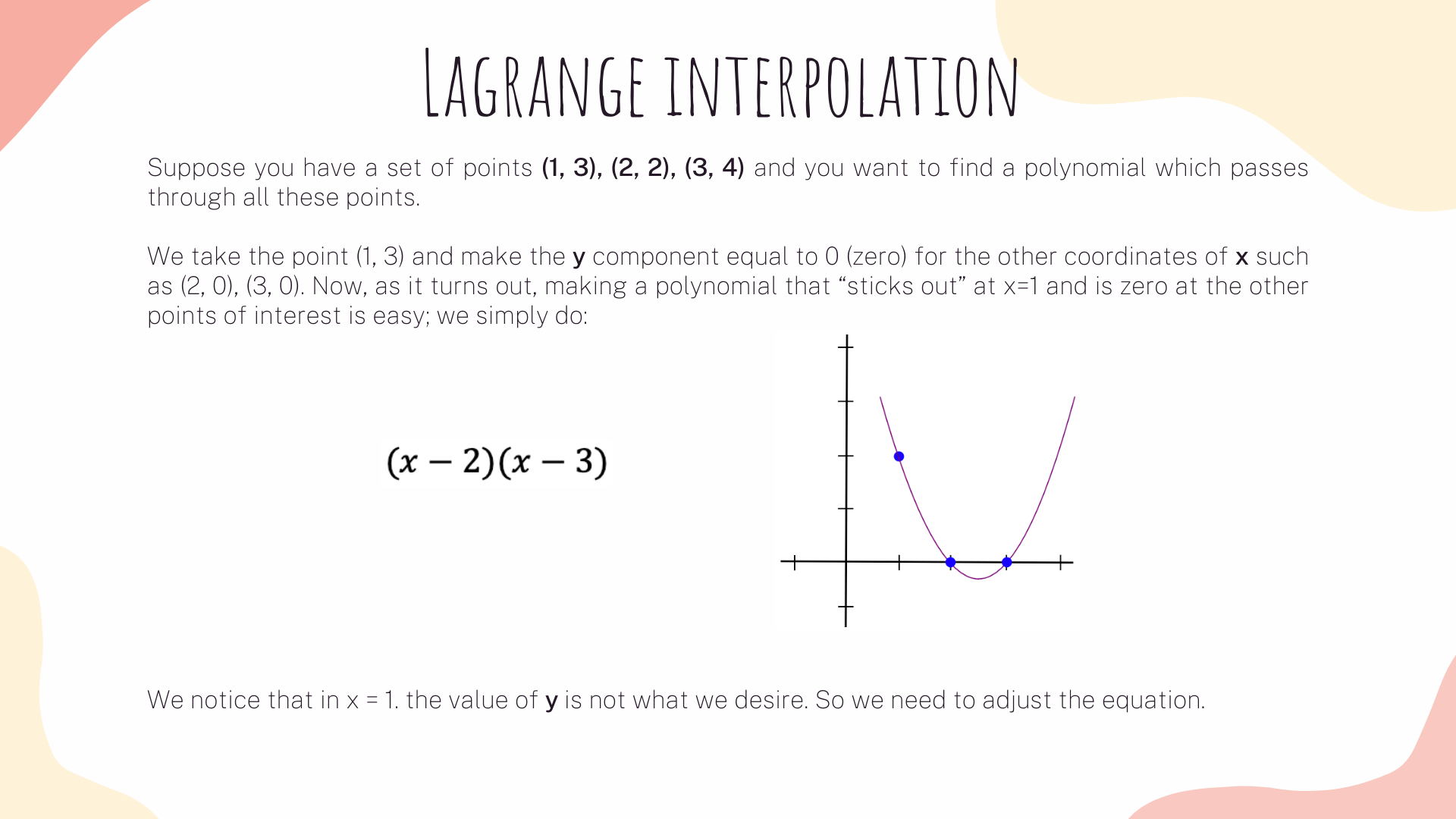
Today we are going to learn how transform the R1CS into Quadratic Arithmetic Program using Lagrange Interpolation. Lagrange interpolating is the unique polynomial of lowest degree that interpolates a given set of data.
We will transform the system of 3 vectors (A, B, C) with length 4x6, into six groups of 3 degree polynomials, where evaluating the polynomials at each x coordinate represent a constraint. To understand how to do it, first let's see a simple example:
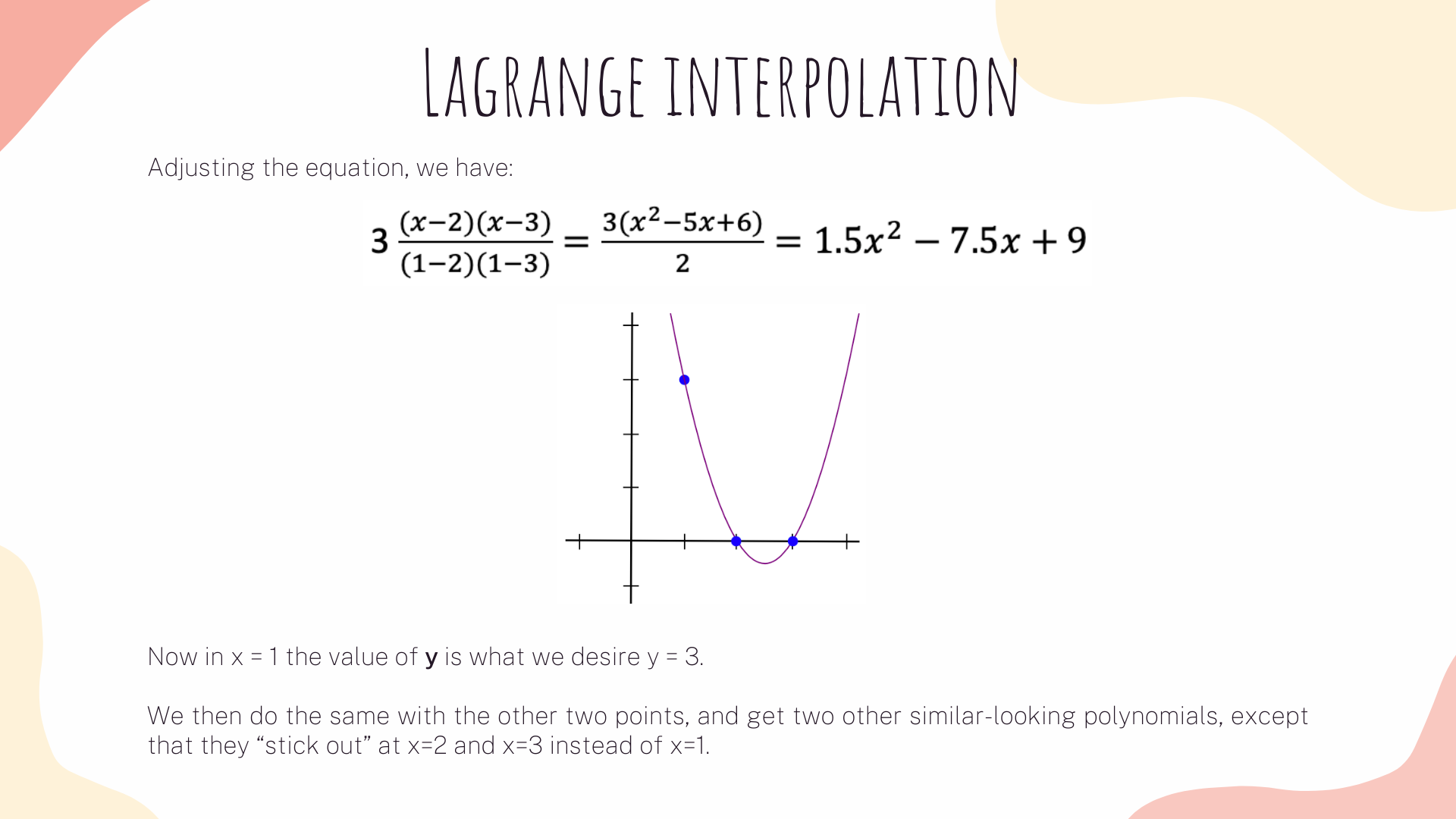
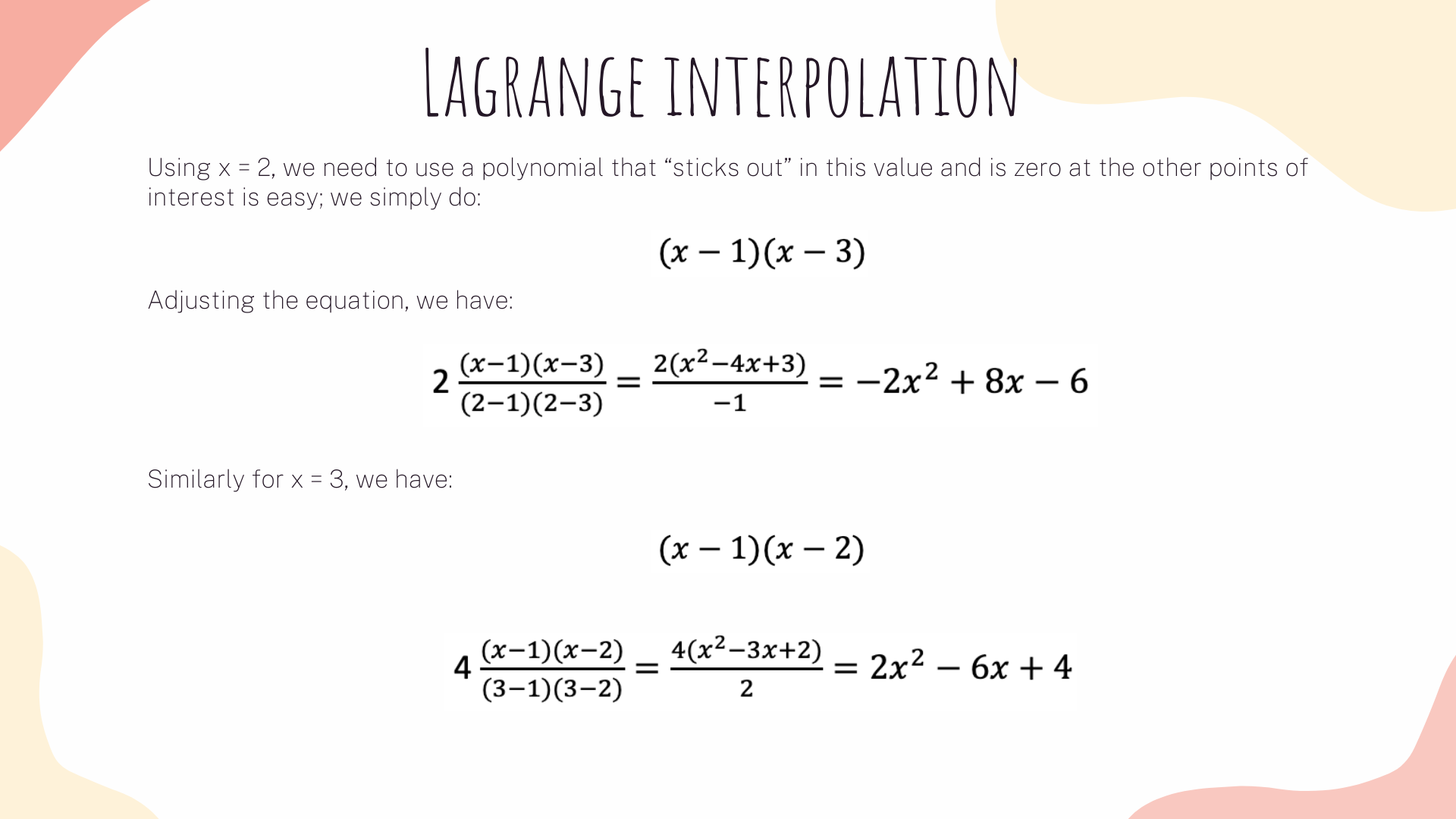
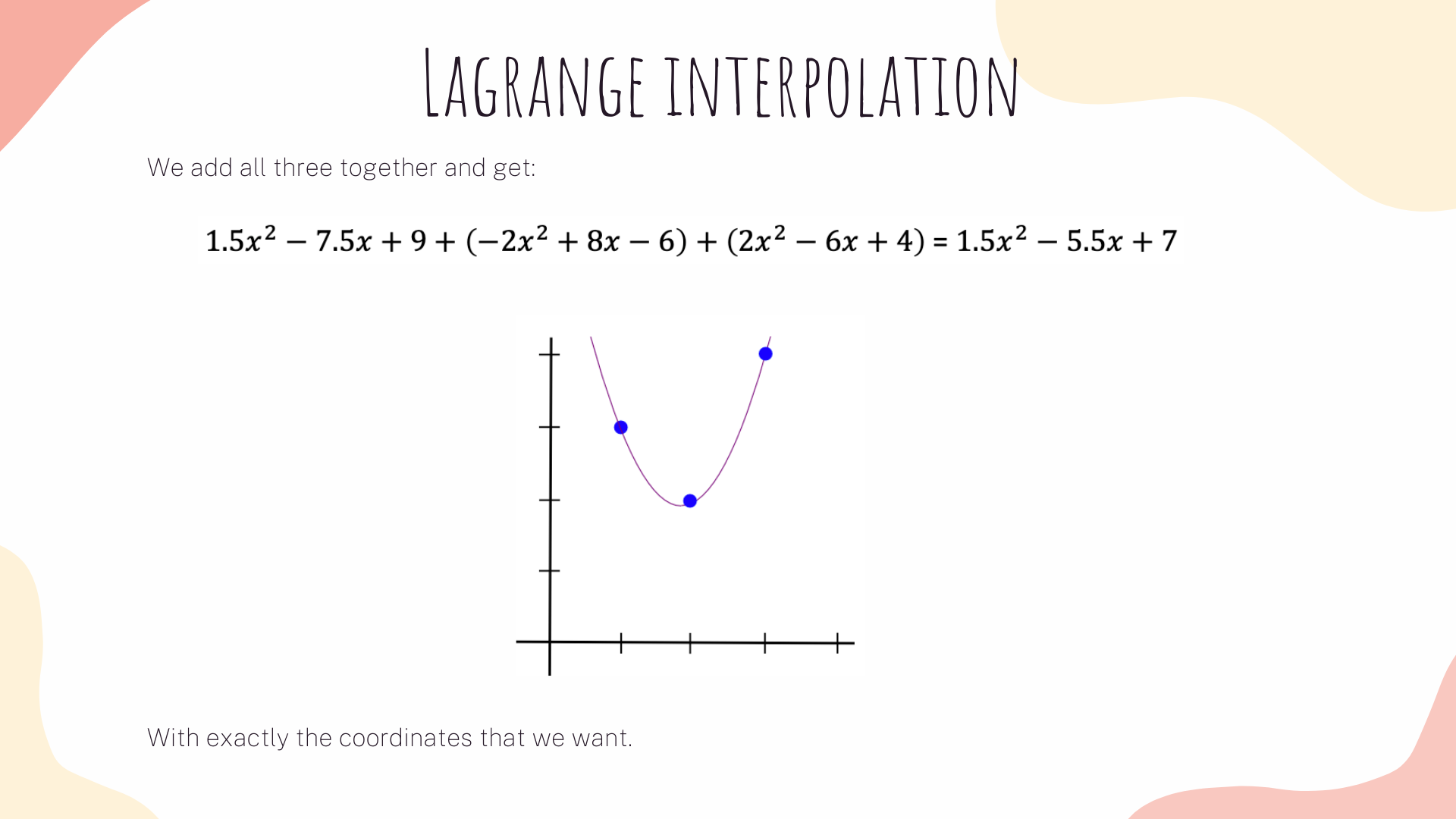
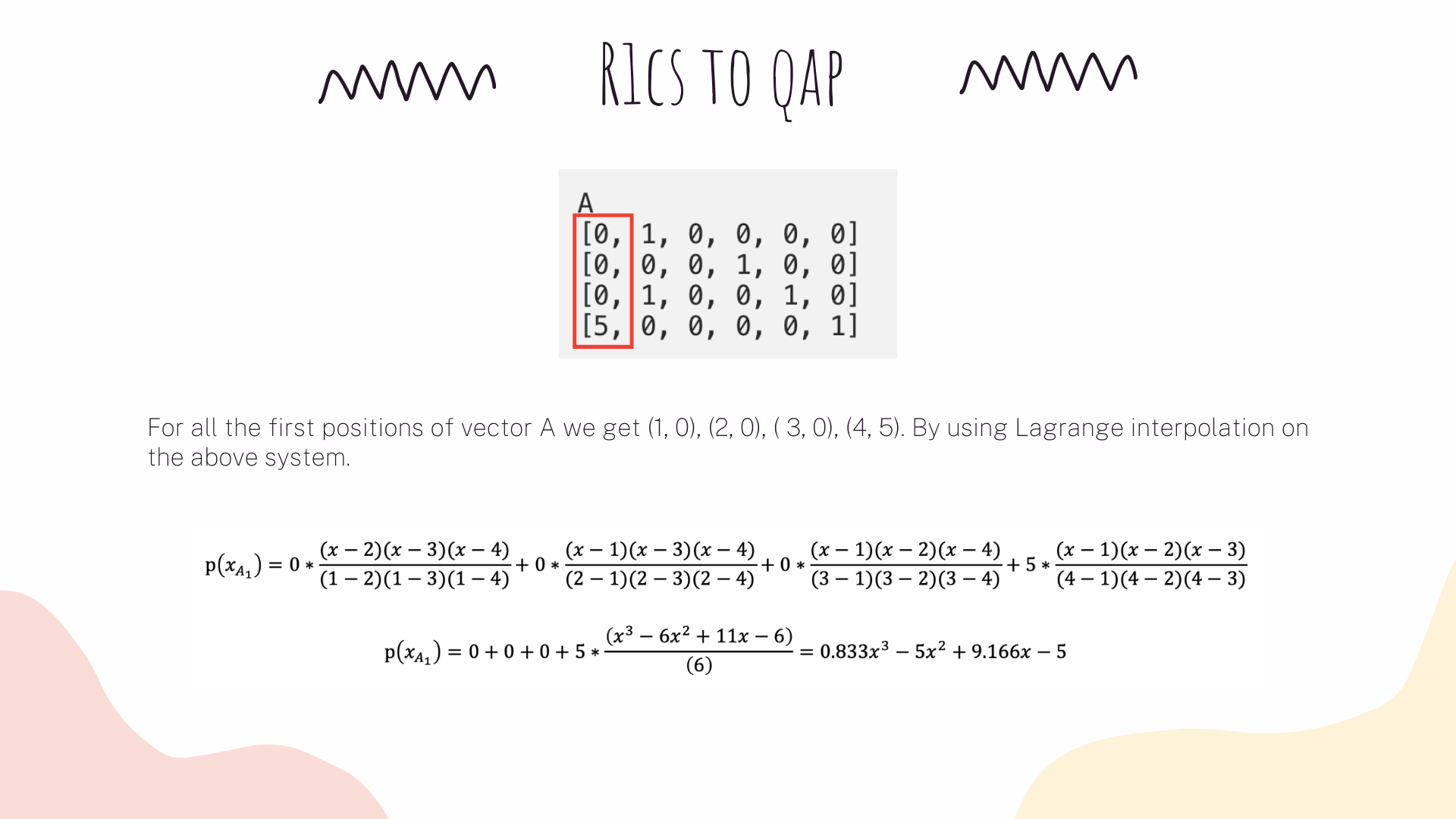
Now, the same strategy will apply to our R1CS. What we are gonna do is to take the first value of every vector a, apply lagrange interpolation to make a polynomial for it. We then will repeat the same process for vectors b and c. We will also apply the same methods on vector's second values, third values and so on.
What’s the point of this crazy transformation? The answer is that instead of checking the constraints in the R1CS individually, we can now check all of the constraints at the same time by doing the dot product check on the polynomials. Tomorrow, we are going to explain how to check the QAP.
That's all for this thread. Thank you for reading! If you liked, follow me @Hasseru and retweet.