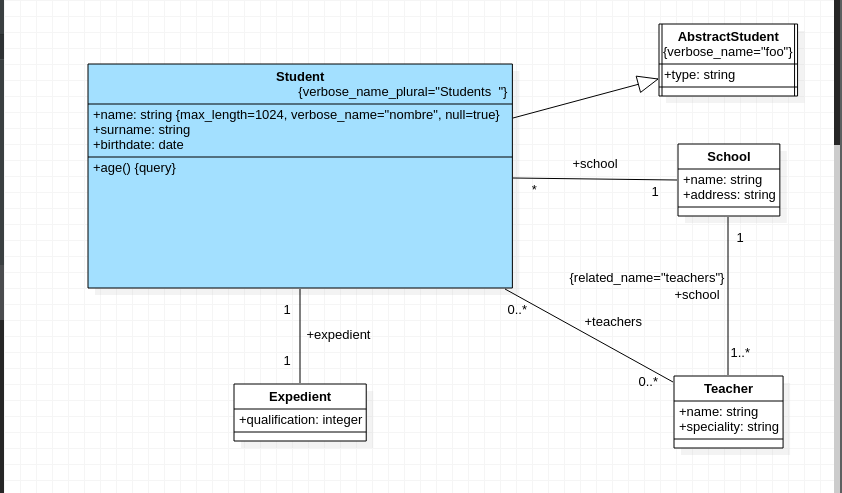
- Auto-generate Django Model Class.
- Auto-generate attributes with the suitable type, using standard
Djando Model Field, provided by Django ORM. - Generate inheritance, (if not exist by default
models.Model). - Generate relationship, using cardinality, create suitable fields,
OneToOne,ForeingKeyandManyToMany. - Auto add attributes in Meta models, using
tags. - Auto add aditional params to model attributes and model relationships fields using defined
tags.
To run auto-generate field with suitable Django Mode Field, is necesary to
have a diagram with a class for each basic type loaded.
You could download this scheme with basic class types
- string:
models.CharField - text:
models.TextField - integer:
models.IntegerField - decimal:
models.DecimalField - boolean:
models.BooleanField - date:
models.DateField - datetime:
models.DateTimeField - email:
models.EmailField - file:
models.FileField
1- Install StarUML, download page.
2- Download or clone this repo.
3- Copy repo files to StarUML extension user folder.
-
MacOS:
~/Library/Application Support/StarUML/extensions/user/staruml-django -
Windows:
C:\Users\<user>\AppData\Roaming\StarUML\extensions\user\staruml-django -
Linux:
~/.config/StarUML/extensions/user/staruml-django
- Click the menu (
Tools > Django Models > Generate Code...) - Select a base model (or package) that will be generated to Django Models.
- Select a folder where generated Python source files (.py) will be placed.
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.db import models
class AbstractStudent(models.Model):
class Meta:
verbose_name='foo'
type = models.CharField()#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.db import models
from AbstractStudent import AbstractStudent
class Student(AbstractStudent):
class Meta:
verbose_name='student'
name = models.CharField(max_length=1024, verbose_name='name', null=True)
surname = models.CharField()
birthdate = models.DateField()
school = models.ForeingKey('School', on_delete=models.PROTECT)
teachers = models.ManyToMany('Teacher')
expedient = models.OneToOne('Expedient')
@property
def age(self, ):
pass#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.db import models
class Teacher(models.Model):
class Meta:
pass
name = models.CharField()
speciality = models.CharField()
school = models.ForeingKey('School', related_name='teachers', on_delete=models.PROTECT)#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.db import models
class School(models.Model):
class Meta:
pass
name = models.CharField()
address = models.CharField()#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.db import models
class Expedient(models.Model):
class Meta:
pass
qualification = NoneThis project is now in beta, not ready for production or profesional use. Use and modify by your own responsability.
- José Miguel López Pérez josmilope@gmail.com
- Based on https://github.com/niklauslee/staruml-python