Fake news detection is a natural language processing technique used to identify and classify misleading or false information in news articles or social media content. The rise of fake news has led to an increased need for automated systems that can analyze and flag potentially deceptive content. In this project, we I explored how to fine-tune a pre-trained model for fake news detection using Hugging Face and share it on the Hugging Face model hub.
Hugging Face is a platform that provides a comprehensive set of tools and resources for natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning tasks. It offers a user-friendly interface and a wide range of pre-trained models, datasets, and libraries that can be utilized by data analysts, developers, and researchers.
Hugging Face offers a vast collection of pre-trained models that are trained on large datasets and designed to perform specific NLP tasks such as text classification, named entity recognition, and sentiment analysis. These models provide a starting point for your analysis and save you time and effort in training models from scratch. For this project, I recommend you take this course to learn all about natural language processing (NLP) using libraries from the Hugging Face ecosystem.
Please, go to the website and sign-in to access all the features of the platform. Read more about Text classification with Hugging Face
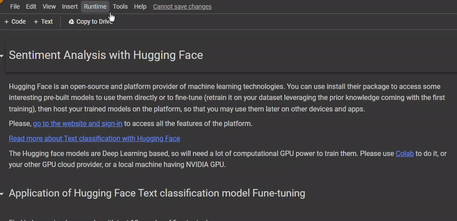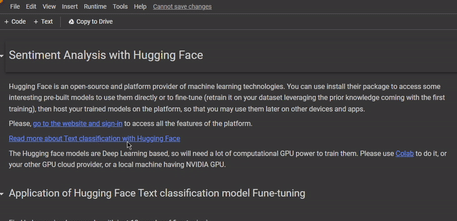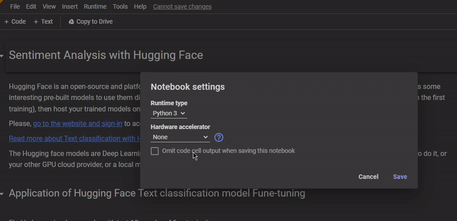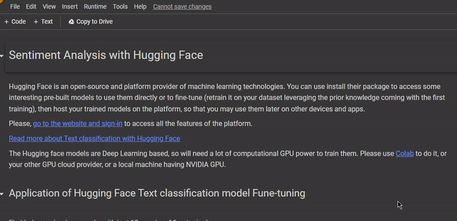
Before we start with the code, it's important to understand why using GPU runtime on Google Colab is beneficial. GPU stands for Graphical Processing Unit, which is a powerful hardware designed for handling complex graphics and computations. The fake news detection models are Deep Learning-based, so they require significant computational power, such as a GPU, to train efficiently. Please use Colab or another GPU cloud provider, or a local machine with an NVIDIA GPU.
In our project, we utilized the GPU runtime on Google Colab to speed up the training process. To access a GPU on Google Colab, all we need to do is select the GPU runtime environment when creating a new notebook. This allows us to take full advantage of the GPU's capabilities and complete our training tasks much faster.
Now that we have understood the importance of using a GPU, let’s dive into the code. We begin by installing the transformers library, which is a python-based library developed by Hugging Face. This library provides a set of pre-trained models and tools for fine-tuning them. We’ll also install other requirements too.
!pip install transformers
!pip install datasets
!pip install --upgrade accelerate
!pip install sentencepieceNext, we import the necessary libraries and load the dataset. In this project, we will be using the dataset from [source of fake news dataset]. You can download the dataset here.
import huggingface_hub # Importing the huggingface_hub library for model sharing and versioning
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from datasets import load_dataset
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from datasets import DatasetDict, Dataset
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
from transformers import TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoConfig
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer, DataCollatorWithPadding
# Load the dataset from [source of fake news dataset]
df = pd.read_csv('path/to/dataset.csv')
# Preprocessing steps...Next, we clean and preprocess the text data. Preprocessing steps may include removing unnecessary characters, tokenization, and normalizing the text. These steps ensure that the data is in a suitable format for training the fake news detection model.
After preprocessing the text data, we need to tokenize it to create numerical representations. Tokenization breaks down the text into smaller units, such as words or subwords, and assigns numerical values to them. This allows the model to process and analyze the text effectively.
checkpoint = "your/pretrained-model"
# define the tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
# Tokenization steps...Now that we have our preprocessed and tokenized data, we can proceed with training the fake news detection model. We'll set the training parameters and initialize the model using the pre-trained checkpoint.
training_args = TrainingArguments(
"fake_news_detection_trainer",
num_train_epochs=10,
load_best_model_at_end=True,
save_strategy='epoch',
evaluation_strategy='epoch',
logging_strategy='epoch',
logging_steps=100,
per_device_train_batch_size=16,
)
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint, num_labels=2)
# Training steps...After training the model, the next steps would be to evaluate its performance, fine-tune further if necessary, and deploy the model for practical use. You can explore different deployment options such as building a web application using frameworks like Streamlit or Gradio. This would allow users to interact with the model and make predictions on new text inputs. For this project, I used streamlit.
In conclusion, we have fine-tuned a pre-trained model for fake news detection using Hugging Face. By following the steps outlined in this README, you can replicate the process and adapt it to your own fake news detection projects.