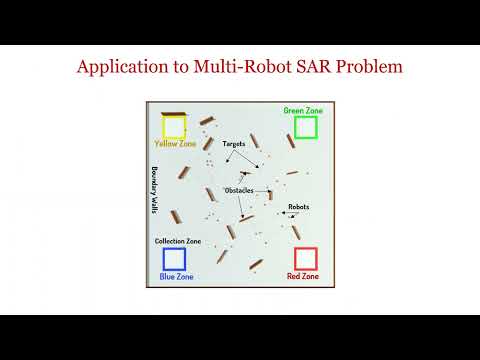
This simulation is based on Unity 3D game engine software. It simulates a multi-robot search and rescue (or foraging) problem with different robots having different knowledge bases. For example, some robots know only to pick up red/blue/green/yellow targets, while some robots know all targets or no targets. All robots have basic collision avoidance and random walk routines in their knowledge base. The simulator has key options for various modalities: 'No Interaction', 'Query-Response-Action', 'Query-Response-Update', 'Eavesdrop-Update', and 'Eavesdrop-Buffer-Update'
A paper describing the framework is available in ArXiv: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.11802
If you use/refer to our work, please consider citing the below paper. Oruganti, S., Parasuraman, R., and Pidaparti, R., “IKT-BT: Indirect Knowledge Transfer Behavior Tree Framework for Multi-Robot Systems Through Communication Eavesdropping”, arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.11802. 2023
Click below for a video presentation on IKT-BT works with a demonstration of BT transfers for various modalities.
Download the latest release here (v4.2).
After downloading the .zip file extract all the contents to a directory.
Open the file BTTransferSimulator.exe
You may have to click "More Info" and "Install Anyway" if your firewall blocks/scans the application.
Note: If you are using an antivirus or antimalware software, you may have to add BTTransferSimulator.exe and LearnBTV1.exe files to the exclusion list.
Once you run the application - the simulator settings Frontend will pop up. Choose your settings as described below and click the "Run Simulations" button. It will take some time to initialize and run the Unity-based simulations (up to a minute in some cases at least in the first trial) and eventually it will create a new window with the simulation visualization. Please wait for this process.
Target Type: There are four target types in the simulator that are colored red, green, yellow and blue and have four corresponding zones at each corner
Target Counts: The number of targets of each type to be initialized in the simulations.
Obstacles: Check to add static obstacles
Scenario: There are currently two scenarios available for the current study
- No Interactions (NI)
- Query-Response-Actions (QRA)
- Query-Response-Update (QRU)
- Eavesdrop-Update (EU)
- Eavesdrop-Buffer-Update (EBU)
Robot Types: There are 3 types of robots,
- I -Ignorant - Robots that have no initial knowledge about any of the targets
- M - Multi-target - Robots that have knowledge about all the targets
- R/G/Y/B - Single-target - Robots that have knowledge about red, green, yellow, and blue colors.
Communication Range: The range within which it can communicate with its neighbors. This is measured in times of the size of the robot.
Total Trials: The number of trials to conduct for data collection
Start Count: Starting trial number count for running simulations. This is to let the user continue simulations from the point they are stopped.
Continuous: If unchecked, simulations stop after each trial and wait for the user to press the exit button on the simulator. If checked a trial instance is closed and a new trial instance is opened automatically.
Parallel Instance Interval: This simulator supports parallel simulation instances. If set to a value more than 1 and if the trials are greater than 1 multiple simultaneous instances are initiated. For e.g., if the trials are 10 and the max parallel instance intervals are 3, only 3 instances are open at a time.
Note: Multiple parallel instances might slow down the simulations, hence a PC with good processing speed and a GPU is recommended
Duration: The maximum number of iterations before stopping. Each iteration has a fixed time of 0.01s.
Targets: Stop after a certain overall percentage of targets are collected.
No Stop: Simulations do not have stopping criterion.
Record Data: Enable this to record data
Auto Name: Auto Names the files and folders (Recommended)
Save Path: Choose save directory for the recorded data.
Config. File: Parameter summary
Simulation Control: Run Simulations -> Click to run simulations after setting the parameters.
Pause/ UnPause: Pause or unpause all instances of simulations
Stop Simulations: Stop all the instances/ terminates all simulation instances.
Note: Do not press stop simulations while the instances are initializing
The simulation parameters segment in an instant shows the parameters transferred from the settings form.
Camera View: Currently there are two views available.
# Robots that can handle: Counts of robots that have knowledge about each target type.
# Known Conditions: Number of robots that are ignorant (None), knowledge about 1, 2 3, and all targets respectively.
# Robot States: Number of robots in different states at a given point of time/ iteration.
-
Dr. Sanjay Sarma Oruganti Venkata -- College of Engineering, University of Georgia (https://github.com/sanjayovs). Currently a postdoctoral researcher at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI).
-
Prof. Ramviyas Parasuraman -- HeRoLab, School of Computing, University of Georgia (https://hero.uga.edu)
-
Prof. Ramana Pidaparti -- DICE Lab, College of Engineering, University of Georgia (https://dice.engr.uga.edu/)
Heterogeneous Robotics Lab (HeRoLab), School of Computing, University of Georgia. http://hero.uga.edu
For further information, contact sanjaysarmaov@uga.edu or Dr. Ramviyas Parasuraman ramviyas@uga.edu