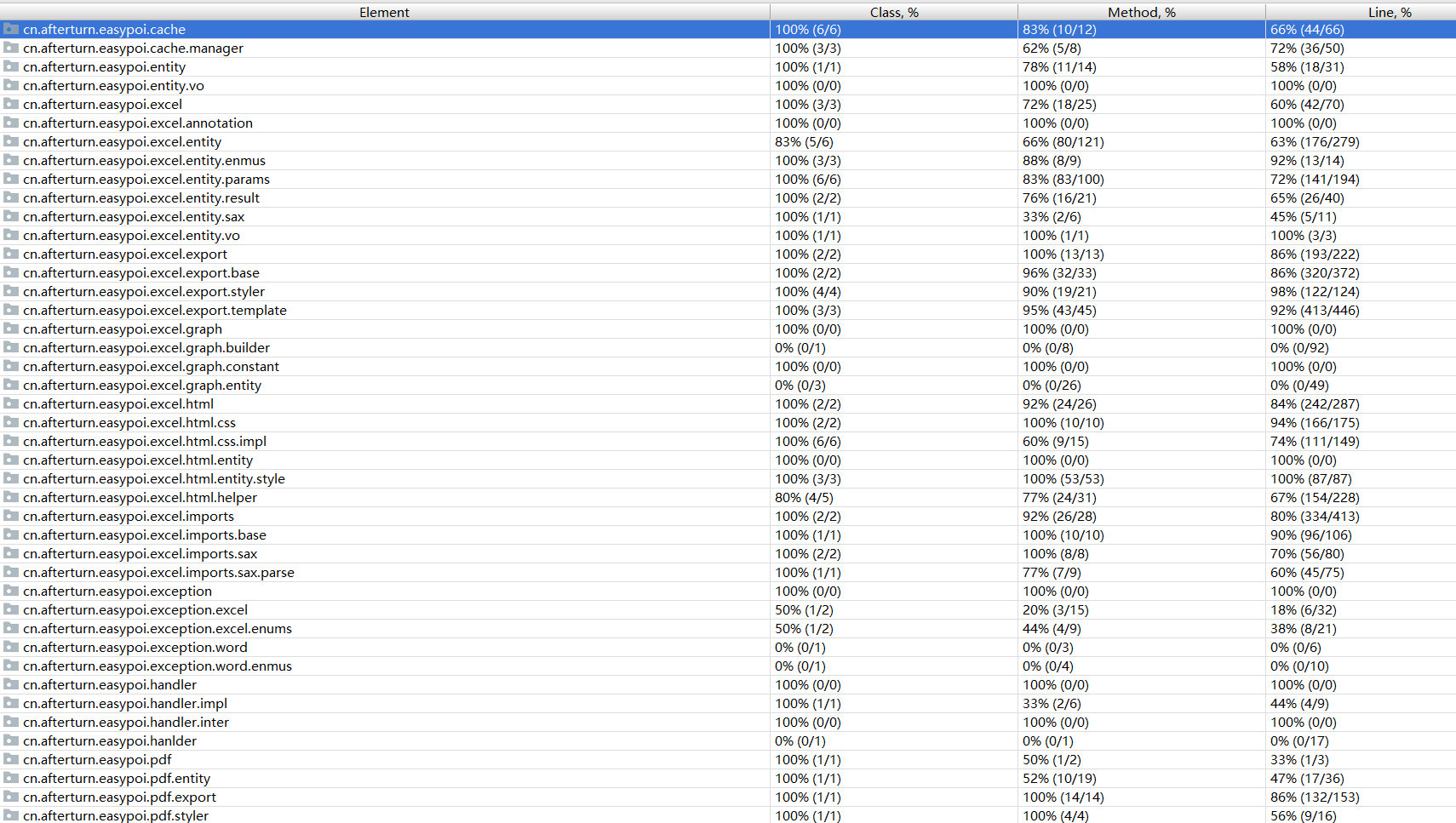
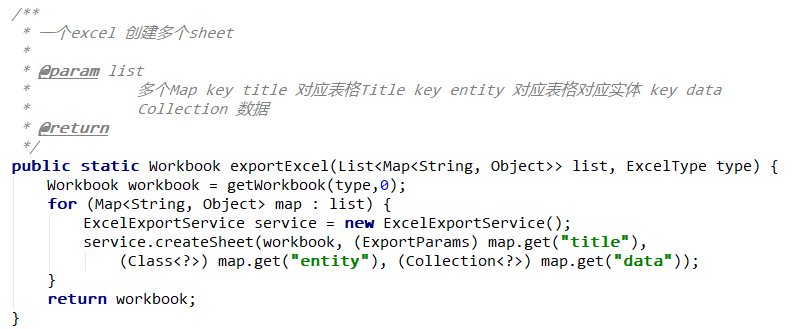
#1. Introduction
##1.1 Foreword
Easypoi, as is clear from the name, it's easy for a developer who never even used poi to export/import Excel, export Excel Template and Word Template, and export PDF. We encapsulate Apache poi in the upper layers. With simple annotations and templates Language (familiar expression syntax) to accomplish previously complex coding.
Website:https://opensource.afterturn.cn/
Email: qrb.jueyue@foxmail.com
Not as many customizations as Apache poi, not as many tags as jxl, Easypoi just coding less, coding less...
Advantages
1.Exquisite Design, easy to use
2.Various Interfaces, easy to extend
3.Coding less do more
4.Support Spring MVC, easy for WEB export
Main Features
For Excel, self-adapt xls and xlsx format. For Word, only docx.
1.Excel Import
- Annotation Import
- Map Import
- Big data Import, sax mode
- Save file
- File validation
- Field validation
2.Excel Export
- Annotation Export
- Template Export
- HTML Export
3.Excel convert to HTML
4.Word Export
5.PDF Export
##1.2 Easypoi Introduction
Target Group
- Not familiar with poi
- Not willing to coding much and repeat too much
- Prefer easy to export and import
- Prefer templates
Goal The goal of Easypoi is not to replace poi, but to help a developer who is not familiar with poi to quickly complete various opearations of Excel and Word, rather than learning lots of apis to complete such work.
How does Easypoi come to be?
Once long agao, when I was an ordinary programmer(still now), I received a task to develop lots of report forms for the business department, each report has different style, different table headers...I wrote a lot of poi code, copy to copy...bored to death. One day I joined the GEECG, there is a small utility class which can handle the simple export with annotations. I had been suddenly enlightened, I can improve it and let me escape from suffering sea. I spent a week to do the first version support export and import on the GEECG which recieved enthusiastic responses. Gradually more and more developer are using it, so I separate this function and create Easypoi. And then more and more requirements are put forward, such as Template, Word, I still keep updating Easypoi and refactoring it with the growth of my experience until now.
Unique functions
- Export/Import based on annotations, you can modify Excel by modifying the annotations
- Support common style customization
- Table Headers based on map which can be defined flexibly
- One-to-many export/import
- Template export, common tags, custom tags
- HTML/Excel conversion
- support Word export, Image export, Excel export
How to begin?
- Dowload demo and run, which include common usage easypoi-test
- Focus on the usage of *Util, which is the key of Easypoi
- Pay attention to the meaning of annotations
- Also to use Template by tags
- Then, you are ready to go
##1.3 Package Guide
- 1.easypoi -- Parent package
- 2.easypoi-annotation -- Basic annotation package, action on entity objects, it's convenient for Maven multi-project management after splitting
- 3.easypoi-base -- Import and export package, realize Excel Import/Export, Word Export
- 4.easypoi-web -- Based on AbstractView, Coupled with spring MVC, greatly simplifies the export function
- 5.sax -- Optional, Export uses xercesImpl, Word Export uses poi-scratchpad
If you don't use spring MVC, only easypoi-base is enough.
If maven, please use following:
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-base</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-web</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-annotation</artifactId>
<version>4.1.0</version>
</dependency>If not maven, please download the jar,alimaven
##1.4 Test Project
Test project includes two parts: common test of Junit and spring view test.
1. Spring view test
- Run Application.java and visit http://127.0.0.1:8080
- The corresponding code is below the view
2. Junit test directory structure
-
test -- entity for test
-
tohtml -- html preview test
-
view -- view test for Export
-
cache
- file -- custom file loader test
-
csv -- csv import and export test
-
html -- htmlToExcel and excelAndHtml Test
-
lombok -- lombok test
-
test
- excel
- export -- export test
- read -- import test
- styler -- custom export style test
- template -- template export
- pdf -- pdf test
- word -- word export
- excel
-
util -- internal test
##1.5 The best practice with my experience:Which method is suitable for which situation
###1.5.1 small amount of data, simple excel Use following methods to Export/Import
/**
* Excel Import
* Datasource: local file, not return validation result
* Import Field type: Integer, Long, Double, Date, String, Boolean
*
* @param file
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
*/
public static <T> List<T> importExcel(File file, Class<?> pojoClass, ImportParams params) {
FileInputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(file);
return new ExcelImportService().importExcelByIs(in, pojoClass, params, false).getList();
} catch (ExcelImportException e) {
throw new ExcelImportException(e.getType(), e);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(), e);
throw new ExcelImportException(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
IOUtils.closeQuietly(in);
}
}
/**
* Excel Import
* Datasource: IO stream, not return validation result
* Import Field type: Integer, Long, Double, Date, String, Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static <T> List<T> importExcel(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
ImportParams params) throws Exception {
return new ExcelImportService().importExcelByIs(inputstream, pojoClass, params, false).getList();
} /**
* @param entity Excel param entity
* @param pojoClass Excel object Class
* @param dataSet Excel object data List
*/
public static Workbook exportExcel(ExportParams entity, Class<?> pojoClass,
Collection<?> dataSet) {
Workbook workbook = getWorkbook(entity.getType(), dataSet.size());
new ExcelExportService().createSheet(workbook, entity, pojoClass, dataSet);
return workbook;
}###1.5.2 Export/Import irregular object
For export,use your own construct ExcelExportEntity
/**
* Create the Excel according to the Map
*
* @param entity Excel param entity
* @param entityList Map entity list
* @param dataSet Excel object data List
*/
public static Workbook exportExcel(ExportParams entity, List<ExcelExportEntity> entityList,
Collection<?> dataSet) {
Workbook workbook = getWorkbook(entity.getType(), dataSet.size());
;
new ExcelExportService().createSheetForMap(workbook, entity, entityList, dataSet);
return workbook;
}For import, use the same method as above,change entity to Map
public class MapImportHandler extends ExcelDataHandlerDefaultImpl<Map<String, Object>> {
@Override
public void setMapValue(Map<String, Object> map, String originKey, Object value) {
if (value instanceof Double) {
map.put(getRealKey(originKey), PoiPublicUtil.doubleToString((Double) value));
} else {
map.put(getRealKey(originKey), value != null ? value.toString() : null);
}
}
private String getRealKey(String originKey) {
if (originKey.equals("name")) {
return "name";
}
if (originKey.equals("ID card")) {
return "IDcard";
}
if (originKey.equals("teacher motto")) {
return "content";
}
if (originKey.equals("subject")) {
return "subjectName";
}
if (originKey.equals("subject score")) {
return "subjectScore";
}
if (originKey.equals("child subject")) {
return "childSubjectName";
}
if (originKey.equals("child subject score")) {
return "childSubjectScore";
}
return originKey;
}
}###1.5.3 A little bit larger data(less than 100,000)
Still recommend the above method, but validation is not recommended. You can use the following parameter to speed up the time. As it is a one-time return, the amount is still a little large, so one-to-many is not supported
/**
* concurrent computing
*/
private boolean concurrentTask = false;For Export, Easypoi use SXSSFWorkbook by default, which not support some other formats, such as pictures. USE_SXSSF_LIMIT is used to decide when to use SXSSFWorkbook.
###1.5.4 Export/Import for big data(less than million), or need take a long time such as validation , or frequent operation which is easy to overflow memory
use sax, which more efficient and low memory, but less supported
/**
* Excel Import
* SAX: suitable for big data import, not support image
* Datasource: local file, not return validation result
* Import Field type: Integer, Long, Double, Date, String, Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @param handler
*/
public static void importExcelBySax(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
ImportParams params, IReadHandler handler) {
new SaxReadExcel().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, handler);
}Instead of dealing with callbacks after processing, we answer each line of processing to make sync to storage and handle exceptions faster.
@Test
public void test() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
params.setStartSheetIndex(1);
long start = new Date().getTime();
ExcelImportUtil.importExcelBySax(
new FileInputStream(
new File(FileUtilTest.getWebRootPath("import/saxtest.xlsx"))),
Map.class, params,
//This is an anonymous class. It's not recommended. Please define your own class for better management and use generics parameter
new IReadHandler<Map>() {
@Override
public void handler(Map o) {
System.out.println(o);
}
//will be called after all data is executed
@Override
public void doAfterAll() {
System.out.println("All done---------");
}
});
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}For big data, processing part by part is recommended, which can stabilize the CPU and memory within a certain range
new IReadHandler<Map>() {
private List list = new ArrayList();
@Override
public void handler(Map o) {
list.add(o);
if(list.size == 1000){
handlerData();
}
}
//will be called after all data is executed
@Override
public void doAfterAll() {
handlerData();
}
private void handlerData(){
//save or other operation
save(list);
list.clear();
}
});###1.5.5 big big data (over million)
CSV is recommended, which is also fairly fast to read millions and low memory usage.
/**
* CSV import: suitable for million data
* Datasource: IO stream, not return validation result
* Import Field type: Integer, Long, Double, Date, String, Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
*/
public static <T> List<T> importCsv(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
CsvImportParams params) {
return new CsvImportService().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, null);
}
/**
* CSV import: suitable for million data
* Datasource: IO stream, not return validation result
* Import Field type: Integer, Long, Double, Date, String, Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
*/
public static void importCsv(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
CsvImportParams params, IReadHandler readHandler) {
new CsvImportService().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, readHandler);
}
/**
* @param params CSV param entity
* @param pojoClass CSV object Class
* @param dataSet CSV object data List
*/
public static void exportCsv(CsvExportParams params, Class<?> pojoClass,
Collection<?> dataSet, OutputStream outputStream) {
new CsvExportService().createCsv(outputStream, params, pojoClass, dataSet);
}
/**
* Create the Excel according to the Map
*
* @param params CSV param entity
* @param entityList Map entity list
* @param dataSet CSV object data List
*/
public static void exportCsv(CsvExportParams params, List<ExcelExportEntity> entityList,
Collection<?> dataSet, OutputStream outputStream) {
new CsvExportService().createCsvOfList(outputStream, params, entityList, dataSet);
}###1.5.6 When to use Template
- Complex styles
- Complex format
- Multiple excel splicin
- Lazy to write code
#2.Excel
##2.1 Excel Import/Export
Excel import and export is the core function of Easypoi, mainly including three modes:
- Annotation
- Template
- HTML
Following is the detail for the three modes.
##2.2 Annotation
###Annotation Introduct
Easypoi is originated from Excel import and export. The original template was the correspondence between entity and Excel: model-row, field-col. So we can easily import and export Excel by using annotations. After a period of development, Easypoi now has five annotitions:
- @Excel - act on field, it's a description for one Excel column
- @ExcelCollection - collection, mainly for one-to-many exports, such as a teacher for more than one subject, the subject can be represented by a collection
- @ExcelEntity - entity to be exported, but it has not much practical meaning, just tells the system that the object also has exported fields.
- @ExcelIgnore - act on fields which indicates the field is ignored to be exported.
- @ExcelTarget - act on the outermost layer, describing the ID of the object so that an object can be processed differently for different exports
The ID usage for @ExcelTarget:
@ExcelTarget("major")
public class TeacherEntity implements java.io.Serializable {
/** name */
@Excel(name = "MajorTeacher_major, SubstituteTeacher_substitute", orderNum = "1", mergeVertical = true,needMerge=true,isImportField = "true_major,true_substitute")
private String name;@ExcelTarget("major"), it means that the TeacherEntity can process differently according to the value of ExcelTarget. For example, when @ExcelTarget("major"), the name of TeacherEntity will be MajorTeacher; for @ExcelTarget("substitute"), the name is SubstituteTeacher. It's similar for ExcelEntity and ExcelCollection.
###@Excel
This annotition is mandatory. You need to be familiar with this annotition which covers the common excel requirements. So it's enough for simple requirement. It mainly deals with the following parts: basic, image, time and merge. The usage of name_id is same with @ExcelTarget ID mentioned above.
| Property | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | null | clolumn name, support name_id |
| needMerge | boolean | fasle | Merge cells vertically(used to the single cell in the list and merge multiple rows created by the list) |
| orderNum | String | "0" | column sorting, support name_id |
| replace | String[] | {} | values replace export is {a_id,b_id}, import is on the contrary |
| savePath | String | "upload" | save path of imported file, default is upload/className/ IconEntity is upload/Icon/ |
| type | int | 1 | export type: 1 text, 2 image, 3 function, 10 number |
| width | double | 10 | column width |
| isStatistics | boolean | fasle | Automatic statistics, add another line to sum all the data[this processing will swallow the exception, please note this] |
| isHyperlink | boolean | false | Hyperlink |
| isImportField | boolean | true | Field verification, if the field not exists in the imported excel, then import failed. support name_id |
| exportFormat | String | "" | Export time format, according to "" or not to determine whether to format the date |
| importFormat | String | "" | Import time format |
| format | String | "" | time format, set up both Export and Import |
| databaseFormat | String | "yyyyMMddHHmmss" | Export time format, for string type, used to convert time format, Date type is no need. |
| numFormat | String | "" | number formatting, the parameter is Pattern and the object is DecimalFormat |
| imageType | int | 1 | export/import type: 1 read from file, 2 read from database |
| suffix | String | "" | for example %, 90 to 90% |
| isWrap | boolean | true | linefeed, that is \n |
| mergeRely | int[] | {} | dependencies of Merge cells, For example, if the second column is merged based on the first column, then {0} is ok |
| mergeVertical | boolean | fasle | vertically merge cells with the same content |
| fixedIndex | int | -1 | column number, for the case of having same column names to ignore the name |
| isColumnHidden | boolean | false | export hidden columns |
###@ExcelCollection
The annotation of one-to-many collection
| Property | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | String | null | id for name_id |
| name | String | null | column name, support name_id |
| orderNum | int | 0 | column sorting, support name_id |
| type | Class<?> | ArrayList.class | create object when imported |
###@ExcelEntity
To mark whether the entiy to be exported, is generally an internal attribute class, it determines whether the tag continues to penetrate. Also, you can customize the internal id of @ExcelEntity.
| Property | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | String | null | id for name_id |
###@ExcelIgnore
Used to ignore a property, Mostly used in circular references
###@ExcelTarget
Act on the outmost entity, define an annotation to the entity, as well as some general settings
| Property | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | String | null | id for name_id |
| height | double | 10 | rows height |
| fontSize | short | 11 | font size |
#2.3 Import/Export Annotation
###2.3.1 Define objects
Let's practice the above annotations with Luffy.
One day, the teacher called luffy to the office and assigned him a task to make a report using Excel. The detail requirement is to export the student information of the class from the education platform, including name, gender, date of birth and date of arrival. Luffy planned to use Easypoi to realize it. Following is the detail realization:
Firstly, define an export object, _ to save space, ignore getter、setter_
public class StudentEntity implements java.io.Serializable {
/**
* id
*/
private String id;
/**
* student name
*/
@Excel(name = "name", height = 20, width = 30)
private String name;
/**
* gender
*/
@Excel(name = "gender", replace = { "male_1", "female_2" })
private int gender;
@Excel(name = "birthday", databaseFormat = "yyyyMMddHHmmss", format = "yyyy-MM-dd", width = 20)
private Date birthday;
@Excel(name = "registerDate", databaseFormat = "yyyyMMddHHmmss", format = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date registerDate;
}The four columns are student name, student gender, date of birth and date of register. For student name, we define row height and width of the column; For the gender, we make a conversion because the type stored in the database is number; For two dates, we format the output; Then, we have completed the requirement of the Excel, just output the sudent list. Generate excel code is as follows:
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("Computer class one","Student"),
StudentEntity .class, list);In this way, we get an excel in Java, and then we get final excel by outputting it.
###2.3.2 Collection
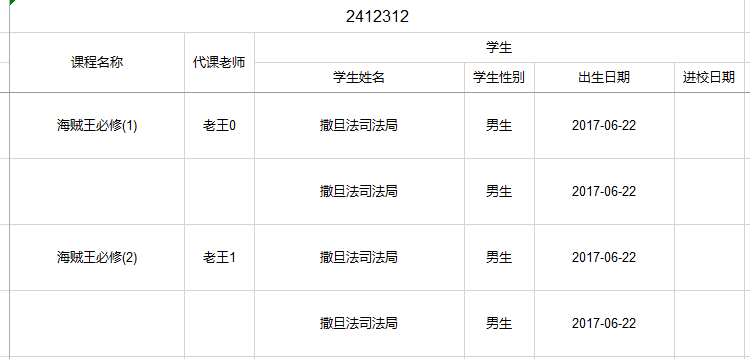
Luffy quickly completed the teacher's task, only spent a cup of coffee time. But after a while, he was called by the teacher again who arranged another task for him: report the courses and the students who choose the courses and also the corresponding teachers of the courses. The task is the embodiment of one-to-many. Luffy quickly thought of Easypoi, where there is one-to-many export. Then he defined the entities: one course corresponds to one teacher one course corresponds to many students Following is the course entity:
@ExcelTarget("courseEntity")
public class CourseEntity implements java.io.Serializable {
/** primary key */
private String id;
/** course name */
@Excel(name = "course name", orderNum = "1", width = 25)
private String name;
/** teacher entity */
@ExcelEntity(id = "substitute")
private TeacherEntity substituteTeacher;
@ExcelCollection(name = "student", orderNum = "4")
private List<StudentEntity> students;
}teacher entity
@ExcelTarget("teacherEntity")
public class TeacherEntity implements java.io.Serializable {
private String id;
/** name */
@Excel(name = "MajorTeacher_major, SubstituteTeacher_substitute", orderNum = "1", isImportField = "true_major,true_substitute")
private String name;Here, one-to-many export is completed for the course entity which meet the teacher's requirment. Meanwhile, ordernum is used to sort the columns. The export code is as follows:
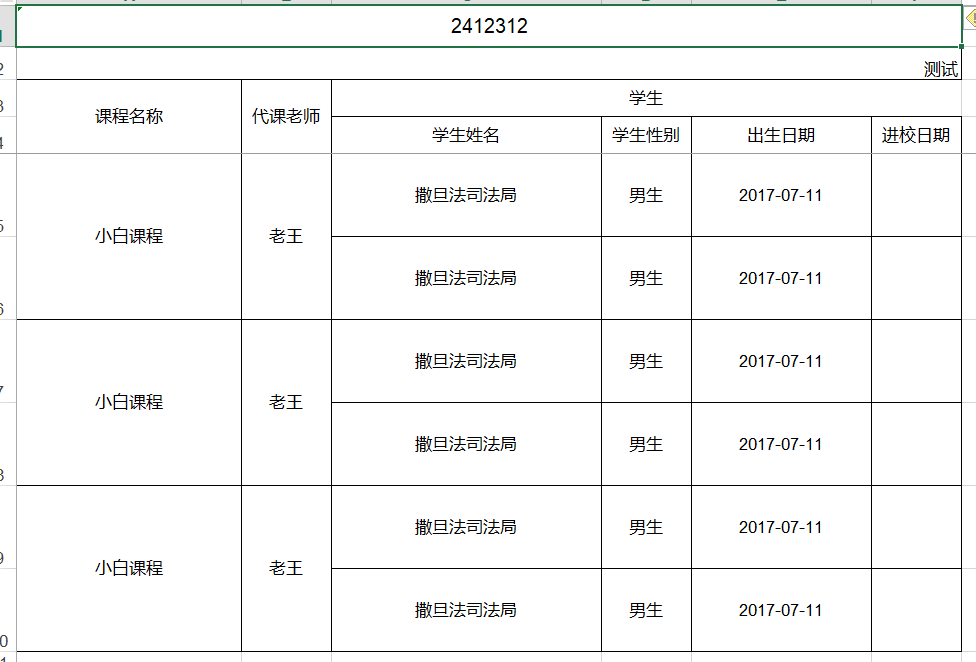
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("2412312", "测试", "测试"),
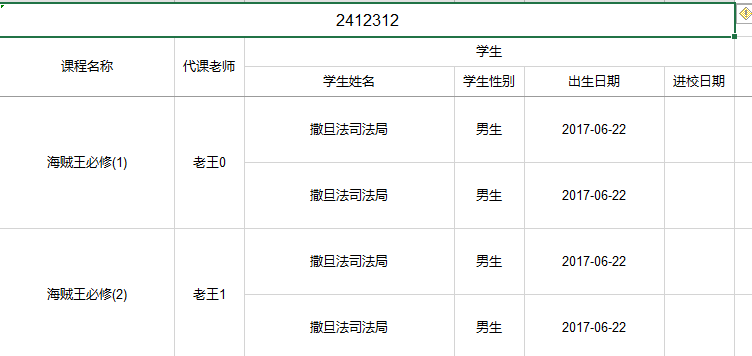
CourseEntity.class, list);Effect Picture 2.3.2-1 But the course name and substitute teacher are not merged, which is not beautiful. Luffy has decisively added the needmerge attribute to the course name and substitute teacher, and then the cell can be merged.
/** course name */
@Excel(name = "course name", orderNum = "1", width = 25,needMerge = true)
private String name;
//--------------------------------
/** name */
@Excel(name = "MajorTeacher_major, SubstituteTeacher_substitute", orderNum = "1",needMerge = true, isImportField = "true_major,true_substitute")Effect Picture2.3.2-2 With this, luffy has completed the teacher's task perfectly.
###2.3.3 Image Export
Easypoi provides two kinds of image export methods.
@Excel(name = "company logo", type = 2, width = 40, height = 20, imageType = 1)
private String companyLogo;- type=2 indicates that the field type is imge; imageType=1 (default value, you can leave it blank), indicates that read from file, the filed type is string, support both relative path and absolute path, absolute path is high priority.
@Excel(name = "company logo", type = 2 ,width = 40, height = 20, imageType = 2)
private byte[] companyLogo;- imageType=2, indicates that read from database or already have completed reading, the filed type is byte array.
Width and height is recommended for imge cell, will scale 100% to the cell size, not the original size
List<CompanyHasImgModel> list;
@Before
public void initData() {
list = new ArrayList<CompanyHasImgModel>();
list.add(new CompanyHasImgModel("Alibaba", "imgs/company/alibaba.png", "Zhejiang, China"));
list.add(new CompanyHasImgModel("Tencent", "http://www.tencent.com/img/index/tencent_logo.png", "Shenzhen, China"));
list.add(new CompanyHasImgModel("Baidu", "https://www.baidu.com/img/bd_logo1.png", "Beijing, China"));
}
@Test
public void exportCompanyImg() throws Exception {
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams(), CompanyHasImgModel.class, list);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/ExcelExportHasImgTest.exportCompanyImg.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}Effect Picture
###2.3.4 Excel Import
The configuration of annotation-based import is the same as export, but the way is reversed. For example, when the replacement type(male_1) is exported, 1 is replaced by male, 2 is replaced by female, and when imported, it is reversed: male becomes 1, the female becomes 2. It's similar for the date type. When exported, date is formatted as "2017-8-25" when imported, "2017-8-25" is formated as date type.
Following is the basic code of import; the usage of annotation is same with export, will not repeat here.
@Test
public void test2() {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
params.setHeadRows(1);
long start = new Date().getTime();
List<MsgClient> list = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(
new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/ExcelExportMsgClient.xlsx")),
MsgClient.class, params);
System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - start);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(list.get(0)));
}For ImportParams parameter
| Property | Type | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| titleRows | int | 0 | number of title rows |
| headRows | int | 1 | number of heading rows |
| startRows | int | 0 | the distance between the true value of the field and the column title |
| keyIndex | int | 0 | set up the primary key.If the cell has no value, skip it; or assume that this is the value in the list, this column must have a value, otherwise it is considered as invalid data |
| startSheetIndex | int | 0 | sheet position to start reading |
| sheetNum | int | 1 | the number of sheets to be read |
| needSave | boolean | false | whether to save the uploaded excel |
| needVerfiy | boolean | false | whether to verify the uploaded excel |
| saveUrl | String | "upload/excelUpload/" | the directory to save the uploaded Excel, for example, the saved directory for TestEntity is upload/excelUpload/Test/yyyyMMddHHmss_12345 nameTime_five random number |
| verifyHanlder | IExcelVerifyHandler | null | custom interface for hadling verification |
| lastOfInvalidRow | int | 0 | invalid rows in the last, unread rows |
| readRows | int | 0 | manually control the read rows number |
| importFields | String[] | null | validate template of the data on import to determine if Excel is correct |
| keyMark | String | ":" | Key-Value tag, this is as Key, the next Cell as Value; and if multiple, change to ArrayList |
| readSingleCell | boolean | false | scan Excel globally according to the key-value rule, but skip List reading to improve performance; only support titleRows + headRows + startRows and lastOfInvalidRow |
| dataHanlder | IExcelDataHandler | null | the data processing interface, this's the main one, replace and format is all behind this. |
###2.3.5 Small feature of Excel Import
-
Read the specified sheet For example, to read the second sheet, just set startsheetindex=1
-
How many sheets to read If read the first two sheets, then set sheetNum=2
-
Read the second to fifth sheet Set startSheetIndex=1 and sheetNum=4
-
Read all sheets Set a bigger number for sheetNum
-
Save Excel Set needVerfiy=true,the default directory is upload/excelUpload/Test/yyyyMMddHHmss_34587 NameTime_Five random number For custom directory, just modify saveUrl, which is also the saved path of the uploaded image.
-
Determine whether an excel is legal or not
The values set for importFields, show the fields that must be included in the header. If one of the fields is missing, it is illegal to import.
###2.3.6 Image Import
The configuration is the same with Image Export, but need set the saved path(saveUrl).
-
saveUrl, default is "upload/excelUpload", and can be modified manually
Example:
@Test
public void test() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setNeedSave(true);
List<CompanyHasImgModel> result = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(
new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/imgexcel.xls")),
CompanyHasImgModel.class, params);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(result.get(i)));
}
Assert.assertTrue(result.size() == 4);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}The import logs
16:35:43.081 [main] DEBUG c.a.e.e.imports.ExcelImportServer - Excel import start, class is class cn.afterturn.easypoi.test.entity.img.CompanyHasImgModel
16:35:43.323 [main] DEBUG c.a.e.e.imports.ExcelImportServer - start to read excel by is ,startTime is 1503650143323
16:35:43.344 [main] DEBUG c.a.e.e.imports.ExcelImportServer - end to read excel by is ,endTime is 1503650143344
16:35:43.429 [main] DEBUG c.a.e.e.imports.ExcelImportServer - end to read excel list by pos ,endTime is 1503650143429
cn.afterturn.easypoi.test.entity.img.CompanyHasImgModel@1b083826[companyName=Alibaba,companyLogo=imgs/company/alibaba.png,companyAddr=Zhejiang, China]
cn.afterturn.easypoi.test.entity.img.CompanyHasImgModel@105fece7[companyName=Tencent,companyLogo=imgs/company/tencent_logo.png,companyAddr=Shenzhen, China]
cn.afterturn.easypoi.test.entity.img.CompanyHasImgModel@3ec300f1[companyName=Baidu,companyLogo=imgs/company/baidu_logo.png,companyAddr=Beijing, China]###2.3.7 Multiple Sheets Export
At present, there are many export ways of single Sheet and single Class, but the way of multiple sheets is still blank. Here is an explanation: Basically, ExportParams is used for parameter configuration. We need to define a basic configuration object for the the multiple Sheet export.
public class ExportView {
public ExportView(){
}
private ExportParams exportParams;
private List<?> dataList;
private Class<?> cls;
public ExportParams getExportParams() {
return exportParams;
}
public void setExportParams(ExportParams exportParams) {
this.exportParams = exportParams;
}
public Class<?> getCls() {
return cls;
}
public void setCls(Class<?> cls) {
this.cls = cls;
}
public List<?> getDataList() {
return dataList;
}
public void setDataList(List<?> dataList) {
this.dataList = dataList;
}
public ExportView(Builder builder) {
this.exportParams = builder.exportParams;
this.dataList = builder.dataList;
this.cls = builder.cls;
}
public static class Builder {
private ExportParams exportParams=null;
private List<?> dataList=null;
private Class<?> cls=null;
public Builder() {
}
public Builder exportParams(ExportParams exportParams) {
this.exportParams = exportParams;
return this;
}
public Builder dataList(List<?> dataList) {
this.dataList = dataList;
return this;
}
public Builder cls(Class<?> cls) {
this.cls = cls;
return this;
}
public ExportView create() {
return new ExportView(this);
}
}
}ExportView mainly has three attributes: // Used to configure the export
- ExportParams exportParams // Corresponding to the datalist of Object Instance
- List<?> dataList // Corresponding to the class
- Class<?> cls
Generics are not used here, because when multiple sheets are exported, different annotation objects will be referenced;
Define a collection of basic configurations
public class ExportMoreView {
private List<ExportView> moreViewList=Lists.newArrayList();
public List<ExportView> getMoreViewList() {
return moreViewList;
}
public void setMoreViewList(List<ExportView> moreViewList) {
this.moreViewList = moreViewList;
}
}Finally, configure and parse the entire collection in the implement method
List<Map<String, Object>> exportParamList=Lists.newArrayList();
// This line is mainly used to obtain business data. Please modify and adjust it according to the specific situation
ExportMoreView moreView=this.getBaseTransferService().mergeExportView(templateTypeCode);
// Iterate over the export object to write the corresponding configuration to the actual
for(ExportView view:moreView.getMoreViewList()){
Map<String, Object> valueMap=Maps.newHashMap();
valueMap.put(NormalExcelConstants.PARAMS,view.getExportParams());
valueMap.put(NormalExcelConstants.DATA_LIST,view.getDataList());
valueMap.put(NormalExcelConstants.CLASS,view.getCls());
exportParamList.add(valueMap);
}
// Implement export configuration
modelMap.put(NormalExcelConstants.FILE_NAME,new DateTime().toString("yyyyMMddHHmmss"));
// Put the transformed configuration into the export
modelMap.put(NormalExcelConstants.MAP_LIST,exportParamList);
return NormalExcelConstants.JEECG_EXCEL_VIEW;
If not in the MVC way, please configure the transformation in the following way:
##2.4 Annotation variant - freer export
One day, the teacher asked luffy to export the overall information of the class.
@Excel(name = "name", height = 20, width = 30, isImportField = "true_st")
private String name;
@Excel(name = "gender", replace = { "male_1", "female_2" }, isImportField = "true_st")
private int sex;
@Excel(name = "birthday", databaseFormat = "yyyyMMddHHmmss", format = "yyyy-MM-dd", isImportField = "true_st", width = 20)
private Date birthday;
@Excel(name = "registerday", databaseFormat = "yyyyMMddHHmmss", format = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date registrationDate;Luffy quickly done by usine the above knowledge. Then, again, the teacher asked Luffy to export the information except birthday. (Feel helpless for the teacher's requirement). Luffy created another bean.
@Excel(name = "name", height = 20, width = 30, isImportField = "true_st")
private String name;
@Excel(name = "gender", replace = { "male_1", "female_2" }, isImportField = "true_st")
private int sex;
@Excel(name = "registerday", databaseFormat = "yyyyMMddHHmmss", format = "yyyy-MM-dd")
private Date registrationDate;Although solves the teacher's needs, it is not a perfect solution. Here is a freer solution.
For annotation export, the model and annotation must be prepared. Each exported excel is fixed, and the exported columns cannot be controlled dynamically. Although the case can be processed by ID, the freedom is far from enough. Here is a variant support(List), which basically supports all functions of annotation
For Export based on List, ExcelExportEntity is an entity translated by annotation processing, and which is almost the same with annotation, so if we want to dynamically customize the export column, we just need to dynamically assemble ExcelExportEntity. Following is the entity:
/**
* If it is Map Export, this is the key of the Map
*/
private Object key;
private double width = 10;
private double height = 10;
/**
* Image type: 1 for file, 2 for database
*/
private int exportImageType = 0;
/**
* sort order
*/
private int orderNum = 0;
/**
* linefeed, that is \n
*/
private boolean isWrap;
/**
* whether to merge
*/
private boolean needMerge;
/**
* mergeVertical
*/
private boolean mergeVertical;
/**
* merge dependecy
*/
private int[] mergeRely;
/**
* suffix
*/
private String suffix;
/**
* Statistics
*/
private boolean isStatistics;
private String numFormat;
private List<ExcelExportEntity> list;Almost one-to-one correspondence with annotation, List list this is a corresponding one to many export, which is equivalent to a collection. Other exports are basically consistent with the annotation
Follolwing is the demo:
public void test() {
try {
List<ExcelExportEntity> entity = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
//Construction entity is equate to @Excel
ExcelExportEntity excelentity = new ExcelExportEntity("name", "name");
excelentity.setNeedMerge(true);
entity.add(excelentity);
entity.add(new ExcelExportEntity("gender", "sex"));
excelentity = new ExcelExportEntity(null, "students");
List<ExcelExportEntity> temp = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
temp.add(new ExcelExportEntity("name", "name"));
temp.add(new ExcelExportEntity("gender", "sex"));
//List is equate to @ExcelCollection
excelentity.setList(temp);
entity.add(excelentity);
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
//Just put our constructed bean into params
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("test", "test"), entity,
list);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/ExcelExportForMap.tt.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Luffy changed the previous code to following:(The core code, which are basically corresponding to annotation)
List<ExcelExportEntity> beanList = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
beanList .add(new ExcelExportEntity(new ExcelExportEntity("name", "name"));
beanList .add(new ExcelExportEntity("gender", "sex"));
beanList .add(new ExcelExportEntity("registerday", "registrationDate"));
if(needBirthday()){
beanList .add(new ExcelExportEntity("birthday", "birthday"));
}
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(new ExportParams("test", "test"), beanList, list);Finally, Luffy used the same code to perfectly meet the different needs of the teacher.
##2.5 Map导入,自由发挥
这天,老师把路飞叫到办公室,总是被叫,能者的悲哀啊,让他临时导入一批数据,到数据库,但是中间需要处理一些字段逻辑没办法直接导入到数据库, 这时路飞首先想到构造一个bean然后标记注解,导入处理对象,但是想想一次的对象太过于浪费,不如用map试试,获取map处理map也是一样的 导入的逻辑就变成了
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setDataHanlder(new MapImportHanlder());
long start = new Date().getTime();
List<Map<String, Object>> list = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(
new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/check.xls")), Map.class, params);导入后,处理每个map,然后入库完美的解决了老师的需求,简单更快捷,和bean导入基础没有区别,省去了bean的构造时间
PS:这个作者也只是在临时方案中或者一次性活当中使用,一般还是推荐注解这种方式,拥有更高的代码阅读性 !!!测试了时间的,最好导入使用文本格式,可以获取时间格式可能无法获取
##2.6 Excel的样式自定义
"路飞,来办公室一趟",就这样路飞又被叫到了办公室,这次老师的需求是,想要一个漂亮点的Excel,希望路飞可以点缀下Excel,思来想去还是需要用poi的style来解决,但是如果每个都写style是不是太麻烦,而且Excel的styler数量是有限制的,这里就需要尽量复用已经创造的style,看看之前的Excel表格,大体上可以分为[标题,表头,表体],那可以说的就是创建一个接口每次调用这三个接口就可以了不说干就干
public interface IExcelExportStyler {
/**
* 列表头样式
* @param headerColor
* @return
*/
public CellStyle getHeaderStyle(short headerColor);
/**
* 标题样式
* @param color
* @return
*/
public CellStyle getTitleStyle(short color);
/**
* 获取样式方法
* @param Parity
* @param entity
* @return
*/
public CellStyle getStyles(boolean Parity, ExcelExportEntity entity);
}实现类尽量复用已经创建的Styler,切记
这样路飞先造了一个带边框的styler ,ExcelExportStylerBorderImpl
效果如下
客官看到这里应该就大体理解了我们的实现方法了吧, 最后路飞实现了一个复杂的按照老师要求的样式交差了
styler接口用法 上面两个表头和标题样式不用解释 后面这个是传入当前列的以及奇偶行,用户可以根据需求实现业务,包括去掉Excel的小箭头(也就是设置数字为数字格式的Cell),完成居中,字体等等各式各样的需求 但是这里无法实现特别没的Excel,如果有这种需求可以使用模板来实现,在Excel点点就可以完美实现
##2.7 如何自定义数据处理
导入导出总有一些自定义格式转换,EasyPoi虽然定义了很多服务,但是也无法满足所有客户的需求,这个时候就需要咱们自己定义数据处理 EasyPoi提供了
/**
* Excel 导入导出 数据处理接口
*
* @author JueYue
* 2014年6月19日 下午11:59:45
*/
public interface IExcelDataHandler<T> {
/**
* 导出处理方法
*
* @param obj
* 当前对象
* @param name
* 当前字段名称
* @param value
* 当前值
* @return
*/
public Object exportHandler(T obj, String name, Object value);
/**
* 获取需要处理的字段,导入和导出统一处理了, 减少书写的字段
*
* @return
*/
public String[] getNeedHandlerFields();
/**
* 导入处理方法 当前对象,当前字段名称,当前值
*
* @param obj
* 当前对象
* @param name
* 当前字段名称
* @param value
* 当前值
* @return
*/
public Object importHandler(T obj, String name, Object value);
/**
* 设置需要处理的属性列表
* @param fields
*/
public void setNeedHandlerFields(String[] fields);
/**
* 设置Map导入,自定义 put
* @param map
* @param originKey
* @param value
*/
public void setMapValue(Map<String, Object> map, String originKey, Object value);
/**
* 获取这个字段的 Hyperlink ,07版本需要,03版本不需要
* @param creationHelper
* @param obj
* @param name
* @param value
* @return
*/
public Hyperlink getHyperlink(CreationHelper creationHelper, T obj, String name, Object value);
}简单的使用方法如下
CourseHandler hanlder = new CourseHandler();
hanlder.setNeedHandlerFields(new String[] { "课程名称" });
exportParams.setDataHandler(hanlder);我们自己实现以下这个类,也可以继承ExcelDataHandlerDefaultImpl ,避免实现多余的接口 setNeedHandlerFields 这个是需要我们自己处理的字段,需要手动设置
让我们看一个demo
public class MapImportHandler extends ExcelDataHandlerDefaultImpl<Map<String, Object>> {
@Override
public void setMapValue(Map<String, Object> map, String originKey, Object value) {
if (value instanceof Double) {
map.put(getRealKey(originKey), PoiPublicUtil.doubleToString((Double) value));
} else {
map.put(getRealKey(originKey), value != null ? value.toString() : null);
}
}
private String getRealKey(String originKey) {
if (originKey.equals("交易账户")) {
return "accountNo";
}
if (originKey.equals("姓名")) {
return "name";
}
if (originKey.equals("客户类型")) {
return "type";
}
return originKey;
}
}这里我们在map导入的时候把map的key给转了,从中文转为习惯的英文
##2.8 Excel导入校验
校验,是一个不可或缺的功能,现在java校验主要是JSR 303 规范,实现方式主流的有两种
- Hibernate Validator
- Apache Commons Validator
这个EasyPoi没有限制,只要你防止一个实现丢到maven中就可以了,但是Hibernate Validator用的貌似多一些 之前的版本EasyPoi有定义自己的实现,但是后来抛弃了,没有必要造这种轮子,这个了功能已经够丰富了
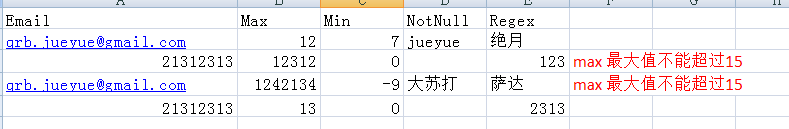
对象
EasyPoi的校验使用也很简单,对象上加上通用的校验规则或者这定义的这个看你用的哪个实现 然后params.setNeedVerfiy(true);配置下需要校验就可以了 看下具体的代码
/**
* Email校验
*/
@Excel(name = "Email", width = 25)
private String email;
/**
* 最大
*/
@Excel(name = "Max")
@Max(value = 15,message = "max 最大值不能超过15" ,groups = {ViliGroupOne.class})
private int max;
/**
* 最小
*/
@Excel(name = "Min")
@Min(value = 3, groups = {ViliGroupTwo.class})
private int min;
/**
* 非空校验
*/
@Excel(name = "NotNull")
@NotNull
private String notNull;
/**
* 正则校验
*/
@Excel(name = "Regex")
@Pattern(regexp = "[\u4E00-\u9FA5]*", message = "不是中文")
private String regex;这里的校验规则都是JSR 303 的,使用方式也是的,这里就不做解释了 然后使用方式是
@Test
public void basetest() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setNeedVerfiy(true);
params.setVerfiyGroup(new Class[]{ViliGroupOne.class});
ExcelImportResult<ExcelVerifyEntity> result = ExcelImportUtil.importExcelMore(
new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/verfiy.xlsx")),
ExcelVerifyEntity.class, params);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/ExcelVerifyTest.basetest.xlsx");
result.getWorkbook().write(fos);
fos.close();
for (int i = 0; i < result.getList().size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(result.getList().get(i)));
}
Assert.assertTrue(result.getList().size() == 1);
Assert.assertTrue(result.isVerfiyFail());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}***ExcelImportResult ***
我们会返回一个ExcelImportResult 对象,比我们平时返回的list多了一些元素
/**
* 结果集
*/
private List<T> list;
/**
* 是否存在校验失败
*/
private boolean verfiyFail;
/**
* 数据源
*/
private Workbook workbook;一个是集合,是一个是是否有校验失败的数据,一个原本的文档,但是在文档后面追加了错误信息
注意,这里的list,有两种返回
- 一种是只返回正确的数据
- 一种是返回全部的数据,但是要求这个对象必须实现IExcelModel接口,如下
IExcelModel
public class ExcelVerifyEntityOfMode extends ExcelVerifyEntity implements IExcelModel {
private String errorMsg;
@Override
public String getErrorMsg() {
return errorMsg;
}
@Override
public void setErrorMsg(String errorMsg) {
this.errorMsg = errorMsg;
}
}*IExcelDataModel 获取错误数据的行号
public interface IExcelDataModel {
/**
* 获取行号
* @return
*/
public int getRowNum();
/**
* 设置行号
* @param rowNum
*/
public void setRowNum(int rowNum);
}需要对象实现这个接口
每行的错误数据也会填到这个错误信息中,方便用户后面自定义处理 看下代码
@Test
public void baseModetest() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setNeedVerfiy(true);
ExcelImportResult<ExcelVerifyEntityOfMode> result = ExcelImportUtil.importExcelMore(
new FileInputStream(new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/verfiy.xlsx"))),
ExcelVerifyEntityOfMode.class, params);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/baseModetest.xlsx");
result.getWorkbook().write(fos);
fos.close();
for (int i = 0; i < result.getList().size(); i++) {
System.out.println(ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(result.getList().get(i)));
}
Assert.assertTrue(result.getList().size() == 4);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}IExcelVerifyHandler
加入上面的不满足你,你可以用接口实现自己的校验规则,比如唯一性校验,等等,需要返回错误信息和成功与否
public interface IExcelVerifyHandler<T> {
/**
* 导入校验方法
*
* @param obj
* 当前对象
* @return
*/
public ExcelVerifyHanlderResult verifyHandler(T obj);
}调用顺序是先通用的,再接口,到这里校验的就完整了,下面给大家看下错误的excel返回
##2.9 Excel 大数据读取
大数据量,避免内存溢出,以及提升读取效率,最好行数在10万行级别以上使用,否则我感觉意义不算大 ###2.9.1 ExceL by sax读取 by sax这个函数经过几轮修改,也差不多勉强到达可以用的环节了下面讲解下如何使用,修改来就该去就剩这一个方法了,不在返回数据用户自己实现IReadHandler来保存数据,不提供错误校验
/**
* Excel 通过SAX解析方法,适合大数据导入,不支持图片
* 导入 数据源本地文件,不返回校验结果 导入 字 段类型 Integer,Long,Double,Date,String,Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @param handler
*/
public static void importExcelBySax(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
ImportParams params, IReadHandler handler) {
new SaxReadExcel().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, handler);
}主要是自己实现IReadHandler,easypoi解析完每个对象都会调用,handler方法,全部解析完成后会调用doAfterAll 方法
public interface IReadHandler<T> {
/**
* 处理解析对象
* @param t
*/
public void handler(T t);
/**
* 处理完成之后的业务
*/
public void doAfterAll();
}- 不支持校验
- 不支持图片
- 不支持一对多
Demo如下,基本用法和其他的没啥去呗,自己处理handler就可以了
@Test
public void test() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
long start = new Date().getTime();
ExcelImportUtil.importExcelBySax(
new FileInputStream(
new File("import/ExcelExportMsgClient.xlsx")),
MsgClient.class, params, new IReadHandler<MsgClient>() {
@Override
public void handler(MsgClient o) {
System.out.println(ReflectionToStringBuilder.toString(o));
}
@Override
public void doAfterAll() {
}
});
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}###2.9.2 CSV导入 csv处理参考 ##7.1
##2.10 Excel大数据导出
大数据导出是当我们的导出数量在几万,到上百万的数据时,一次从数据库查询这么多数据加载到内存然后写入会对我们的内存和CPU都产生压力,这个时候需要我们像分页一样处理导出分段写入Excel缓解Excel的压力 EasyPoi提供的是两个方法 ***强制使用 xssf版本的Excel ***
/**
* @param entity
* 表格标题属性
* @param pojoClass
* Excel对象Class
* @param dataSet
* Excel对象数据List
*/
public static Workbook exportBigExcel(ExportParams entity, Class<?> pojoClass,
Collection<?> dataSet) {
ExcelBatchExportServer batachServer = ExcelBatchExportServer
.getExcelBatchExportServer(entity, pojoClass);
return batachServer.appendData(dataSet);
}
public static void closeExportBigExcel() {
ExcelBatchExportServer batachServer = ExcelBatchExportServer.getExcelBatchExportServer(null,
null);
batachServer.closeExportBigExcel();
}添加数据和关闭服务,关闭服务不是必须的,可以调也可以不掉 我们只需要for循环写入Excel就可以了
@Test
public void bigDataExport() throws Exception {
List<MsgClient> list = new ArrayList<MsgClient>();
Workbook workbook = null;
Date start = new Date();
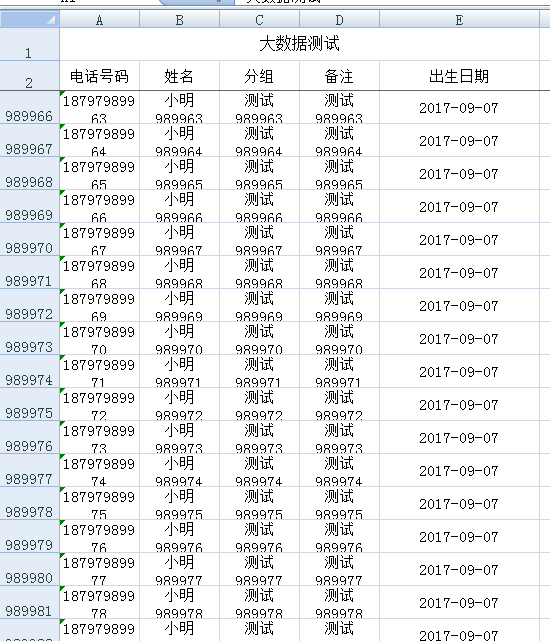
ExportParams params = new ExportParams("大数据测试", "测试");
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) { //一百万数据量
MsgClient client = new MsgClient();
client.setBirthday(new Date());
client.setClientName("小明" + i);
client.setClientPhone("18797" + i);
client.setCreateBy("JueYue");
client.setId("1" + i);
client.setRemark("测试" + i);
MsgClientGroup group = new MsgClientGroup();
group.setGroupName("测试" + i);
client.setGroup(group);
list.add(client);
if(list.size() == 10000){
workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportBigExcel(params, MsgClient.class, list);
list.clear();
}
}
ExcelExportUtil.closeExportBigExcel();
System.out.println(new Date().getTime() - start.getTime());
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/ExcelExportBigData.bigDataExport.xlsx");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}多次测试用时统计,速度还是可以接受的,^^
| 数据量 | 用时 | 文件大小 | 列数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100W | 16.4s | 24.3MB | 5 |
| 100W | 15.9s | 24.3MB | 5 |
| 200W | 29.5s | 48.5MB | 5 |
| 100W | 30.8s | 37.8MB | 10 |
| 200W | 58.7s | 76.1MB | 10 |
##2.11 导入获取Key-Value
from 3.0.1
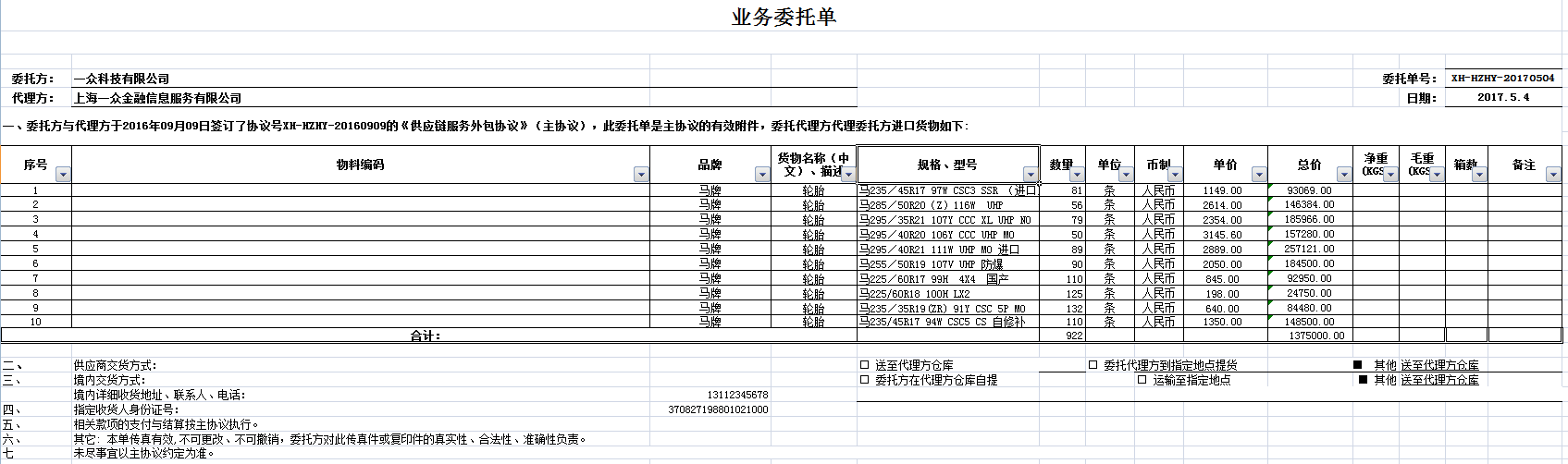
工作中是否会遇到导入读取一些特定的字段比如
@Test
public void test() {
try {
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setKeyMark(":");
params.setReadSingleCell(true);
params.setTitleRows(7);
params.setLastOfInvalidRow(9);
ExcelImportResult<Map> result = ExcelImportUtil.importExcelMore(
new File(PoiPublicUtil.getWebRootPath("import/业务委托单.xlsx")),
Map.class, params);
for (int i = 0; i < result.getList().size(); i++) {
System.out.println(result.getList().get(i));
}
Assert.assertTrue(result.getList().size() == 10);
System.out.println(result.getMap());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error(e.getMessage(),e);
}
}需要设置两个或者一个值 params.setKeyMark(":"); 判断一个cell是key的规则,可以自定义,默认就是 ":" params.setReadSingleCell(true); 是否需要读取这种单独的sql 读取完毕后,通过result.getMap() 就可以拿到自己想要的值了比如上面的Excel读取到的map就是
{境内详细收货地址、联系人、电话:=1.3112345678E10, 委托方:=一众科技有限公司, 代理方:=上海一众金融信息服务有限公司, 委托单号:=XH-HZHY-20170504, 日期:=2017.5.4, 供应商交货方式:=, 合计:=, 境内交货方式:=, 指定收货人身份证号:=3.7082719880102099E17}
这样就比较方便的处理较为复杂的Excel导入了
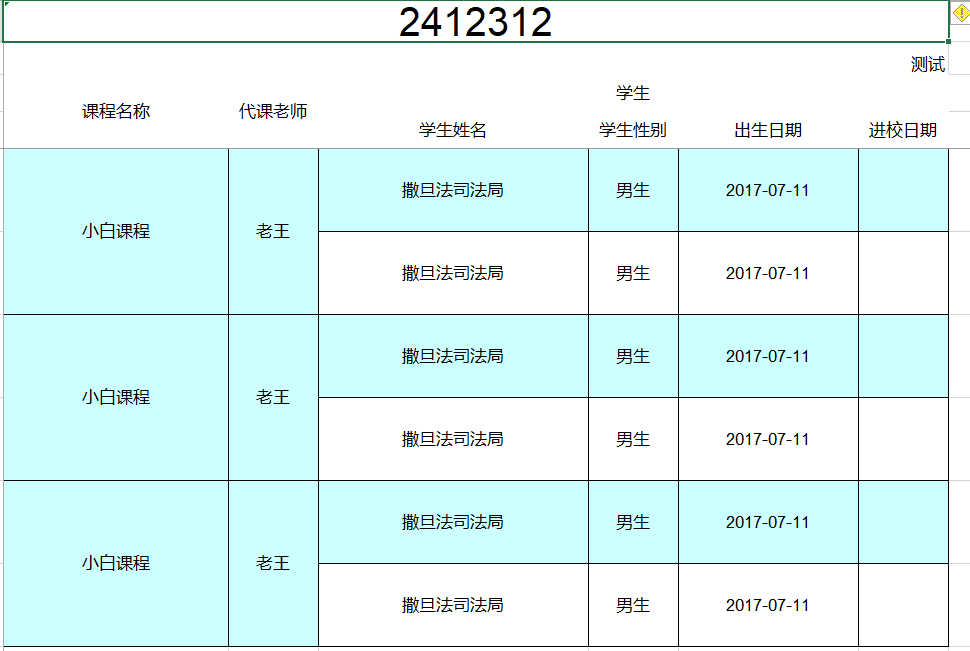
##2.12 groupname和ExcelEntity的name属性
之前一直没想好,双号表头如何处理数据,直到前几天突然想到了groupname这个属性,下面先介绍下这两个属性解决的问题,也是之前很多朋友问到的问题
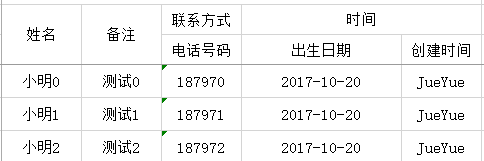
- 简单的groupname
比如这里的时间算是两个时间的聚合,单也是对象当中的元素而已,我们要导出这样的数据现在只要设置下groupname就可以了
@Excel(name = "电话号码", groupName = "联系方式", orderNum = "1")
private String clientPhone = null;
// 客户姓名
@Excel(name = "姓名")
private String clientName = null;
// 备注
@Excel(name = "备注")
private String remark = null;
// 生日
@Excel(name = "出生日期", format = "yyyy-MM-dd", width = 20, groupName = "时间", orderNum = "2")
private Date birthday = null;
// 创建人
@Excel(name = "创建时间", groupName = "时间", orderNum = "3")
private String createBy = null;这样就会把两个groupname合并到一起展示,使用也比较简单
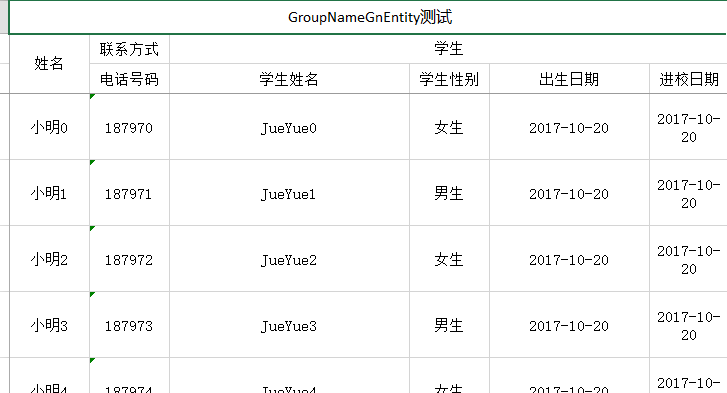
- ExcelEntity 一个对象在一起
假如我们需要一个对象属性统一在一起,name我们需要设置下这个对象的name属性,并且show=true 这两个是 且的关系 比如
@Excel(name = "电话号码", groupName = "联系方式", orderNum = "1")
private String clientPhone = null;
@Excel(name = "姓名")
private String clientName = null;
@ExcelEntity(name = "学生", show = true)
private GnStudentEntity studentEntity;学生对象的内部就是普通的注解
@Excel(name = "学生姓名", height = 20, width = 30, orderNum = "2")
private String name;
@Excel(name = "学生性别", replace = {"男_1", "女_0"}, suffix = "生", orderNum = "3")
private int sex;
@Excel(name = "出生日期", format = "yyyy-MM-dd", width = 20, orderNum = "4")
private Date birthday;
@Excel(name = "进校日期", format = "yyyy-MM-dd", orderNum = "5")
private Date registrationDate;使用起来还是很简单的,导入的话同样设置就可以获取到了
- 排序问题
导出时,表头双行显示,聚合,排序以最小的值参与总体排序再内部排序 导出排序跟定义了annotation的字段的顺序有关 可以使用a_id,b_id来确实是否使用 优先弱与 @ExcelEntity 的name和show属性
简单说就是先排外部顺序,再排内部顺序
##2.13 多线程导入基于ForkJoin @Since4.1
鉴于4.0已经开始使用jdk8了,我们的功能也是时候升级下了,现在导入支持了fork/join的线程支持,使用限制 1.因为是采用分隔读取的所以不支持一对多 2.4.1是不支持图片的 3.线程数我测试是根据CPU来的不知是否正确
使用方法很简单ImportParams 新加了两个参数,设置为true就可以了,critical是最新的分隔符,可以自定义下
/**
* 是否并行计算
*/
private boolean concurrentTask = false;
/**
* 最小截取大小
*/
private Integer critical = 1000;demo如下
@Test
public void testConCurrent() {
try {
Date start = new Date();
LOGGER.debug("start");
ImportParams params = new ImportParams();
params.setTitleRows(1);
params.setConcurrentTask(true);
List<MsgClient> result = ExcelImportUtil.importExcel(
new File(FileUtilTest.getWebRootPath("import/BigDataExport.xlsx")),
MsgClient.class, params);
LOGGER.debug("end,time is {}", ((new Date().getTime() - start.getTime()) / 1000));
Assert.assertTrue(result.size() == 200000);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
Assert.assertTrue(result.get(i).getClientName().equalsIgnoreCase("小明" + i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}我测试数据结果和正常读取的逾期是一直的
#3. Excel模板处理 ##3.1 模板 指令介绍
模板是处理复杂Excel的简单方法,复杂的Excel样式,可以用Excel直接编辑,完美的避开了代码编写样式的雷区,同时指令的支持,也提了模板的有效性 下面列举下EasyPoi支持的指令以及作用,最主要的就是各种fe的用法
- 空格分割
- 三目运算 {{test ? obj:obj2}}
- n: 表示 这个cell是数值类型 {{n:}}
- le: 代表长度{{le:()}} 在if/else 运用{{le:() > 8 ? obj1 : obj2}}
- fd: 格式化时间 {{fd:(obj;yyyy-MM-dd)}}
- fn: 格式化数字 {{fn:(obj;###.00)}}
- fe: 遍历数据,创建row
- !fe: 遍历数据不创建row
- $fe: 下移插入,把当前行,下面的行全部下移.size()行,然后插入
- #fe: 横向遍历
- v_fe: 横向遍历值
- !if: 删除当前列 {{!if:(test)}}
- 单引号表示常量值 '' 比如'1' 那么输出的就是 1
- &NULL& 空格
- ]] 换行符 多行遍历导出
- sum: 统计数据
整体风格和el表达式类似,大家应该也比较熟悉 采用的写法是{{}}代表表达式,然后根据表达式里面的数据取值
关于样式问题 easypoi不会改变excel原有的样式,如果是遍历,easypoi会根据模板的那一行样式进行复制
在cn.afterturn.easypoi.test.excel.template 这个目录下面 https://gitee.com/lemur/easypoi-test/tree/master/src/test/java/cn/afterturn/easypoi/test/excel/template
##3.2 基本导出
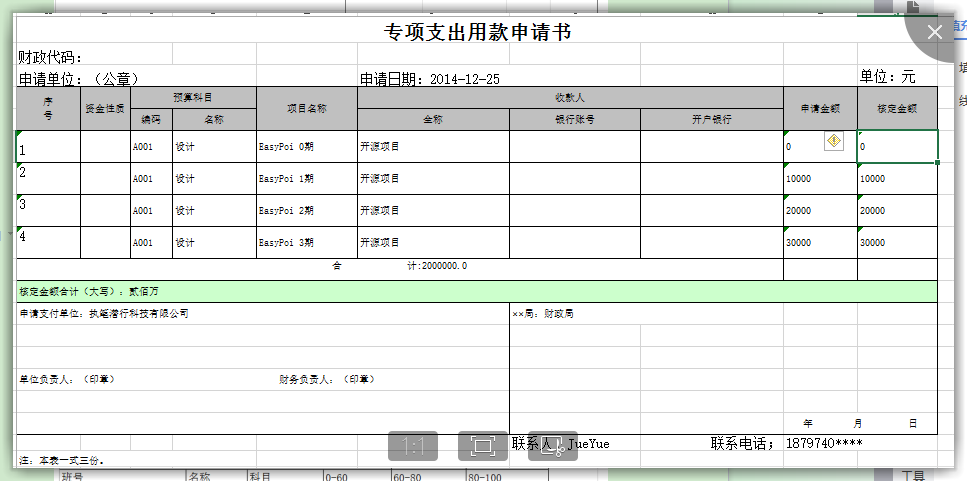
看一个常见的到处模板--专项支出用款申请书
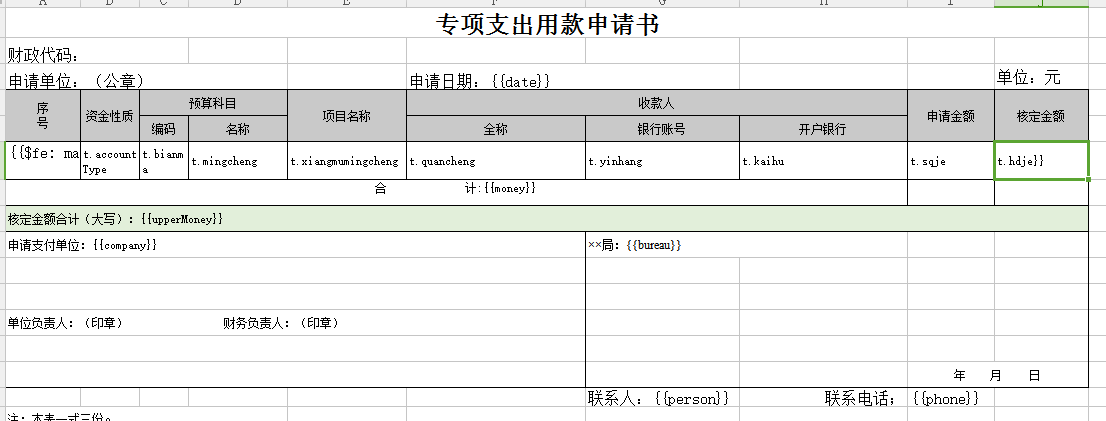
fe的写法 fe标志 冒号 list数据 单个元素数据(默认t,可以不写) 第一个元素 {{$fe: maplist t t.id }}
看下数据代码,主要是构造数据TemplateExportParams是主要的参数数据
@Test
public void fe_map() throws Exception {
TemplateExportParams params = new TemplateExportParams(
"WEB-INF/doc/专项支出用款申请书_map.xls");
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("date", "2014-12-25");
map.put("money", 2000000.00);
map.put("upperMoney", "贰佰万");
map.put("company", "执笔潜行科技有限公司");
map.put("bureau", "财政局");
map.put("person", "JueYue");
map.put("phone", "1879740****");
List<Map<String, String>> listMap = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
Map<String, String> lm = new HashMap<String, String>();
lm.put("id", i + 1 + "");
lm.put("zijin", i * 10000 + "");
lm.put("bianma", "A001");
lm.put("mingcheng", "设计");
lm.put("xiangmumingcheng", "EasyPoi " + i + "期");
lm.put("quancheng", "开源项目");
lm.put("sqje", i * 10000 + "");
lm.put("hdje", i * 10000 + "");
listMap.add(lm);
}
map.put("maplist", listMap);
Workbook workbook = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(params, map);
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/专项支出用款申请书_map.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}##3.3 模板当中使用注解
##3.4 图片导出
模板图片导出,没有注解导出图片那么容易,但也不算复杂,构建一个ImageEntity 设置下高宽,地址或者byte[]及可以了
ImageEntity image = new ImageEntity();
image.setHeight(200);
image.setWidth(500);
image.setUrl("imgs/company/baidu.png");具体的导出代码
@Test
public void one() throws Exception {
TemplateExportParams params = new TemplateExportParams(
"doc/exportTemp_image.xls", true);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
// sheet 2
map.put("month", 10);
Map<String, Object> temp;
for (int i = 1; i < 8; i++) {
temp = new HashMap<String, Object>();
temp.put("per", i * 10);
temp.put("mon", i * 1000);
temp.put("summon", i * 10000);
ImageEntity image = new ImageEntity();
image.setHeight(200);
image.setWidth(500);
image.setUrl("imgs/company/baidu.png");
temp.put("image", image);
map.put("i" + i, temp);
}
Workbook book = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcel(params, map);
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/exportTemp_image.xls");
book.write(fos);
fos.close();
}##3.5 clone sheet导出多个模板一致的表格 @Since 4.1
poi4.0支持了sheet clone功能,这个为我们的一个模板导出N个sheet提供了基础支持,鉴于此该功能面世,使用也相当简单
/**
* 导出文件通过模板解析只有模板,没有集合
* 每个sheet对应一个list,按照数量进行导出排序,key是sheet的NUM
* @param params
* 导出参数类
* @param map
* 模板集合
* @return
*/
public static Workbook exportExcelClone(Map<Integer, List<Map<String, Object>>> map,
TemplateExportParams params) {
return new ExcelExportOfTemplateUtil().createExcelCloneByTemplate(params, map);
}把自己需要导出很多份的数据组装到list里面统一个模板的map放到一个list,然后就是原始的模板sheetIndex,这样对比下来给你组装成你想要的,具体可以参考下demo
@Test
public void cloneTest() throws Exception {
TemplateExportParams params = new TemplateExportParams(
"doc/exportTemp.xls", true);
params.setHeadingRows(2);
params.setHeadingStartRow(2);
params.setStyle(ExcelStyleType.BORDER.getClazz());
List<Map<String, Object>> numOneList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
//sheet 1
map.put("year", "2013" + i);
map.put("sunCourses", list.size());
Map<String, Object> obj = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("obj", obj);
obj.put("name", list.size());
// sheet 2
map.put("month", 10);
Map<String, Object> temp;
for (int j = 1; j < 8; j++) {
temp = new HashMap<String, Object>();
temp.put("per", j * 10 + "---" + i);
temp.put("mon", j * 1000);
temp.put("summon", j * 10000);
map.put("i" + j, temp);
}
map.put(SHEET_NAME, "啊啊测试SHeet" + i);
numOneList.add(map);
}
List<Map<String, Object>> numTowList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
Map<String, Object> oneMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
oneMap.put("list", list);
oneMap.put(SHEET_NAME, "第二个测试SHeet" + i);
numTowList.add(oneMap);
}
// 把两个list 数据 put到对应的模板KEY 下面去
Map<Integer, List<Map<String, Object>>> realMap = new HashMap<>();
realMap.put(1, numOneList);
realMap.put(2, numTowList);
Workbook book = ExcelExportUtil.exportExcelClone(realMap, params);
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/exportCloneTemp.xls");
book.write(fos);
fos.close();
}##3.6 模板支持多层循环 @Since 4.1.1
模板嵌套,写法和之前没有什么改变,可以判断字段是不是集合然后进行遍历,并对非集合字段自行单元格合并
效果如下模板
#4.Excel&Html互转 ##4.1 Excel 的Html预览
Excel预览,这里支持了比较简单的预览,样式也都可以转换过去,支持03 和 更高版本 使用也是简单的很ExcelXorHtmlUtil.excelToHtml(params),也支持图片的预览,demo如下
/**
* 07 版本EXCEL预览
*/
@RequestMapping("07")
public void toHtmlOf07Base(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
ExcelToHtmlParams params = new ExcelToHtmlParams(WorkbookFactory.create(POICacheManager.getFile("exceltohtml/testExportTitleExcel.xlsx")));
response.getOutputStream().write(ExcelXorHtmlUtil.excelToHtml(params).getBytes());
}
/**
* 03 版本EXCEL预览
*/
@RequestMapping("03img")
public void toHtmlOf03Img(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, InvalidFormatException {
ExcelToHtmlParams params = new ExcelToHtmlParams(WorkbookFactory.create(POICacheManager.getFile("exceltohtml/exporttemp_img.xls")),true,"yes");
response.getOutputStream().write(ExcelXorHtmlUtil.excelToHtml(params).getBytes());
}返回一个string的html界面,输出到前台就可以了
##4.2 html转Excel更神奇的导出
这个是一个MM提出的需求,需求原因是,她要导出一个比较复杂的Excel,无论用模板还是注解都比较难实现,所以她想到了这个方案,然后就实现了如下的方法,我的使用方法如下 自己搞个html,然后用模板引擎,beetl,freemark等生成html,然后调用easypoi提供的方法转换成Excel,因为html的标签以及规则大家比Excel要熟悉的多,更容易编写复杂的table,然后easypoi转换成Excel再导出,麻烦了点,但是可以处理一些特定的情况,也同样生成两个版本的Excel都支持 使用demo
@Test
public void htmlToExcelByStr() throws Exception {
StringBuilder html = new StringBuilder();
Scanner s = new Scanner(getClass().getResourceAsStream("/html/sample.html"), "utf-8");
while (s.hasNext()) {
html.append(s.nextLine());
}
s.close();
Workbook workbook = ExcelXorHtmlUtil.htmlToExcel(html.toString(), ExcelType.XSSF);
File savefile = new File("D:\\home\\lemur");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\home\\lemur\\htmlToExcelByStr.xlsx");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
workbook = ExcelXorHtmlUtil.htmlToExcel(html.toString(), ExcelType.HSSF);
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\home\\lemur\\htmlToExcelByStr.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}
@Test
public void htmlToExcelByIs() throws Exception {
Workbook workbook = ExcelXorHtmlUtil.htmlToExcel(getClass().getResourceAsStream("/html/sample.html"), ExcelType.XSSF);
File savefile = new File("D:\\home\\lemur");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\home\\lemur\\htmlToExcelByIs.xlsx");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
workbook = ExcelXorHtmlUtil.htmlToExcel(getClass().getResourceAsStream("/html/sample.html"), ExcelType.HSSF);
fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\home\\lemur\\htmlToExcelByIs.xls");
workbook.write(fos);
fos.close();
}提供了流或者字符串的入参,内部都多了缓存,多次生成不会重复解析
#5.word模板处理 ##5.1 word模板导出
word模板和Excel模板用法基本一致,支持的标签也是一致的,仅仅支持07版本的word也是只能生成后缀是docx的文档,poi对doc支持不好,所以这里也就懒得支持了,支持表格和图片,具体demo如下
/**
* 简单导出包含图片
*/
@Test
public void imageWordExport() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("department", "Easypoi");
map.put("person", "JueYue");
map.put("time", format.format(new Date()));
WordImageEntity image = new WordImageEntity();
image.setHeight(200);
image.setWidth(500);
image.setUrl("cn/afterturn/easypoi/test/word/img/testCode.png");
image.setType(WordImageEntity.URL);
map.put("testCode", image);
try {
XWPFDocument doc = WordExportUtil.exportWord07(
"cn/afterturn/easypoi/test/word/doc/Image.docx", map);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/image.docx");
doc.write(fos);
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 简单导出没有图片和Excel
*/
@Test
public void SimpleWordExport() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("department", "Easypoi");
map.put("person", "JueYue");
map.put("time", format.format(new Date()));
map.put("me","JueYue");
map.put("date", "2015-01-03");
try {
XWPFDocument doc = WordExportUtil.exportWord07(
"cn/afterturn/easypoi/test/word/doc/Simple.docx", map);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/simple.docx");
doc.write(fos);
fos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}##5.2 单模板生成多页数据 应用场景,比如一个订单详情信息模板,但是有很多订单,需要导入到一个word里面
#6.PDF处理 //TODO 为完成
#7. CSV处理 ##7.1 CSV导入处理
导入提供两个方法,两个方法类似,都是基于注解或者Map,一个返回list,一个不返回list,数据量小用第一个,数据量大用第二个,推荐第二个,IReadHandler参考2.9方法是一一致的
/**
* Csv 导入流适合大数据导入
* 导入 数据源IO流,不返回校验结果 导入 字段类型 Integer,Long,Double,Date,String,Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
*/
public static <T> List<T> importCsv(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
CsvImportParams params) {
return new CsvImportService().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, null);
}
/**
* Csv 导入流适合大数据导入
* 导入 数据源IO流,不返回校验结果 导入 字段类型 Integer,Long,Double,Date,String,Boolean
*
* @param inputstream
* @param pojoClass
* @param params
* @return
*/
public static void importCsv(InputStream inputstream, Class<?> pojoClass,
CsvImportParams params, IReadHandler readHandler) {
new CsvImportService().readExcel(inputstream, pojoClass, params, readHandler);
}CsvImportParams 的参数描述如下
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| encoding | String | UTF8 | 文件编码 |
| spiltMark | String | , | 分隔符 |
| textMark | String | " | 字符串识别,可以去掉,需要前后一致 |
| titleRows | int | 0 | 表格头,忽略 |
| headRows | int | 1 | 标题 |
| startRows | int | 0 | 标题起忽略行数 |
| verifyGroup | Class[] | null | 校验,参考java validation |
| needVerify | boolean | false | 是否需要校验,默认false |
| verifyHandler | IExcelVerifyHandler | null | 自定义校验接口 |
| lastOfInvalidRow | int | 0 | 最后跳过行 |
| keyIndex | int | null | 重要字段,判断是否需要读取 |
demo如下,CsvImportParams.GBK需要指定文件编码,这个希望大家注意
@Test
public void test() {
try {
Date start = new Date();
LOGGER.debug("start");
CsvImportParams params = new CsvImportParams(CsvImportParams.GBK);
params.setTitleRows(1);
CsvImportUtil.importCsv(new FileInputStream(
new File(FileUtilTest.getWebRootPath("csv/BigDataExport.csv"))),
MsgClient.class, params, new IReadHandler() {
@Override
public void handler(Object o) {
}
@Override
public void doAfterAll() {
}
});
LOGGER.debug("end,time is {}", ((new Date().getTime() - start.getTime()) / 1000));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}##7.2 CSV导出
csv的导出基本上和excel的导出一致,大体参数也是一致的 CsvExportParams 的参数描述如下
| 属性 | 类型 | 默认值 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|---|
| encoding | String | UTF8 | 文件编码 |
| spiltMark | String | , | 分隔符 |
| textMark | String | " | 字符串识别,可以去掉,需要前后一致 |
| titleRows | int | 0 | 表格头,忽略 |
| headRows | int | 1 | 标题 |
| exclusions | String[] | 0 | 忽略的字段 |
| isCreateHeadRows | boolean | true | 创建表头 |
使用起来也十分简单,基本和excel保持了一直方式,一个是对象导出,一个是自由导出参考##2.6自由的导出,不同的是没有返回对象,需要自己把流传入,我给你直接写入,从速度和效率上来讲,速度远超excel
/**
* @param params 表格标题属性
* @param pojoClass Excel对象Class
* @param dataSet Excel对象数据List
*/
public static void exportCsv(CsvExportParams params, Class<?> pojoClass,
Collection<?> dataSet, OutputStream outputStream) {
new CsvExportService().createCsv(outputStream, params, pojoClass, dataSet);
}
/**
* 根据Map创建对应的Excel
*
* @param params 表格标题属性
* @param entityList Map对象列表
* @param dataSet Excel对象数据List
*/
public static void exportCsv(CsvExportParams params, List<ExcelExportEntity> entityList,
Collection<?> dataSet, OutputStream outputStream) {
new CsvExportService().createCsvOfList(outputStream, params, entityList, dataSet);
}一个简单的小demo
@Test
public void exportCsv() throws IOException {
List<MsgClient> list = new ArrayList<MsgClient>();
Date start = new Date();
CsvExportParams params = new CsvExportParams();
for (int i = 0; i < 500000; i++) {
MsgClient client = new MsgClient();
client.setBirthday(new Date());
client.setClientName("小明" + i);
client.setClientPhone("18797" + i);
client.setCreateBy("JueYue");
client.setId("1" + i);
client.setRemark("测试" + i);
list.add(client);
}
File savefile = new File("D:/excel/");
if (!savefile.exists()) {
savefile.mkdirs();
}
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/excel/ExcelExportBigData.bigDataExport.csv");
CsvExportUtil.exportCsv(params, MsgClient.class, list, fos);
fos.flush();
fos.close();
System.out.println("导出完成" + (new Date().getTime() - start.getTime()));
}#8.Spring MVC #8.1 View 介绍
easypoi view 项目是为了更简单的方便搭建在导出时候的操作,利用spring mvc 的view 封装,更加符合spring mvc的风格 view下面包括多个 view的实现
- EasypoiBigExcelExportView 大数据量导出
- EasypoiMapExcelView map 列表导出
- EasypoiPDFTemplateView pdf导出
- EasypoiSingleExcelView 注解导出
- EasypoiTemplateExcelView 模板导出
- EasypoiTemplateWordView word模板导出
- MapGraphExcelView 图表导出
view的是使用方法大同小异,都有一个对应的bean,里面保护指定的参数常量 同意用modelmap.put(‘常量参数名’,‘值’)就可以,最后返回这个view名字
注解目录扫描的时候加上 cn.afterturn.easypoi.view 就可以使用了
##8.2 大数据导出View的用法
EasypoiBigExcelExportView 是针对大数据量导出特定的View,在跳转到这个View的时候不需要查询数据,而且这个View自己去查询数据,用户只要实现IExcelExportServer接口就可以了 对应的常量类BigExcelConstants
public interface IExcelExportServer {
/**
* 查询数据接口
* @param obj 查询条件
* @param page 当前页数
* @return
*/
public List<Object> selectListForExcelExport(Object obj, int page);
}EasypoiBigExcelExportView 判断是否还有下一页的条件是,如果selectListForExcelExport 返回null就认为是最后一页了,如果返回有数据这page+1继续查询 在我们自己的controller中
@RequestMapping("load")
public void downloadByPoiBaseView(ModelMap map, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
ExportParams params = new ExportParams("2412312", "测试", ExcelType.XSSF);
params.setFreezeCol(2);
map.put(BigExcelConstants.CLASS, MsgClient.class);
map.put(BigExcelConstants.PARAMS, params);
//就是我们的查询参数,会带到接口中,供接口查询使用
map.put(BigExcelConstants.DATA_PARAMS, new HashMap<String,String>());
map.put(BigExcelConstants.DATA_INTER,excelExportServer);
PoiBaseView.render(map, request, response, BigExcelConstants.EASYPOI_BIG_EXCEL_VIEW);
}我们需要把参数条件封装成map或者其他类型,上面的obj可以把参数自己转回来 参数名字 BigExcelConstants.DATA_PARAM 然后把实现查询的接口注入进来就可以了 map.put(BigExcelConstants.DATA_INTER,excelExportServer); 后面就和其他View一样了
##8.3 注解导出View用法
注解导出的View是这个EasypoiSingleExcelView,其实View大家可以忽略不看,主要用到的还是他对应的bean对象 NormalExcelConstants 注解到处还比较简单,大家只要把datalist,class和params 这几个参数put下就可以了。 具体的案例
@RequestMapping()
public String download(ModelMap map) {
List<MsgClient> list = new ArrayList<MsgClient>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
MsgClient client = new MsgClient();
client.setBirthday(new Date());
client.setClientName("小明" + i);
client.setClientPhone("18797" + i);
client.setCreateBy("JueYue");
client.setId("1" + i);
client.setRemark("测试" + i);
MsgClientGroup group = new MsgClientGroup();
group.setGroupName("测试" + i);
client.setGroup(group);
list.add(client);
}
ExportParams params = new ExportParams("2412312", "测试", ExcelType.XSSF);
params.setFreezeCol(2);
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.DATA_LIST, list); // 数据集合
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.CLASS, MsgClient.class);//导出实体
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.PARAMS, params);//参数
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.FILE_NAME, params);//文件名称
return NormalExcelConstants.EASYPOI_EXCEL_VIEW;//View名称
}和非View导出基本一致,只是把调用方法封装了而已,其他参数还都是一样的,具体可以看下测试项目的 EasypoiSingleExcelViewTest
##8.4 注解变种Map类型的导出View
作为动态注解存在的 List ,也提供的单独的View方便大家使用,**EasypoiMapExcelView ** 使用方法都是一样,直接看下例子吧
@RequestMapping()
public String download(ModelMap modelMap) {
List<ExcelExportEntity> entity = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
ExcelExportEntity excelentity = new ExcelExportEntity("姓名", "name");
excelentity.setNeedMerge(true);
entity.add(excelentity);
entity.add(new ExcelExportEntity("性别", "sex"));
excelentity = new ExcelExportEntity(null, "students");
List<ExcelExportEntity> temp = new ArrayList<ExcelExportEntity>();
temp.add(new ExcelExportEntity("姓名", "name"));
temp.add(new ExcelExportEntity("性别", "sex"));
excelentity.setList(temp);
entity.add(excelentity);
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
Map<String, Object> map;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
map.put("name", "1" + i);
map.put("sex", "2" + i);
List<Map<String, Object>> tempList = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
tempList.add(map);
tempList.add(map);
map.put("students", tempList);
list.add(map);
}
ExportParams params = new ExportParams("2412312", "测试", ExcelType.XSSF);
params.setFreezeCol(2);
modelMap.put(MapExcelConstants.MAP_LIST, list); //数据集合
modelMap.put(MapExcelConstants.ENTITY_LIST, entity); //注解集合
modelMap.put(MapExcelConstants.PARAMS, params);//参数
modelMap.put(MapExcelConstants.FILE_NAME, "EasypoiMapExcelViewTest");//文件名称
return MapExcelConstants.EASYPOI_MAP_EXCEL_VIEW;//View名称
}具体案例参考EasypoiMapExcelViewTest
##8.5Excel模板导出View
模板导出提供的EasypoiTemplateExcelView以及对应的bean TemplateExcelConstants 案例
@RequestMapping()
public String download(ModelMap modelMap) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>();
TemplateExportParams params = new TemplateExportParams(
"doc/foreach.xlsx");
List<TemplateExcelExportEntity> list = new ArrayList<TemplateExcelExportEntity>();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
TemplateExcelExportEntity entity = new TemplateExcelExportEntity();
entity.setIndex(i + 1 + "");
entity.setAccountType("开源项目");
entity.setProjectName("EasyPoi " + i + "期");
entity.setAmountApplied(i * 10000 + "");
entity.setApprovedAmount((i + 1) * 10000 - 100 + "");
list.add(entity);
}
map.put("entitylist", list);
map.put("manmark", "1");
map.put("letest", "12345678");
map.put("fntest", "12345678.2341234");
map.put("fdtest", null);
List<Map<String, Object>> mapList = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1; i++) {
Map<String, Object> testMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
testMap.put("id", "xman");
testMap.put("name", "小明" + i);
testMap.put("sex", "1");
mapList.add(testMap);
}
map.put("maplist", mapList);
mapList = new ArrayList<Map<String, Object>>();
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
Map<String, Object> testMap = new HashMap<String, Object>();
testMap.put("si", "xman");
mapList.add(testMap);
}
map.put("sitest", mapList);
modelMap.put(TemplateExcelConstants.FILE_NAME, "用户信息"); //文件名
modelMap.put(TemplateExcelConstants.PARAMS, params);//参数
modelMap.put(TemplateExcelConstants.MAP_DATA, map);//数据
return TemplateExcelConstants.EASYPOI_TEMPLATE_EXCEL_VIEW;//view名称
}具体案例EasypoiTemplateExcelViewTest
##8.6 PoiBaseView.render view的补救
假如因为不可抗拒或者其他神奇的原因,view导出无法使用,作者遇到过好几次了,各种神奇原因都有,提供一个统一的封装,算是一个补救措施吧 上面的modelMap写法和设置参数还是一样,最后直接输出就可以了 PoiBaseView.render(modelMap, request, response,View名称);
看个简单demo
@RequestMapping("load")
public void downloadByPoiBaseView(ModelMap map, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
List<MsgClient> list = new ArrayList<MsgClient>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
MsgClient client = new MsgClient();
client.setBirthday(new Date());
client.setClientName("小明" + i);
client.setClientPhone("18797" + i);
client.setCreateBy("JueYue");
client.setId("1" + i);
client.setRemark("测试" + i);
MsgClientGroup group = new MsgClientGroup();
group.setGroupName("测试" + i);
client.setGroup(group);
list.add(client);
}
ExportParams params = new ExportParams("2412312", "测试", ExcelType.XSSF);
params.setFreezeCol(2);
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.DATA_LIST, list);
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.CLASS, MsgClient.class);
map.put(NormalExcelConstants.PARAMS, params);
PoiBaseView.render(map, request, response, NormalExcelConstants.EASYPOI_EXCEL_VIEW);
}#9.spring boot #9.1 spring boot start
随着spring boot的越来越流行,不可免俗的我们也推出了easypoi-spring-boot-starter,方便大家的引用和依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.afterturn</groupId>
<artifactId>easypoi-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0</version>
</dependency>加入其他不需要改动就可以完美的玩耍了,如果你不需要web服务,那只要依赖easypoi-base就可以了
#10.常见问题解答 ###10.1 导入时为啥这行为空还读取 或者为啥只有3行却读取了100行数据 在导入参数ImportParams 有一个属性keyIndex
/**
* 主键设置,如何这个cell没有值,就跳过 或者认为这个是list的下面的值
* 大家不理解,去掉这个
*/
private Integer keyIndex = null;最早是默认为0的,但是很多说有问题,就取消默认值了,如果你遇到上面的问题,请不他改为你肯定不为空的一列比如0,就可以解决上面问题了 ###10.2 模板如何合并单元格 提供了PoiMergeCellUtil类供大家生成wb之后,自己再调用
/**
* 纵向合并相同内容的单元格
*
* @param sheet
* @param startRow 开始行
* @param columns 需要处理的列
*/
public static void mergeCells(Sheet sheet, int startRow, Integer... columns) {
if (columns == null) {
throw new ExcelExportException("至少需要处理1列");
}
Map<Integer, int[]> mergeMap = new HashMap<Integer, int[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < columns.length; i++) {
mergeMap.put(columns[i], null);
}
mergeCells(sheet, mergeMap, startRow, sheet.getLastRowNum());
}这个逻辑是,只要一列连续值是相同的就合并 ###10.3 如何让单元格是数组 参考2.7样式自定义,让你这个单元格是数组类型的样式就可以了
如果是模板 n:
###10.4 类找不到怎么办 https://www.findjar.com/index.x
###10.5 replace NULL值问题 @excel replace = { "客户银行卡_OA01", "客户金账户_OA02", "客户存管账户_OA03","渠道金账户_OA04", "营销款账户_OA05"} private String outAccountType 当outAccountType 值为null的时候,excel会转为 null字符串
可以这么配置**"_null"**,就可以解决上述问题
@Excel(name = "出账账户类型", width = 20, replace = { "客户银行卡_OA01", "客户金账户_OA02", "客户存管账户_OA03"
,"渠道金账户_OA04", "营销款账户_OA05", "_null"}, orderNum = "6")###10.6 无表头或者表头重复不好判断如何解决 fixedIndex 字段可以直接让你固定列跳过那些判断直接读取数据
if (excelEntity.getFixedIndex() != -1) {
temp.put("FIXED_" + excelEntity.getFixedIndex(), excelEntity);
} else {
temp.put(excelEntity.getName(), excelEntity);
}你可以在@Excel上使用,也可以在自己ExcelImportEntity是写 ###10.7 模板导出一对多,如何合并单元格和循环