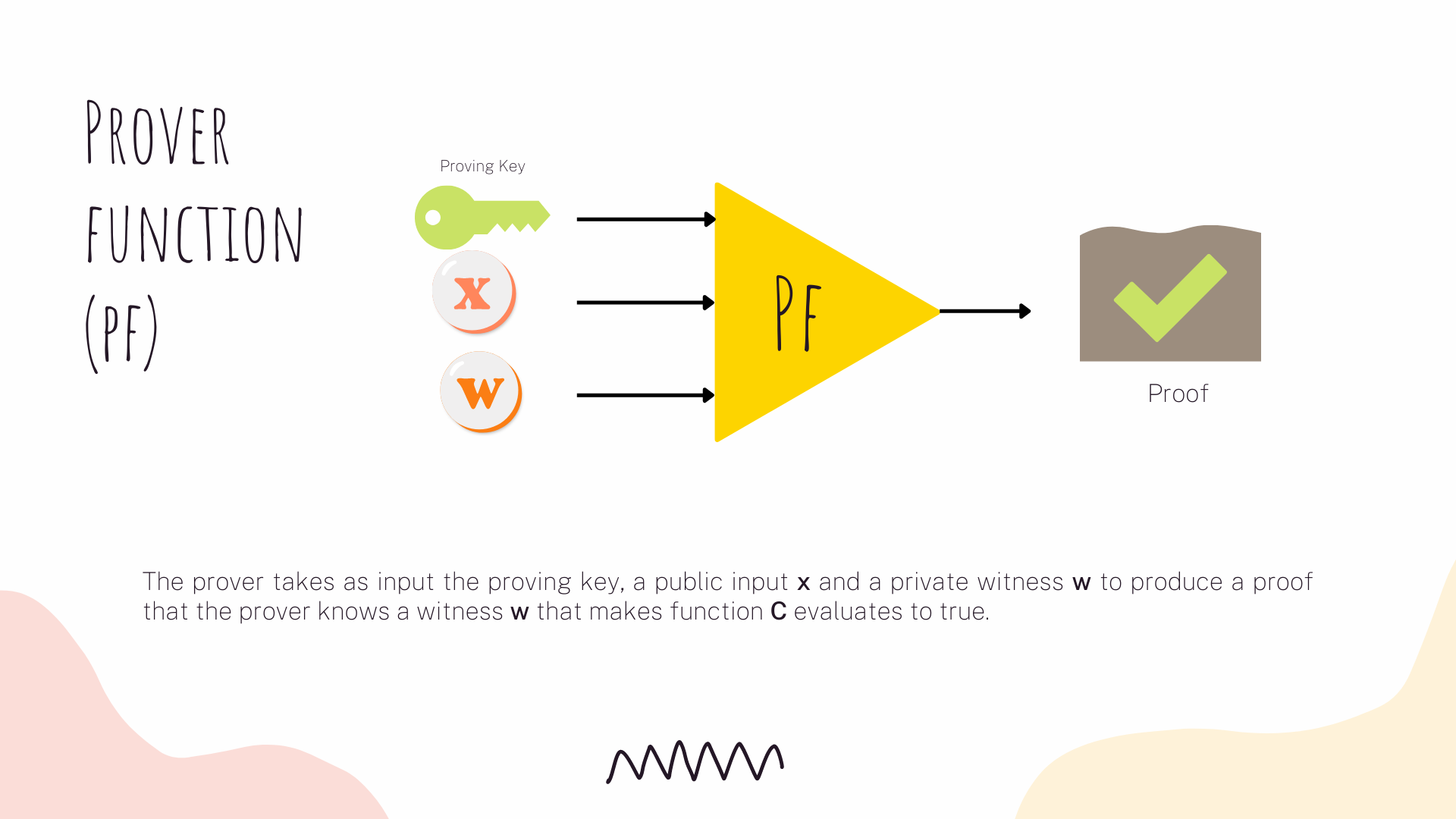
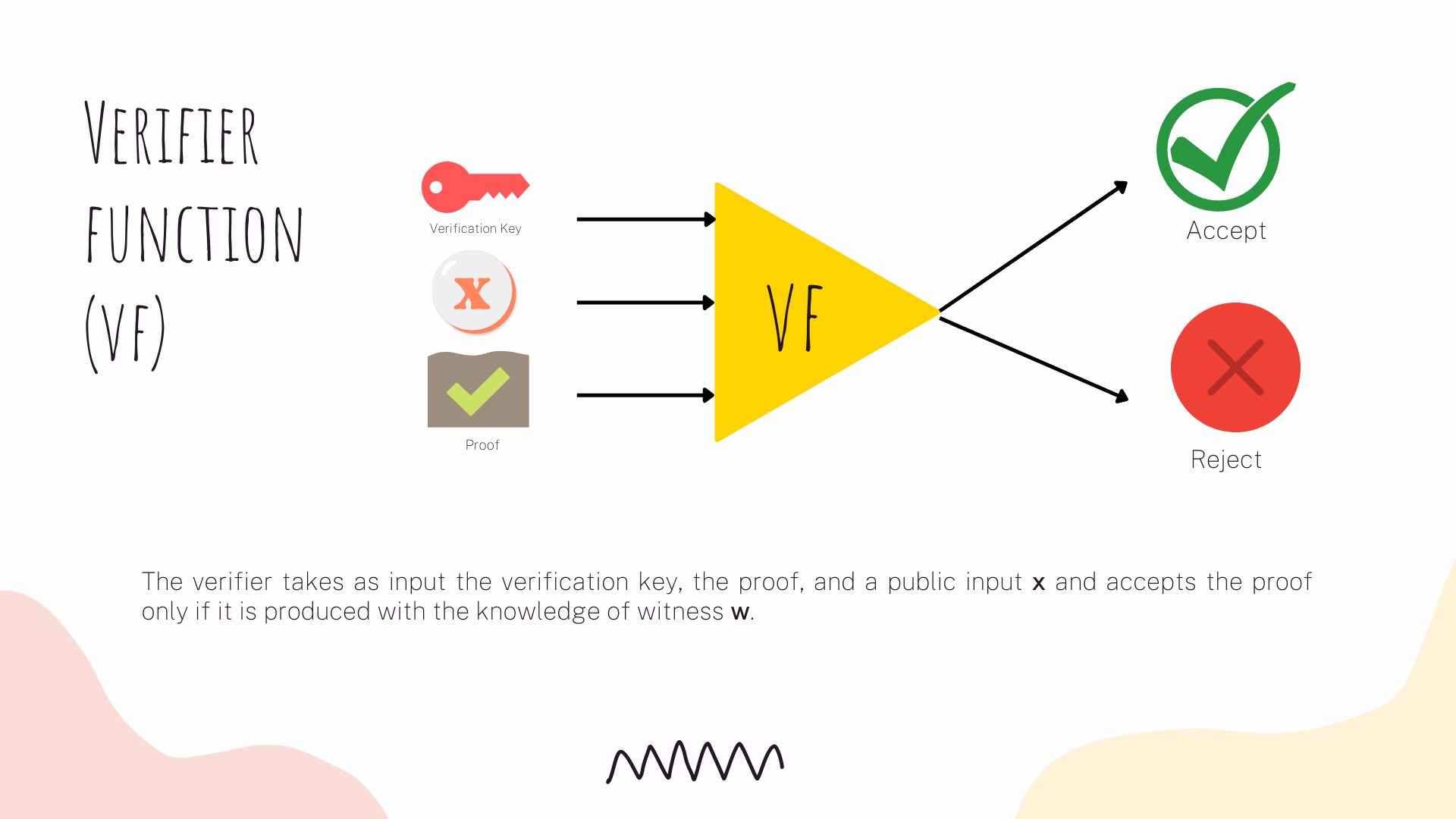
This protocol uses three algorithms:
When zk-SNARKs are used in blockchains, both the key and proof generation are executed off-chain. Only the general verification algorithm is run inside a smart contract on chain. Also, if we want to use a non-interactive protocol, we need to use a trusted setup. The trusted setup is the process which generates part of the public data used by a prover when computing her proof.
Non-interactivity is only useful if we want to allow multiple independent verifiers to verify a given proof without each one having to individually query the prover. Succinctness is necessary only if the medium used for storing the proofs is very expensive and/or if we need very short verification times.
That's all for this thread. Thank you for reading! If you liked this thread, follow me @Hasseru and retweet.