- Introduction
- Create a Task
- Get a Result
- Delete Task when Task is complete
- Get started with image-categorization
The image-categorization API enables you to categorize images based on a list of categories you specify using Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk). This is useful in the field of computer vision, such as categorizing user-generated content, e.g., pictures from a restaurant visit, into categories such as interior, exterior, food, and menu.
The API takes as input a URL for the image to be analyzed, and an array of categories that could match the image. It returns an array of containing the categories that best fits the image. When you call this API, it uses your MTurk Requester account and AWS account to automatically create HITs for Workers on MTurk to complete, and automatically processes answers from Workers and returns the result.
{
"input": {
"image": {"url": "https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/...1m.png"},
"categories": [
{"label": "Ankle Boot",
"description": "Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot up to ankle.",
"positiveExamples": : [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1d.jpg'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.jpg'}}
]
},
{"label": "Wedge",
"description": "Heeled shoe where sole is in the form of a wedge." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1l.png'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.png'}}
]
}
]
}
}| "image" |
|---|
 |
Note you can host images on Amazon S3 if you do not have your own server.
{
"result": {
"matches": [{"label" : "Wedge"}]
}
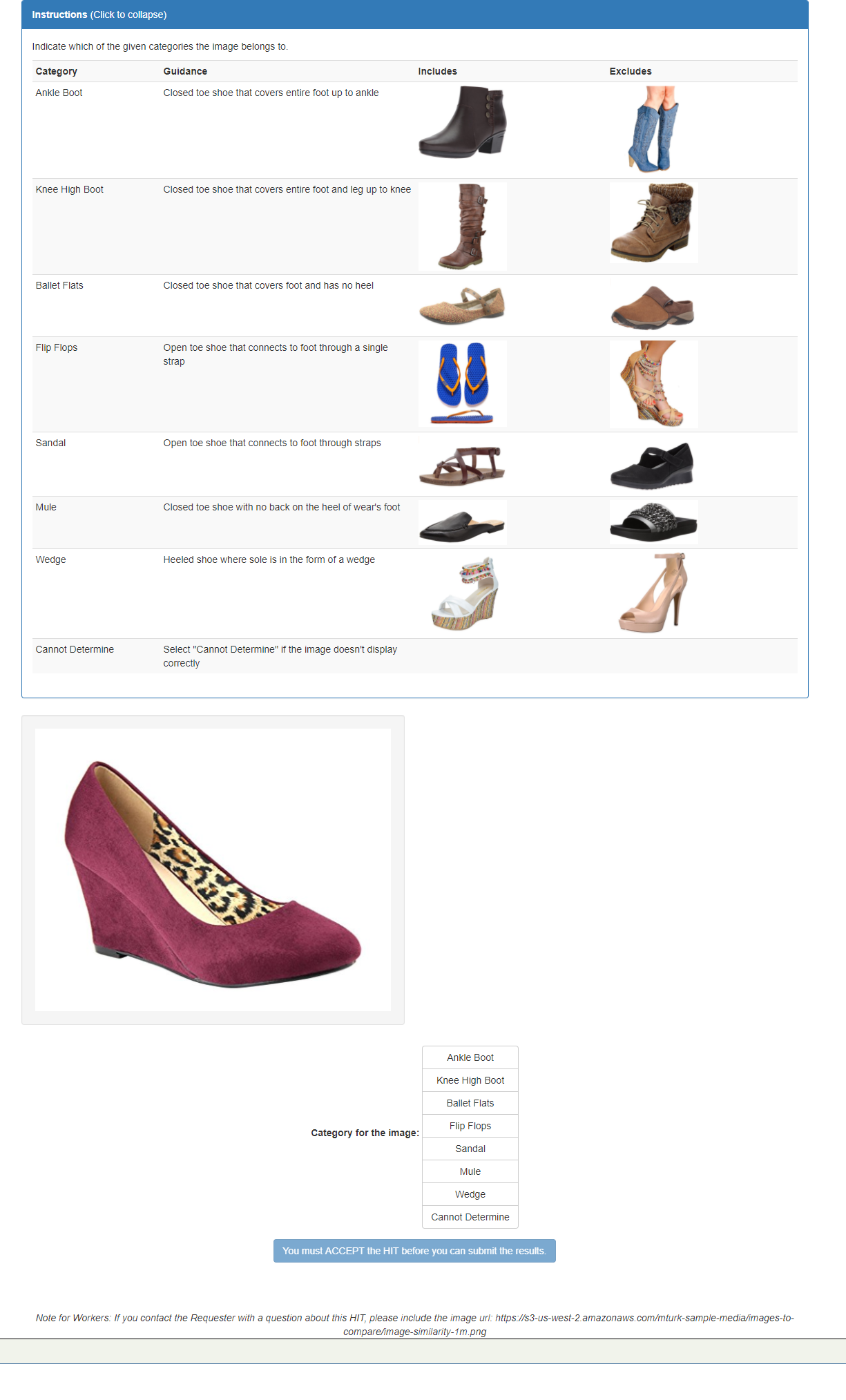
}Here’s how the input might be presented in a HIT to Workers on MTurk.
The API implements an adjudication strategy based on Worker agreement and returns results only when it reaches confidence.
All of the single purpose APIs follow the same REST pattern as described in our REST API reference. They require a function name indicating which API you want to call, and a unique Task name used to represent your input and the corresponding result.
image-categorization-test is a version of the image-categorization API meant for testing your integration. It has the same interface as the production version, but Tasks always complete quickly with mock results. HITs are not created on MTurk, so you don’t need to pay Workers for rewards.
Note: This will return a random mock result when you call
get_taskwithimage-categorization-test.
The rest of this article provides instructions on using the image-categorization API using the MTurk Python Client.
Download Sample Python code for image-categorization-test.
This Python sample calls the image-categorization API using Boto3 and the MTurk Python client.
Tasks are created by calling put_task. For more details on how to use put_task, check out Instructions for creating your first Task for a MTurk single purpose API.
Note: Before you create your Task, make sure you try to view the image using the URL in your browser to ensure it displays correctly.
The body of a put_task request looks like this:
{
"input": {
"image": {"url": "<image you want analyzed>"},
"categories": <array of user-supplied categories>
}
}
| Name | Description | Type | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| "image" | image you want to be analyzed | JSON Object | Yes |
| "url" | link to image hosted online (<= 400 characters) | String | Yes |
| "categories" | up to ten user-supplied categories, each with a label, description, and examples | Array of JSON Objects | Yes |
| "label" | the label representing the name of a single category (<= 100 characters) | String | Yes |
| "description" | clarifying details about the category presented to Workers | String | No |
| "positiveExamples" | up to two examples that fit the single category | Array of JSON Objects | No |
| "negativeExamples" | up to two examples that do not fit the single category | Array of JSON Objects | No |
Note you can host images on Amazon S3 if you do not have your own server.
image_url = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1m.png'
label1 = 'Ankle Boot'
label2 = 'Knee High Boot'
label3 = 'Ballet Flats'
label4 = 'Wedge'
description1 = 'Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot up to ankle'
description2 = 'Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot and leg up to knee'
description3 = 'Closed toe shoe that covers foot and has no heel'
description4 = 'Heeled shoe where sole is in the form of a wedge'
image_url_1 = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1d.jpg'
image_url_2 = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1z.jpg'
image_url_3 = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1dd.png'
image_url_4 = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1l.png'
image_url_1b = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1i.jpg'
image_url_2b = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1f.jpg'
image_url_3b = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1y.png'
image_url_4b = 'https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mturk-sample-media/images-to-compare/image-similarity-1i.png'
categories = [{ 'label': label1 ,
'description' : description1,
'positiveExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_1}}
],
'negativeExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_1b}}
]},
{ 'label': label2,
'description': description2: [
{'image': {'url': image_url_2}}
],
'negativeExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_2b}}
]},
{ 'label': label3,
'description': description3,
'positiveExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_3}}
],
'negativeExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_3b}}
]},
{ 'label': label4,
'description': description4,
'positiveExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_4}}
],
'negativeExamples': [
{'image': {'url': image_url_4b}}
]
}]
put_result = crowd_client.put_task('image-categorization', 'my-task-name',
{'image': {'url': image_url}, 'categories': categories })
{
"taskName": "my-task-name",
"input": {
"image": {"url":"https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/...1m.png"},
"categories": [
{"label": "Ankle Boot",
"description" : "Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot up to ankle." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1d.jpg'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.jpg'}}
]
},
{"label": "Wedge",
"description": "Heeled shoe where sole is in the form of a wedge." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1l.png'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.png'}}
]
}
]
},
"problemDetails": null,
"state": "processing",
"result": null
}
This Python sample calls the image-categorization API using Boto3 and the MTurk Python client.
After creating a Task, users can call the get_task to poll its current state.
Remember it can take some time for a Worker to complete a Task, so you might have to wait before getting a result.
For more details for how to use get_task, check out Instructions for creating your first Task for a MTurk single purpose API.
client.get_task('image-categorization', 'my-task-name')
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| "taskName" | user-provided Task name | String |
| "input" | input provided by user when Task was created | JSON Object |
| "problemDetails" | if the "state" is "failed" - details about a failed Task | JSON Object or null |
| "state" | current Task state - one of "processing", "completed" or "failed" | String |
| "result" | if the "state" is "completed" - the results of the completed Task | JSON Object or null |
| Name | Value | Type |
|---|---|---|
| "matches" | matching categories selected by Workers | Array of JSON Objects |
| "label" | the label representing the name of a single category | String |
Currently, the API only returns one match, as an array of one.
Example response for a successful Task:
{
"taskName": "my-task-name",
"input": {
"image": {"url": "https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/...1m.png"},
"categories": [
{"label": "Ankle Boot",
"description": "Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot up to ankle." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1d.jpg'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.jpg'}}
]
},
{"label": "Wedge",
"description": "Heeled shoe where sole is in the form of a wedge." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1l.png'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.png'}}
]
}
]
},
"problemDetails": null,
"state": "completed",
"result": {
"matches": [{"label" : "Wedge"}]
}
}
Example response for a failed Task:
{
"taskName": "my-task-name",
"input": {
"image": {"url": ""https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/...1m.png"},
"categories": [
{"label": "Ankle Boot",
"description": "Closed toe shoe that covers entire foot up to ankle." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1d.jpg'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.jpg'}}
]
},
{"label": "Wedge",
"description": "Heeled shoe where sole is in the form of a wedge." ,
"positiveExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1l.png'}}
] ,
"negativeExamples": [
{'image': {'url':'https://s3-...1i.png'}}
]
}
]
},
"problemDetails": {
"code": "Expired",
"message": "Not enough Workers provided answers for your task within the allotted time."
},
"state": "failed",
"result": null
}
This Python sample calls the image-categorization API using Boto3 and the MTurk Python client.
A user can optionally delete a finished Task (one whose state is either “completed” or “failed”). After you delete a Task, you can reuse the Task name for a future Task.
Note: Deleting a Task that is still being processed (i.e., whose state is “processing”) is not allowed.
For more details for how to use delete_task, check out Instructions for creating your first Task for a MTurk single purpose API.
client.delete_task('image-categorization', 'my-task-name')
A successful request for the delete_task operation returns with no errors and an empty body.
- Set up your Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) Requester account and AWS account
- Set up permissions to call an MTurk single purpose API
- Instructions for creating your first Task for a MTurk single purpose API
MTurk has released several APIs for common use cases, click here to see a list of all the available APIs.
If you have any questions or feedback, such as methods you wish our client supported, please contact our product team, or submit a pull request on GitHub adding additional functionality to our client.