Fountain是监查、捕捉MySQL数据库的增量变化,分发数据变化给消费者处理的一套解决方案。
Fountain,英[ˈfaʊntən],是”源泉“的意思,MySQL数据库源源不断的下发增量,因此而得名。
任何需要快速、准确接收MySQL数据变化增量的场景均适用,例如
- 广告传输流:输出到本地增量文件
- 数据同步:可数据库同构复制,也可以跨异构数据源sync,比如MySQL到一些NoSQL,例如redis、mongodb,或者es、solr等提供搜索服务,或者MQ如bigpipe、RabbitMQ。
- 缓存失效:数据变化收敛到MySQL,利用增量变化触发memcache或者redis缓存失效。
- 数据监控:监控数据库中的异常数据,攻击行为数据。
- 历史操作记录:数据库业务变化,同步到另外的数据库表,供查询操作记录
- 其他你所想到场景...
Fountain支持MySQL的row base binlog协议,稳定测试版本支持MySQL5.1-5.6。
- 简单易用
- 快速部署
- 处理高效率、低延迟
- 提供丰富的接口和内部缺省实现,用户可以选择使用缺省实现也可以自己定制,支持高度定制,符合开闭原则的设计原则。
Fountain是一个Java类库,不是一套服务或平台,通过模块依赖方式使用。
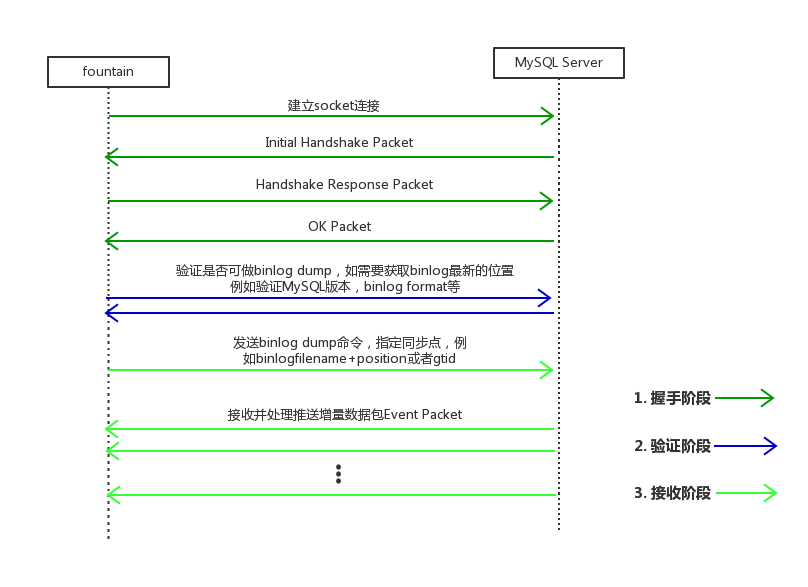
Fountain将自己伪装为MySQL的从库,通过binlog dump命令请求MySQL Server,通过主从复制协议获取到MySQL Server不断推送过来的row based binlog日志,解析出数据变化增量,封装为Java的POJO对象,供消费者消费使用。
整个生命周期分为三个阶段:1、握手阶段,2、验证阶段,3、接收阶段。如下图所示。
这里注意,Fountain要求MySQL的日志格式必须是row based格式,不能是statement或者mixed。
Fountain的处理流程进行了规范抽象化,如下架构图所示,其中每一步均是可定制扩展的、可组装的,符合设计模式中的开闭原则。
整体流程是:
-
- 数据的接收依靠fountain-producer,一个fountain-producer新建一个复制线程(replication socket),对应一个MySQL Server,进行握手,成功后发送binlog dump命令请求MySQL Server推送binlog日志。
-
- Fountain-producer复制线程,按照MySQL binlog或者databus协议解析数据,进行按表名称,匹配的正则表达式进行过滤,然后将数据抽象为BinglogTracable的子类实例POJO对象,由于MySQL 推送的Event Packet可以分包,因此Fountain内部做了事务控制,可以积攒到事务所有数据后统一下发,也可以接到一个Event Packet后处理完直接下发,这取决于Fountain的配置。事务数据积攒,可以积累整个事务的数据,然后整个事务下发或者重新分块下发。事务处理被抽象成策略接口,缺省实现是不积攒数据,也可以配置超过指定数据行的事务数据会被全部丢失并记录同步点日志(缺省的最大数据行是20000条),同时fountain也支持innodb和myisam混合使用时,判断事务数据是否是脏数据,事务主要用于innodb和myisam混合使用时,防止脏数据的下发,也用于其他一些需要整事务处理的场景。进行数据下发操作,可以包含序列化操作,发送到内存缓冲区,实际内部一般是一个内存队列。
-
- 数据的接收和下发通过内存缓存区进行解耦,保证接收和下发按照各自的处理能力handle。内部缓冲区有容量控制,防止进程内存耗尽,可以对变化数据包进行切分,按照可扩展消费者的处理能力进行消费。
-
- 消费者可以进行数据监听,可进行数据接收的过滤,反序列化后,进入可扩展消费者中,这个可扩展消费者一般依赖于consumer-spi模块,实现其中的Consumer 接口,消费者扩展要自行处理异常,防止消费线程中断,可以选择在本进程内消费,如打印日志或者输出数据文件,也可以将增量变化进一步推送到远程消费端,例如bigpipe、MQ等。Consumer可以控制同步点的保存,保证消费成功才记录同步点(SyncPoint)。同步点记录方式是消费者记录,生产者读取,这样保证只有被成功消费数据后才记录。
JDK版本、Maven/Gradle依赖、日志配置以及使用说明请见参考链接
下面的所有例子请参考SingleShardBinlogSyncerTest和SingleShardBinlogSyncerV51Test
由于Fountain使用后台线程做同步,因此下面的例子都使用了CountDownLatch来做延迟,生产环境请使用守护线程,或者容器中运行。
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769").username("beidou").password("u7i8o9p0"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
可以配置多个MySQL,当一个不可用时,默认切换为另外一个。
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769,10.94.37.23:8769")
.username("beidou,beidou")
.password("u7i8o9p0,beidou")
.slaveId("123,124"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.0.0.1:3306,10.0.0.2:3306")
.username("beidou,beidou")
.password("u7i8o9p0,u7i8o9p0")
.slaveId("123,124"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.whiteTables("fountain_test.*")
.blackTables("abc.*")
.soTimeout(60000) //一旦超时,会自动切换另外一个数据源,fountain保证多数据源之间的HA
.transactionPolicy(new MiniTransactionPolicy()) //max 30000 row changes
.messageQueueSize(30000) // max 20000 events
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
上述的例子都是使用默认的EventConsumer,只打印一些简单信息,可以自定义EventConsumer。
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769").username("beidou").password("u7i8o9p0"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.consumer(new EventConsumer() {
@Override
public void onEvent(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet) {
printTableData(changeDataSet);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, DisposeEventPositionBridge positionBridge) {
//do nothing
}
@Override
public void onFail(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, Throwable t) {
logger.info("Some problem occurred..." + t.getMessage());
}
})
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 自定义逻辑的方法
void printTableData(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet) {
Map<String, List<RowData>> tableData = changeDataSet.getTableData();
for (String tableName : tableData.keySet()) {
logger.info("{}->size={}", tableName, tableData.get(tableName).size());
for (RowData rowData : tableData.get(tableName)) {
logger.info("before:" + rowData.getBeforeColumnList());
logger.info("after:" + rowData.getAfterColumnList());
}
}
}
处理完增量如果成功,一般推荐在onSuccess中存储同步点,下面的例子存储同步点在本地。
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769").username("beidou").password("u7i8o9p0"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.disposeEventPosition(new LocalFileGtIdSetDisposeEventPosition("/Users/baidu/work/fountain-git/test"))
.consumer(new EventConsumer() {
@Override
public void onEvent(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet) {
printTableData(changeDataSet);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, DisposeEventPositionBridge positionBridge) {
positionBridge.getDisposeEventPosition(changeDataSet.getInstanceName())
.saveSyncPoint(changeDataSet.getSyncPoint());
}
@Override
public void onFail(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, Throwable t) {
logger.info("Some problem occurred..." + t.getMessage());
}
})
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
AsyncFixedRateDisposeEventPosition eventPosition = new AsyncFixedRateDisposeEventPosition();
eventPosition.setInitDelayMs(10000);
eventPosition.setPeriodMs(15000);
eventPosition.setDelegate(new LocalFileGtIdSetDisposeEventPosition("/Users/baidu/work/fountain-git/test"));
eventPosition.init();
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769").username("beidou").password("u7i8o9p0"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.disposeEventPosition(eventPosition)
.consumer(new EventConsumer() {
@Override
public void onEvent(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet) {
printTableData(changeDataSet);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, DisposeEventPositionBridge positionBridge) {
positionBridge.getDisposeEventPosition(changeDataSet.getInstanceName())
.saveSyncPoint(changeDataSet.getSyncPoint());
}
@Override
public void onFail(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, Throwable t) {
logger.info("Some problem occurred..." + t.getMessage());
}
})
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(120L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
详细参考【高可用】使用Zookeeper做多实例热备以及存储同步点
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogGtIdV56DumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
SingletonZkClientProvider zkClient = new SingletonZkClientProvider();
zkClient.setZookeeperConnectionString("127.0.0.1:2181");
zkClient.setConnectionTimeoutMs(30000);
zkClient.setSessionTimeoutMs(30000);
ZkDisposeEventPosition zkEventPosition = new ZkDisposeEventPosition();
zkEventPosition.setZkRootPath("/fountain/eventposition/testha");
zkEventPosition.setZkClientProvider(zkClient);
zkEventPosition.setSyncPointFactory(new GtIdSyncPointFactory());
AsyncFixedRateDisposeEventPosition eventPosition = new AsyncFixedRateDisposeEventPosition();
eventPosition.setInitDelayMs(10000);
eventPosition.setPeriodMs(15000);
eventPosition.setDelegate(zkEventPosition);
eventPosition.init();
ZkHaGuard haGuard = new ZkHaGuard();
haGuard.setZkClientProvider(zkClient);
haGuard.setLatchPath("/fountain/leader/testha");
BinlogSyncer syncer = BinlogSyncBuilder.newBuilder()
.producerName("producer00")
.dataSource(DataSource.of("10.94.37.23:8769").username("beidou").password("u7i8o9p0"))
.binlogDumpStrategy(dumpStrategy)
.disposeEventPosition(eventPosition)
.haGuard(haGuard)
.consumer(new EventConsumer() {
@Override
public void onEvent(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet) {
printTableData(changeDataSet);
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, DisposeEventPositionBridge positionBridge) {
positionBridge.getDisposeEventPosition(changeDataSet.getInstanceName())
.saveSyncPoint(changeDataSet.getSyncPoint());
}
@Override
public void onFail(ChangeDataSet changeDataSet, Throwable t) {
logger.info("Some problem occurred..." + t.getMessage());
}
})
.build();
syncer.start();
latch.await(300L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
修改BinlogPositionDumpStrategy实现如下,
BinlogFileNamePositionDumpStrategy dumpStrategy = new BinlogFileNamePositionDumpStrategy();
dumpStrategy.setIsChecksumSupport(true);
如果使用本地同步点存储使用
LocalFileBinlogAndOffsetDisposeEventPosition
现在你已经具备了fountain的基本概念已经看过了Quick Start,更多内容内容索引见下。
MySQL 5.X对接-使用binlogname+position