Connect your Samsung SmartThings to Watson IoT
Per the September 8, 2020 announcement IBM Watson IoT Platform (5900-A0N) has been withdrawn from marketing effective December 9, 2020.
- Log in to your account on SmartThings/dev
- Create a new SmartApp
- Click
From Codeand paste in the content ofwatsoniot.groovyfrom this repository - Click
Create - Click
Save - Click
Publish
Using the SmartThings mobile application navigate to Marketplace > SmartApps > My Apps, here you will find the application IBM Watson IoT Bridge that we created previously.
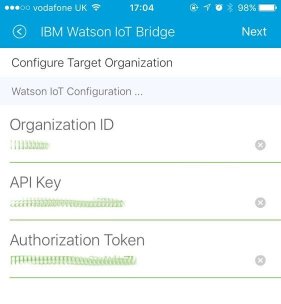
You will need to have generated an API key from your Watson IoT dashboard (or have been provided one by whoever oversees the Watson IoT organization you wish to connect to).
The API key requires the following permissions:
- Create Devices
- Update Devices
- View Devices
- Publish/send an event
Of the default roles, both Standard Application and Backend Trusted Application are suitable for use with this application, providing the abilty to register devices and submit events on behalf of devices.
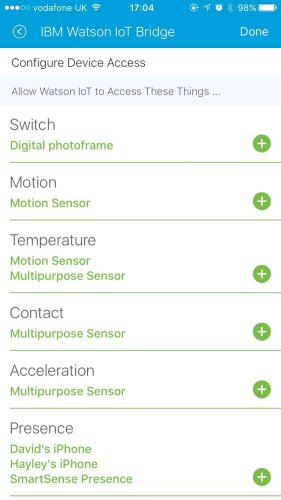
You also need to explicitly grant access to each individual device capability that you want to Watson IoT to work with
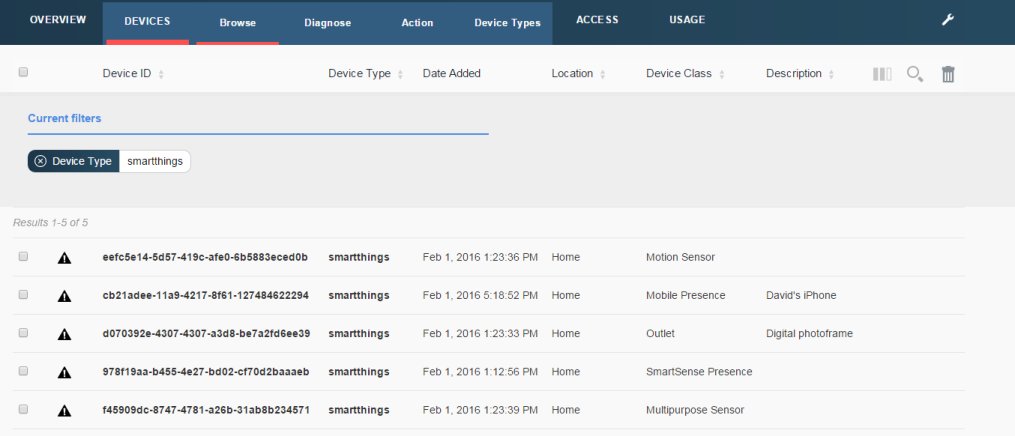
After the setup is complete you should be able to see the application listed when you navigate to My Home > SmartApps
- Devices are automatically registered in Watson IoT
- All SmartThings are created with a
typeIdofsmartthings - The unique identifier of each device is used as the
deviceId - The class of SmartThing is recorded in
deviceInfo.deviceClass(e.g. "Motion Sensor", "Multipurpose Sensor")
- All SmartThings are created with a
- Device metadata is synced to Watson IoT:
- The custom label you applied to each device is recorded in
deviceInfo.description - The name of your location is recorded in
deviceInfo.descriptiveLocation(e.g. "My Home") - The version of the bridge is recorded in
metadata.smartthings.bridge.version - The capabilities of each device are recorded as an array in
metadata.smartthings.capabilities - The longitude and latitude for the center of your geofence is recorded in each device's location record
- Device metadata updates occur when the application is installed or reconfigured
- The custom label you applied to each device is recorded in
{
"clientId": "d:abc123:smartthings:a0c9872a-afad-49e4-8201-3adf98a09c5e",
"typeId": "smartthings",
"deviceId": "a0c9872a-afad-49e4-8201-3adf98a09c5e",
"deviceInfo": {
"deviceClass": "Water Leak Sensor",
"description": "Bathroom Window",
"descriptiveLocation": "Home"
},
"metadata": {
"smartthings": {
"bridge": {
"version": "0.2.0"
},
"capabilities": [
"temperature",
"battery"
]
}
}
}- Device events are streamed in real time into Watson IoT
State updates are published to Watson IoT in real time. The events sent by any device are defined by it's capabilities. Watson IoT eventId's match 1:1 with SmartThings capabilities, all events are sent in JSON format.
SmartThings often represents boolean (true or false) states as a string (e.g. on|off, active|inactive). The Watson IoT bridge converts these into simple boolean values to ease analytics and rule generation:
- SmartThings acceleration state:
activeis converted to an acceleration event with value oftrue - SmartThings contact state:
closedis converted to a contact event with value oftrue - SmartThings motion state:
activeis converted to a motion event with value oftrue - SmartThings presence state:
presentis converted to a presence event with value oftrue - SmartThings switch state:
onis converted to a switch event with value oftrue - SmartThings water state:
wetis converted to a water event with value oftrue
If a SmartThings device has multiple capabilities it will emit multiple events into Watson IoT. For example, a multipurpose sensor will emit up to four different events based on the level of access granted to the bridge application: acceleration, battery, contact & temperature
{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"acceleration": true
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"battery": 0.83
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"contact": true
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"motion": true
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"power": 3.0
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"presence": true
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"switch": true
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"temperature": 15
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"x": 1,
"y": 50,
"z": 62
}{
"timestamp": "2016-02-03T14:56:13+00:00",
"water": true
}The bridge only works one way right now, commands can not be sent to SmartThings through the Watson IoT Bridge yet