JCat是一只我们手撸的Tomcat,实现了“纯种”Tomcat处理Servlet请求、动态类加载、Web应用程序隔离等功能。在本项目中,您可以学习到以下内容:
- 发送/处理HTTP协议请求
- Servlet的处理流程
- 编写自定义ClassLoader
- 监控文件目录的变化情况
JCat主要是由Server、Request、Response、Context这几个组件组成的。其中,Context由多个ContextEntry组成,而ContextEntry由包括了用于Servlet管理的ServletMapping,以及ContextEntry状态监控的Listeners。
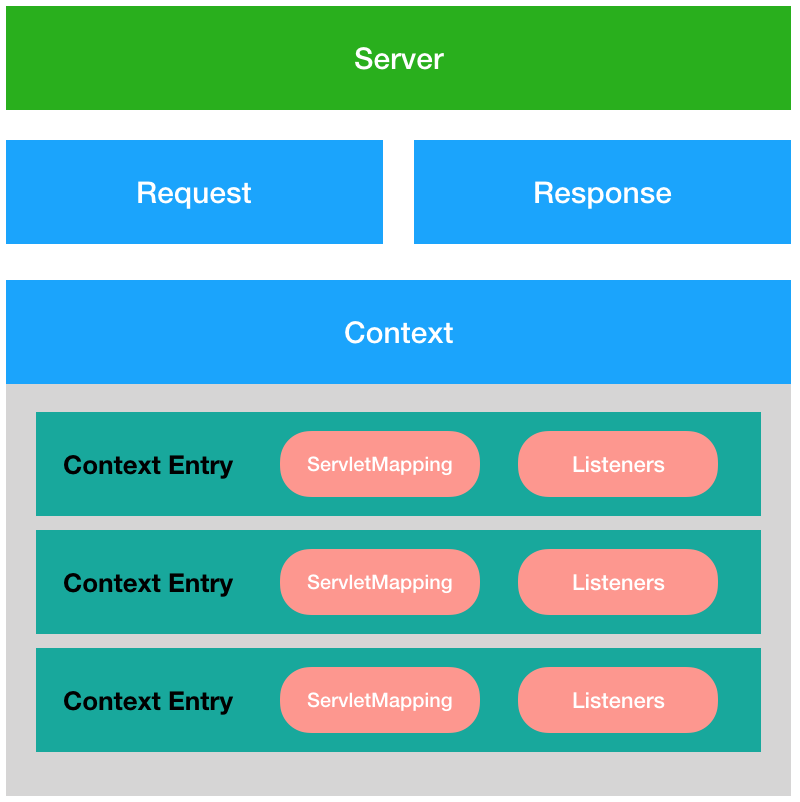
Request组件就是我们平时编写Servlet的doGet/doPost方法中HttpReqest类,该组件的主要作用是将Socket的inputStream进行封装,并将Http请求中的内容解析为HttpReqest类的相关属性(例如:Http请求的Method、URI以及Host等),以便于在Servlet中使用。
Response组件就是我们平时编写Servlet的doGet/doPost方法中HttpResponse类,该组件的主要作用是将Socket的outputStream进行封装,当需要返回数据时,直接调用Response.write()方法即可。
Context组件是Context Entry的集合,作用是便于JCat管理Web应用程序,包括Web应用中Class加载,以及在Class变化后,Class文件如何重载等。
import java.io.IOException;
import org.jcat.request.HttpRequest;
import org.jcat.response.HttpResponse;
public class HelloWorldServlet extends org.jcat.servlet.Servlet
{
public HelloWorldServlet() {}
public void doGet(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response)
{
try
{
String content = "[Get] I'm HelloWorldServlet! Under the [webapp1] directory!</br>";
content = content + " My Class Loader is [" + getClass().getClassLoader().toString() + "]";
response.write(content);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void doPost(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response)
{
try
{
String content = "[Post] I'm HelloWorldServlet! Under the [webapp1] directory!</br>";
content = content + " My Class Loader is [" + getClass().getClassLoader().toString() + "]";
response.write(content);
}
catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}