While working locally may seem enough for some people sometimes we need to collaborate with others so, this is where a remote place to store our code comes into place, and our remote is GitHub a cloud platform used to share code with others and collaborate on projects.
-
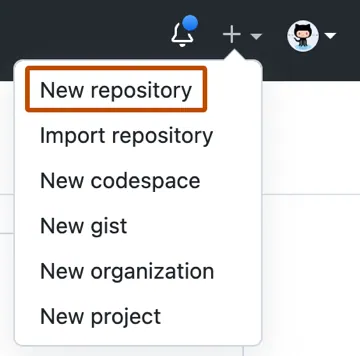
In the upper-right corner of any page, use the ➕ drop-down menu, and select New repository.
-
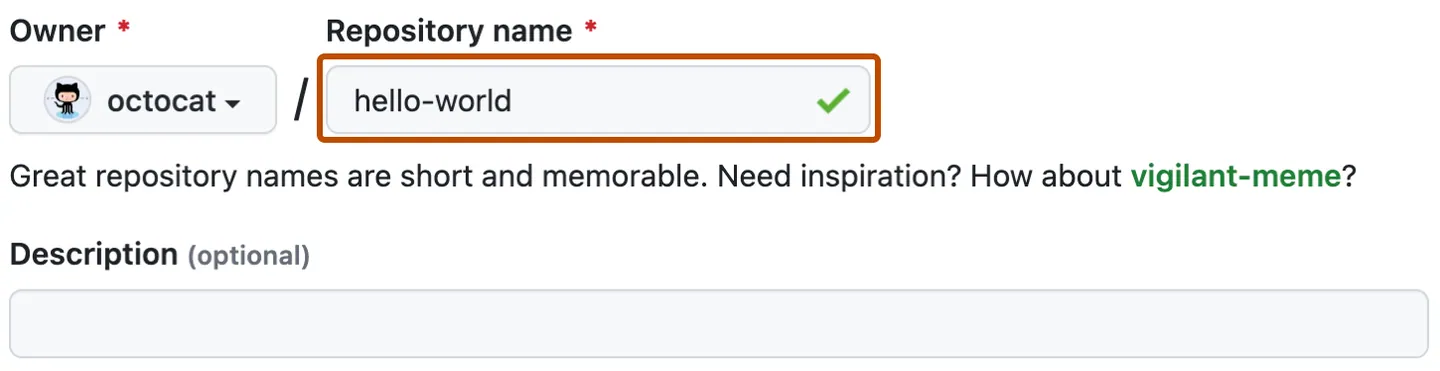
Type a short, memorable name for your repository. For example, "hello-world".
-
Optionally, add a description of your repository. For example, "My first repository on GitHub."
-
Choose a repository visibility. For more information, see "About repositories".
-
Select Initialize this repository with a README.
-
Select Create repository.
-
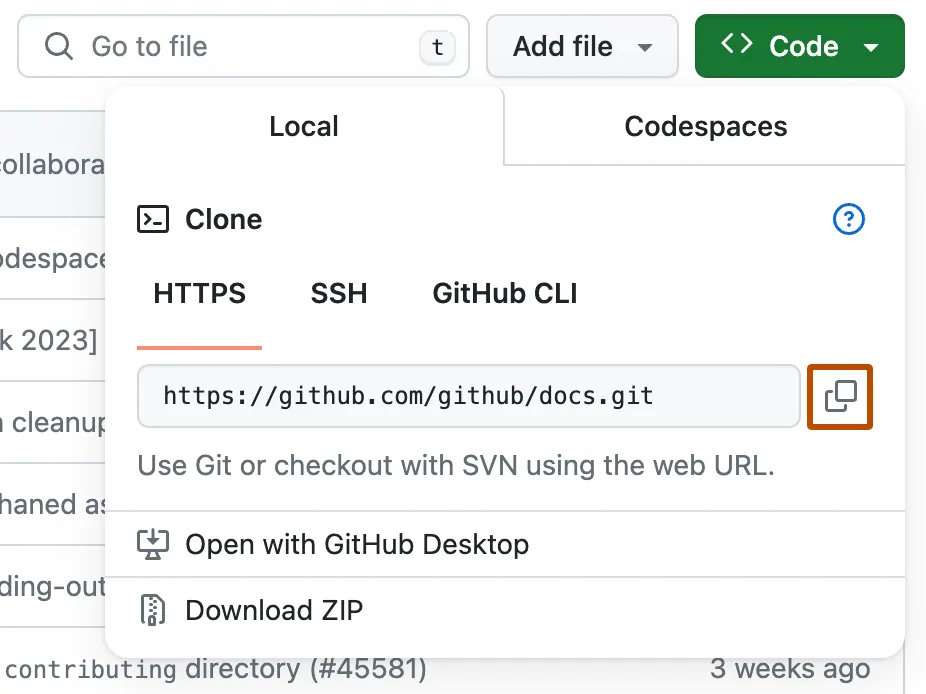
Above the list of files, select <> Code.
-
Copy the HTTPS URL for the repository.
-
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command replacing the URL with the URL you copied earlier
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/hello-world
This command:
- takes the path to an existing repository
- by default will create a directory with the same name as the repository that's being cloned
- can be given a second argument that will be used as the name of the directory
- will create the new repository inside of the current working directory
-
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to change the directory to the newly cloned repository's directory
cd hello-world -
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to make some changes
echo "My first sentence on GitHub." > new-file.txt
-
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to add the changes
git add . -
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to add the changes
git commit -m "Initial commit" -
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to push the changes to GitHub
git push
-
Inside your GitHub repository, make any changes to anyfile you want using GitHub's UI. (For example, edit the README.md file)
-
Inside Git Bash, execute the following command to pull the changes from GitHub.
git pull
- Visit this repository john0isaac/git-workshop-pr.
- In the top-right corner of the page, click Fork.
- Select Create fork.
- Clone the repository locally.
- Make changes to the repository by adding your name to the contribution list.
- Add, Commit, and Push your changes.
- Go back to the forked version of the repository on GitHub.
- Select Contribute followed by Open a pull request to add your changes to the original repository.
- Select Create pull request.
- Enter a Title for your pull request. For example, YOUR-NAME contribution.
- Select Create pull request.
Congratulations! You have successfully created and cloned a GitHub repository. The repository you created can be shared with anyone which enables you to collaborate with others. You have also made your first contribution to another project. If you want to continue to grow your skills:
- Learn more about GitHub on Microsoft Learn.
- Finish Introduction to version control with Git learning path.