知识点:
- 利用定位new表达式来将内存分配和构造分开
- 学习
is_trivially_destructible测试类型是否为普通易损坏类型, 如果是的话那么不需要调用其析构函数- 包括内置标量类型
is_scalar - 还有一些特定的类(使用隐式的析构函数,它的成员本身也是普通易损坏类型)
- 包括内置标量类型
- 明白forward的实现原理
实现:
- 实现allocator
- 实现forward完美转发
is_trivially_destructible
forward
为什么需要衰减类型? 当我们使用引用作为函数形参时,默认的转换规则时不生效的(比如数组转指针,函数转指针,去掉cv等)。使用decay允许在引用类型上发生这种类型转换.
This is useful to hide signatures on compile time when a particular condition is not met, since in this case, the member enable_if::type will not be defined and attempting to compile using it should fail.
decay
enable_if
What is std::decay and when it should be used?
根据功能划分为五种:
- input
- output
- forward
- Bidrectional
- RandomAcess
指针也算某种意义上的迭代器, 迭代器的操作它大多都支持.
为了既支持萃取自定义迭代器又支持萃取指针迭代器的属性,iterator_traits采取了模板类的设计方式:
- 如果是指针迭代器,那么直接在模板类里面定义了类型成员
- 如果是普通迭代器,首先通过编译器静态检查,检查其是否包含
iterator_category成员,并且检查该iterator_category成员是否是从基类input_iterator_tag或out_iterator_tag继承而来.
通过萃取iterator_category 属性然后判断属于五种中的哪一种
C++的模板帮助我们在编写程序时不知道类型的情况,利用模板可以让我们定义出各种容器类和模板函数来复用代码。
而C++是静态语言,静态语言的类型检查是编译期进行的,为了约束我们的模板类/函数,标准库提供了type_traits 该头文件定义了一系列类,以获得有关编译时的类型信息。
Function objects are objects specifically designed to be used with a syntax similar to that of functions. In C++, this is achieved by defining member function operator() in their class, like for example:
vector DONE
文档阅读:
- Only if T is guaranteed to not throw while moving, implementations can optimize to move elements instead of copying them during reallocations
list DONE
- 底层双向列表实现,因此可以在任意位置常量时间插入/删除元素
- 缺点在于:每个元素都要存储一些额外数据用来定位,并且不能支持随机访问
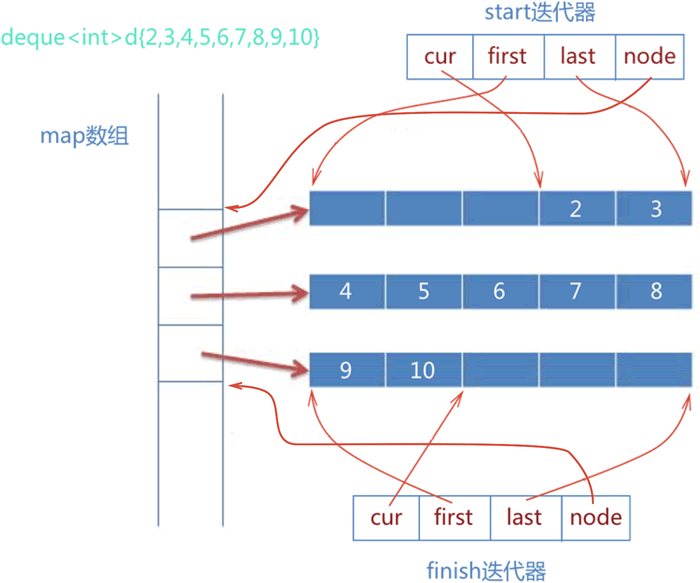
deque DONE
- dynamic sizes ,random access
- they provide a functionality similar to vectors, but with efficient insertion and deletion of elements also at the beginning of the sequence, and not only at its end。
- unlike vectors, deques are not guaranteed to store all its elements in contiguous storage locations: accessing elements in a deque by offsetting a pointer to another element causes undefined behavior.
- Both vectors and deques provide a very similar interface and can be used for similar purposes, but internally both work in quite different ways: While vectors use a single array that needs to be occasionally reallocated for growth, the elements of a deque can be scattered in different chunks of storage, with the container keeping the necessary information internally to provide direct access to any of its elements in constant time and with a uniform sequential interface (through iterators). Therefore, deques are a little more complex internally than vectors, but this allows them to grow more efficiently under certain circumstances, especially with very long sequences, where reallocations become more expensive.
内部数据结构:
unordered_map 【DONE】
- Internally, the elements in the unordered_map are not sorted in any particular order with respect to either their key or mapped values, but organized into buckets depending on their hash values to allow for fast access to individual elements directly by their key values
- unordered_map containers are faster than map containers to access individual elements by their key, although they are generally less efficient for range iteration through a subset of their elements.
unordered_map 和map都属于关联容器,除此之外还有multi版本 。
unordered版本正如其名是“无序”的,这个“无序”意思是它不会按照key或者value的顺序来排列,而是以散列式的存储方式。
template <class Key, class T, class Hash = std::hash<Key>, class Pred = std::equal_to<Key>>
class unordered_map {}
正如它的模板声明一样,unordered_map 底层使用散列表来实现,散列值相当于定位下标,可以很快定位到元素的存储位置。散列值相同的会被存储在同一个桶里,当散列容器中右大量数据时,同一个桶里的数据也会增多,出现访问冲突。所以unordered_map 在插入元素的时候会自动增加桶的数量来避免散列冲突。
散列表是数组的一种扩展结构,它来源于数组,利用的是数组支持下标随机访问元素的特性。一个工业级的散列表应该满足下面这些要求:
- 支持快速查找,删除,添加
- 内存占用合理,不能浪费过多的内存空间
- 性能稳定,极端情况下,散列表的性能不会退化到无法接受的情况
想要解决这些问题:
- 设计一个合理的散列函数,劲量让这些数据均匀的分布在每个桶里面,减少散列冲突
- 定义装载因子,并且设计动态扩容的策略。涉及到大数据量的搬运时,我们可以这样做。 装载因子触发阈值之后,我们只申请空间,但并不将老数据搬移到新散列表中。当新数据要插入的时候,我们再将新数据插入到散列表中,并将老的散列表中拿出一个放入到新散列表中。 这样均摊的思想可以让插入做到o(1)
- 选择合适的散列冲突解决方法。
常见的散列冲突解决办法有两种:
- 开放式寻址法
- 链表法
开放式寻址法的思想是:先通过hash函数计算出下标,然后判断下标位置是否已经被其他占用了,如果已经被占用,就往后寻找空的位置,然后插入.
开放式寻址法适用于数据量规模小,装载因子小的时候,这种情况下是很少会冲突的。如果装载因子过大,那么就意味着越容易产生冲突,我们就需要扩容,这就导致这种方法比链表更浪费空间。
链表法,因为数据是存储在链表结点里面的,所以这部分开销也是有的。所以,链表的散列冲突比较适合存储大数据对象,大数据量的散列表,同时为了提供效率,我们可以把链表改造为跳表,红黑树等结构,这样极端情况下,查询速度可以达到o(logn)
map [TODO]
template <class _Key, class _Tp, class _Compare = less<_Key>,
class _Allocator = allocator<pair<const _Key, _Tp> > >
class map{}
map是有序版本,它采用红黑树来存储,默认通过std::less来判断key的大小, 就这一点来说它的查找时O(logn)级别的,比unordered_map 要慢.
漫画:什么是红黑树?
教你透彻了解红黑树
红黑树详细分析,看了都说好
为什么STL和linux都使用红黑树作为平衡树的实现?
- 不同指针类型不能进行比较,比如
int *和const int * - 指针变量要设置初始值,否则可能会因为垃圾值出现一些奇奇怪怪的问题
- 模板编程