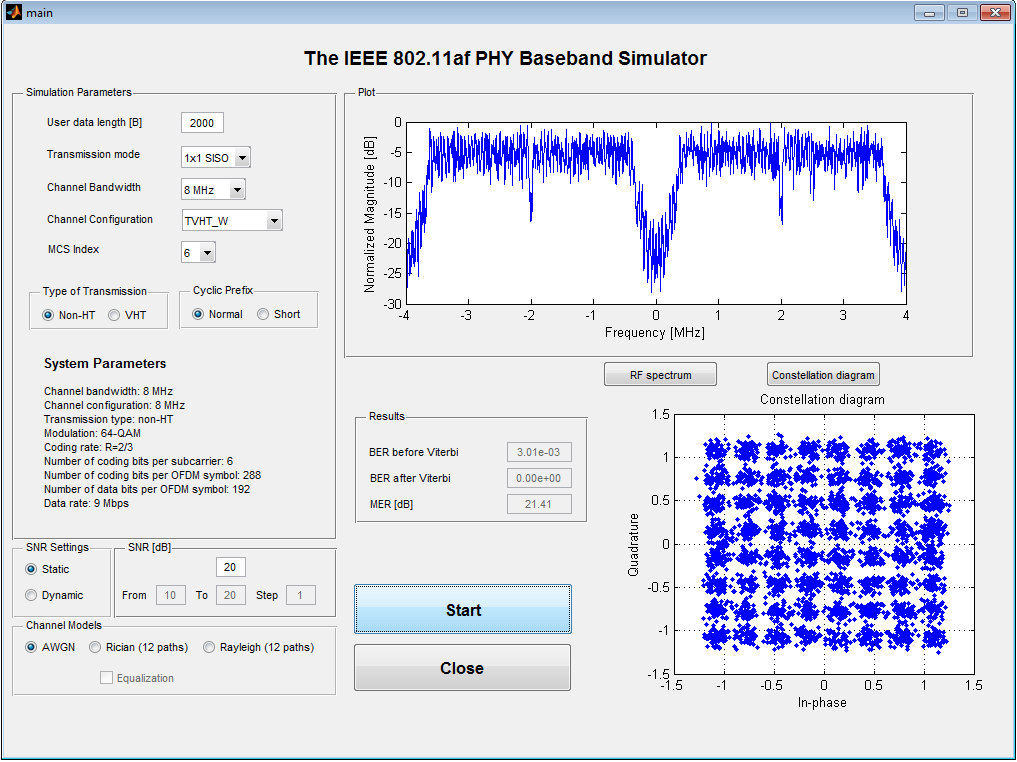
This repository contains the baseband model of the IEEE 802.11ah and IEEE 802.11af physical layer (PHY) simulators as well as the most important information for their run and usage. Both simulators were created in MATLAB on the level of m-files.
All m-files are made entirely by the authors of the simulator. Otherwise, inner functions of the program MATLAB are used.
The m-files of the fading channel models, used in both simulators, were originally developed at the Brno University of Technology within the DVB-T/H Simulator, see paper:
@ARTICLE{PolakRadioeng2010, title={Simulation and measurement of the transmission distortions of the digital television {DVB-T/H} part 3: Transmission in fading channels}, author={Polak, Ladislav and Kratochvil, Tomas}, journal={Radioengineering}, volume={19}, number={4}, pages={703--711}, year={2010}}
The IEEE 802.11ah physical layer (PHY) simulator was created in MATLAB 2015a. Its functionality has been also tested in MATLAB 2018b. To run this simulator, the following MATLAB toolboxes are required: Control System Toolbox, Signal Processing Toolbox, DSP System Toolbox and Communications System Toolbox.
If the use of this simulator leads to a scientific publication, please, cite our work that can be found at the end of this page.
In this part, the main block parts of the IEEE 802.11ah PHY simulator are briefly described. If it is not described ore mentioned, then the presented functional block is implemented in the main m-function of the simulator (main_802_11ah.m). Main blocks in the signal processing chain of the transmitter (TX) part are follows:
Data Input Generation of a random bit streams (bits).
Scrambler It is used to break up long sequences of ones and zeros. The data are scrambled by a signal defined with the generator polynome x7+x4+1. It is called by function scrambler.m.
Convolutional Encoder The Forward Error Correction (FEC) scheme for IEEE 802.11ah, according to the defined modulation and coding schemes (MCSs), uses 4 code rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4 and 5/6. In the IEEE 802.11ah PHY simulator, only convolutional encoder (generated by polynomial coefficients G0 = 133 and G1 = 177) can be used. Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) code is not supported in the current version of the simulator.
Interleaver Block Interleaver (in TX signal processing chain) is used for interleaving of the encoded message (on a bit level). A half of this block is built in the main m-file of the IEEE 802.11ah PHY simulator (main_802_11ah.m). Its second half is called by function longRunsIntrlv.m.
Constellation Mapping According to the defined MCSs, modulations BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM and 256-QAM are used.
Space-Time-Block Coding (STBC) It is utilized to realize MIMO transmission mode (by the using of Alamouti´s technique). The current version of the simulator supports only the using of a 2 x 2 MIMO scheme.
OFDM, Pilot Insertion, IFFT and Cyclic Prefix (CP) Blocks OFDM, Pilot Insertion, IFFT and CP Insertion ensure the creation of the OFDM symbols containing mapped data and pilots, their frequency-to-time domain conversion and extension with cyclic prefix (CP), respectively. The CP is applied to circumvent inter-symbol interference (ISI) caused by multipath propagation. It is possible to select between normal and short CP lengths. At the end of this process, the IEEE 802.11ah baseband signal is created.
Channel Block Channel allows for the user of the simulator to select between the following channel models.
- AWGN channel model ('AWGN') – recommended to use for reference simulations
- Rician channel with 20 independent paths ('Rician') (function Channel.m)
- Rayleigh channel with 20 independent paths ('Rayleigh') (function Channel.m)
The RX part of the IEEE 802.11ah simulator has similar configuration as the TX one, but the signal processing is inverse. It must be note that, Zero-Forcing (ZF) equalization technique is used for the channel estimation, when fading channel models are used in the simulations. Otherwise (in the case of AWGN channel), the ZF equalization technique is not used.
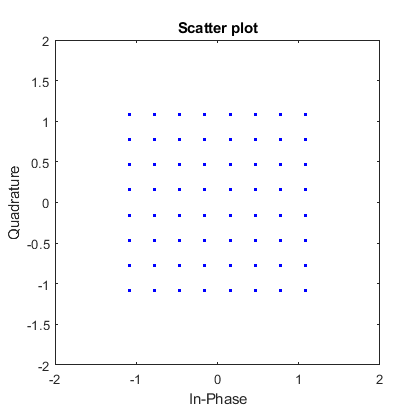
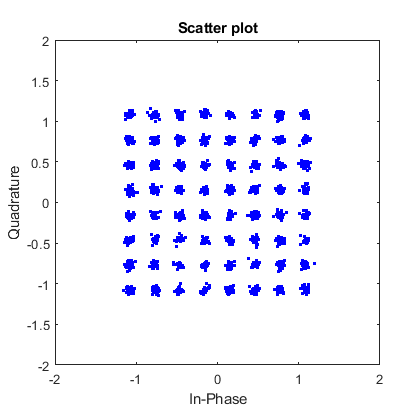
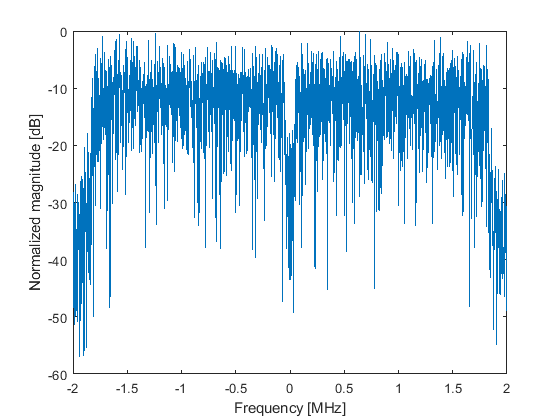
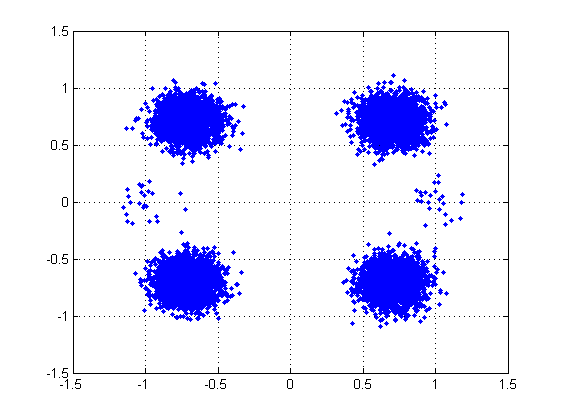
The output of simulations (block Evaluation of the results) can be evaluated in terms of Bit Error Ration - BER (before and after FEC decoding) and Modulation Error Ratio (MER) depending on the value of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Moreover, constellation diagrams of the transmitted and received (in case of equalization – after equalization) signals and normalized spectrum of the received signal are plotted.
The whole simulation, after the set of input parameters, can be run by the file 'main_802_11ah.m'. The parameters that can be set in this function (at the beginning) are as follows:
- 'channelWidth' – signal bandwidth {1, 2, 4, 8, 16}–MHz
- 'param' – the selection of the modulation (it is also depending on the selected SISO/MISO scheme – defined by parameter 'model') – for SISO [0: BPSK, 1,2: QPSK, 3,4: 16QAM, 5,6,7: 64QAM, 8,9: 256QAM, 10: BPSK 2x repetition] and for MIMO [0: BPSK, 1,2: QPSK] – in the case of MIMO, the current version of the simulator supports only the using of BPSK and QPSK modulations
- 'GI' – cyclic prefix (guard interval) – it can be 'normal' and 'short'
- 'model' – the transmission mode – it can be 'SISO' and 'MIMO'
- 'CNR' – CNR/SNR values (in dB)
- 'channelType' – the used channel models: 'AWGN', 'Rician', 'Rayleigh'
- 'useEkvaliz' – the using of equalization: '0' – it is OFF, '1' – it is ON
- 'fc' and 'fs' – the definition of carrier and sampling frequency (both in Hz), respectively
The IEEE 802.11af physical layer (PHY) simulator was developed and created in MATLAB 2013b. It can be run in this version of MATLAB. To make easier the work with the simulator, a Graphical User Interface (GUI) was created. To run this simulator, the following MATLAB toolboxes are required: Control System Toolbox, Signal Processing Toolbox, DSP System Toolbox and Communications System Toolbox. All m-files are made entirely by the authors of the simulator. Otherwise, inner functions of the program MATLAB are used. The IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator supports the TV High Throughput (TVHT) and Non High Throughput (non-HT) modes.
In this part, the main block parts of the IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator are briefly described. If it is not noted, then the presented functional block is implemented in the main m-function of the simulator (main.m). Some parts of the IEEE 802.11ah/af PHY simulators are the same. In such case it we present sentence “See the description of the IEEE 802.11ah PHY simulator.”
Main blocks in the signal processing chain of the transmitter (TX) part are follows:
Data Input The data frame is generated according to the IEEE 802.11af standard. The Physical Layer Protocol Data Unit (PDDU) consists of the SIGNAL and DATA fields. For each 802.11af frame, the PSDU is measured in octets and can reach a maximum size of 4095 bytes. The complete data frame is created by functions PPDU_SIGNAL.m, PSDU_generator.m and PPDU_DATA.m.
Scrambler It is used to break up long sequences of ones and zeros. It is applied only on the DATA part of the frame. The data are scrambled by a signal defined with the generator polynome: x7+x4+1. It is called by function scrambler.m.
Convolutional Encoder The Forward Error Correction (FEC) scheme for IEEE 802.11af, according to the defined modulation and coding schemes (MCSs), can use 4 code rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4 and 5/6. In the IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator, only convolutional encoder (generated by polynomial coefficients G0 = 133 and G1 = 177) can be used.
Interleaver Block Interleaver (in TX signal processing chain) is used for interleaving of the encoded data. It is called by the function interleaver.m. This function is applied on the coded SIGNAL and coded DATA fields separately.
Constellation Mapping According to the defined MCSs, modulations BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM and 64-QAM are used.
Space-Time-Block Coding (STBC) Important note: Current version of the IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator does not support MIMO scheme. This option was disabled due to unpredicted errors in the signal processing chain at the optimization of the simulator. In the future, we will try to add this option into this simulator again. Sorry for any inconveniences!
OFDM, Pilot Insertion, IFFT and Cyclic Prefix (CP) Blocks OFDM, Pilot Insertion, IFFT and CP Insertion ensure the creation of the OFDM symbols containing mapped data and pilots, their frequency-to-time domain conversion and extension with cyclic prefix (CP), respectively. The CP is applied to circumvent inter-symbol interference (ISI) caused by multipath propagation. It is possible to select between normal and short CP lengths. At the end of this process, the IEEE 802.11af baseband signal is created.
Channel Block Channel allows for the user to select between the following channel models:
- AWGN channel model ('AWGN') – recommended to use for reference simulations
- Rician channel with 12 independent paths ('Rician') (function Channel.m)
- Rayleigh channel with 12 independent paths ('Rayleigh') (function Channel.m)
The RX part of the IEEE 802.11ah simulator has similar configuration as the TX one, but the signal processing is inverse. It must be note that, Zero-Forcing (ZF) equalization technique is used for the channel estimation, when fading channel models are used in the simulations. Otherwise (in the case of AWGN channel), the ZF equalization technique is not used.
The output of simulations (block Evaluation of the results) can be evaluated in terms of Bit Error Ration - BER (before and after FEC decoding) and Modulation Error Ratio (MER) depending on the value of signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Moreover, constellation diagram and the normalized spectrum of the received signal are plotted (it is also possible to show them in a spate window – buttons Constellation diagram and RF spectrum).
The GUI is plotted by the run of the 'main.m' function. The parameters that can be set in the GUI are as follows:
- Field – User data length – definition of the length of data in units of Bytes [B]
- Popup Menu – Transmission Mode – currently, only the 'SISO' mode is supported
- Popup Menu – Channel Bandwidth – it is possible to select between signal bandwidths 8, 7 and 6 MHz
- Popup Menu – Channel Configuration – the current version of the simulator allows to use only the Television Very High Throughput (TVHT) configuration – TVHT_W
- Popup Menu – MCS index – the set of MCS index (from 0 to 7). After the set of the MCS number, the information about the system parameters is actualized in the field System Parameters.
- Field – Type of Transmission – it is possible to select between the non-HT and VHT modes
- Field – Cyclic Prefix – it is possible to select between 'normal' and 'short' CP lengths
- Field 'SNR Settings' – it is possible to select between the “Static” mode (simulation for one SNR value) and the “Dynamic” mode (a set of simulations in a defined interval of SNR values). In the case of “Dynamic” mode, the simulation results (SNR, BER before and after Viterbi decoding and MER) are saved in the “Results.xls” file.
- Field 'SNR [dB]' – definition of the values of SNR
- Field 'Channel Models' – the used channel models: 'AWGN', 'Rician (12 paths)', 'Rayleigh (12 paths)'
- Checkbox 'Equalization' – to apply the Zero-Force equalization – it is active and can be applied only for fading channel models (RC12 and RL12)
- Field 'Results' – the simulation results (BER before and after Viterbi decoding, MER) are shown in this field
The GUI of IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator has the following buttons:
- Start – to start the simulation (after the setting of all system parameters)
- Close – to close the GUI of the IEEE 802.11af PHY simulator
- Constellation diagram – to show the constellation diagram in a new window
- RF spectrum – to show the normalized RF spectrum in a new window
If you use the 802.11ah/ay simulator, please, cite our work:
@INPROCEEDINGS{PolakTSP2020, author = {Polak, Ladislav and Jurak, Peter and Milos, Jiri}, title = {{MATLAB}-{B}ased {PHY} {S}imulators for {P}erformance {S}tudy of the {IEEE} 802.11ah/af {S}ystems}, booktitle = {2020 43rd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing (TSP}, year = {2020}, publisher = {IEEE}, pages = {1--4}, month = {July} }
The paper is available via IEEE Explore at: TBD…
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports (MEYS) of the Czech Republic project no. LTC18021 (FEWERCON). For research, infrastructure of the SIX Center was used. The authors would like to thank Peter Jurak and Yaroslav Saprykin for his help with the development of the IEEE 802.11ah and IEEE 802.11af simulator, respectively.
MIT License
Copyright (c) [2020] [Department of Radio Electronics, Brno University of Technology]
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.