- GIT workflow methods
- Creating table-of-contents for MarkDown (.md) files
- Preview MarkDown files locally before commit/push to GitHub
- Getting a micropython prompt on the USB serial port
- Self-Test Idea
- MicroPython C Modules
- Flashing MicroPython
- ADC DMA ideas
- Adding a collaborator's github URL
-
git remote add collaborator https://github.com/<collaborator_username>/culture_shock.git git fetch collaborator
-
based on this StackOverflow (https://stackoverflow.com/a/39628366/253127)
- add the original (kanzure's) repo:
git remote add original https://github.com/kanzure/culture_shock.git
- Fetch the latest changes from the collaborator
git fetch original
- Checkout your local master branch
git checkout master
- reset master to original's version, so your files match theirs exactly
git reset --hard original/master
- Fetch the latest changes from the collaborator
git fetch collaborator
- Merge the collaborator's changes (from master branch)
git merge collaborator/master
- Fetch the latest changes from the collaborator
git fetch collaborator
- Checkout the collaborator's changes (from master branch)
git checkout collaborator/master
- Depending on if merge conflicts are expected
- If not, then use non-interactive rebasing
git rebase master
- If yes (or you want to squash/edit their commits/commit-messages), then use interactive rebasing
git rebase -i master
- If not, then use non-interactive rebasing
- If there are merge conflicts
- show the files in question
git status
- use git's mergetool to see the your changes and their changes side-by-side
- single file
git mergetool path/to/file_of_interest
- all files in question
git mergetool
- single file
- show the files in question
- Create a temporary branch for safety
git checkout -b mergeme
- Go back to your last version of master branch
git checkout master
- Merge your rebased changes into master
git merge mergeme
- I am currently using this method during debugging of the MarkDown syntax used for this note
-
git add DEVELOPER_NOTE.md git commit -m "sqsh" git rebase -i HEAD~2
-
- the last command allows you to modify whether the last (2) commits are applied, how they are applied, in what order
- I see the following output
-
pick 12e8eee added notes for syncing with other github 'forks' (collaborators) pick 7f7aedb sqsh # Rebase aebf933..7f7aedb onto aebf933 (2 command(s)) # # Commands: # p, pick = use commit # r, reword = use commit, but edit the commit message # e, edit = use commit, but stop for amending # s, squash = use commit, but meld into previous commit # f, fixup = like "squash", but discard this commit's log message # x, exec = run command (the rest of the line) using shell # d, drop = remove commit # # These lines can be re-ordered; they are executed from top to bottom. # # If you remove a line here THAT COMMIT WILL BE LOST. # # However, if you remove everything, the rebase will be aborted. # # Note that empty commits are commented out
-
- I would then edit the second line to read
s 7f7aedb sqsh- This squashes the commit into the previous (commit above it)
- the goal is to merge the commit-contents into the previous commit, but hide the fact that the contents actually came from more than one commit (squashing all changes into a single commit)
- save the text file
- now rebase will open the commit-message, showing all the combined messages
-
# This is a combination of 2 commits. # The first commit's message is: added notes for syncing with other github 'forks' (collaborators) # This is the 2nd commit message: sqsh # Please enter the commit message for your changes. Lines starting # with '#' will be ignored, and an empty message aborts the commit. # interactive rebase in progress; onto 7120033 # Last commands done (2 commands done): # pick 3a59de4 added notes for syncing with other github 'forks' (collaborators) # s 63cf084 sqsh # No commands remaining. # You are currently rebasing branch 'master' on '7120033'. # # Changes to be committed: # modified: DEVELOPER_NOTE.md - remove the line starting with
sqsh
-
- save and exit the commit-message
- Done!
- continue working, push, etc
- during this debug cycle, because I continually edit the MarkDown, then squash, to test the web-browser rendering I then have to run a
git push -fto force-push and overwrite the previous commit I made, because it was already made public
- during this debug cycle, because I continually edit the MarkDown, then squash, to test the web-browser rendering I then have to run a
- continue working, push, etc
- What look to be pretty good notes here:
- Setting a specific mergetool/difftool which is already supported by git
- from: https://stackoverflow.com/a/6412645/253127
- example of open-source tools supported
- kdiff3, kompare, tkdiff, meld, xxdiff, emerge, vimdiff, gvimdiff, ecmerge, diffuse, opendiff, p4merge and araxis
- add the following lines to your
~/.gitconfig-
[diff] tool = meld
-
- Setting up mergetool/difftool that isn't supported
- the stackoverflow linked from the prev also works, but looks to be a less-concise copy of this
- see "Git 1.7.x and older" section
- the stackoverflow linked from the prev also works, but looks to be a less-concise copy of this
- get this handy TOC generator
git clone https://github.com/ekalinin/github-markdown-toc
- cd to the culture_shock repo, then run the TOC generator on the .md file of interest
cd culture_shock../github-markdown-toc/gh-md-toc DEVELOPER_NOTE.md
- paste the output into the .md file
- commit and push
- Download
gripwithpippip install grip
cdto culture_shock repo- run
grip- copy the web URL printed on the terminal
- navigate to it using your web-browser
- copy the web URL printed on the terminal
-
Windows: you need to go to 'Device manager', right click on the unknown device, then update the driver software, using the 'pybcdc.inf' file found on this drive. Then use a terminal program like Hyperterminal or putty.
-
Mac OS X: use the command: screen /dev/tty.usbmodem*
-
Linux: use the command: screen /dev/ttyACM0
-
After you have a prompt, you can tell culture shock to do a soft reset <ctl>d or <ctl>x to get out of the REPL (read eval print loop) and back to your system command line. For more on what micropython can do from the REPL, see http://micropython.org/help/ as a starting point.
- Setup 10 pulses with shortest possible pulse-width
- setup list
adc_vals
- setup list
- Setup ADC timer with same freq as pulses, but out of phase 180°
- setup IRQ function callback on ADC timer, the function will:
- read the ADC, append to
adc_vals
- read the ADC, append to
- at end of pulse-train, send
adc_valsout the serial port for printing on the user-terminal
- PA0 and PA1, as seen here in kvboard v0.1, are the wires for pulsing the switched power supply to get high volts.
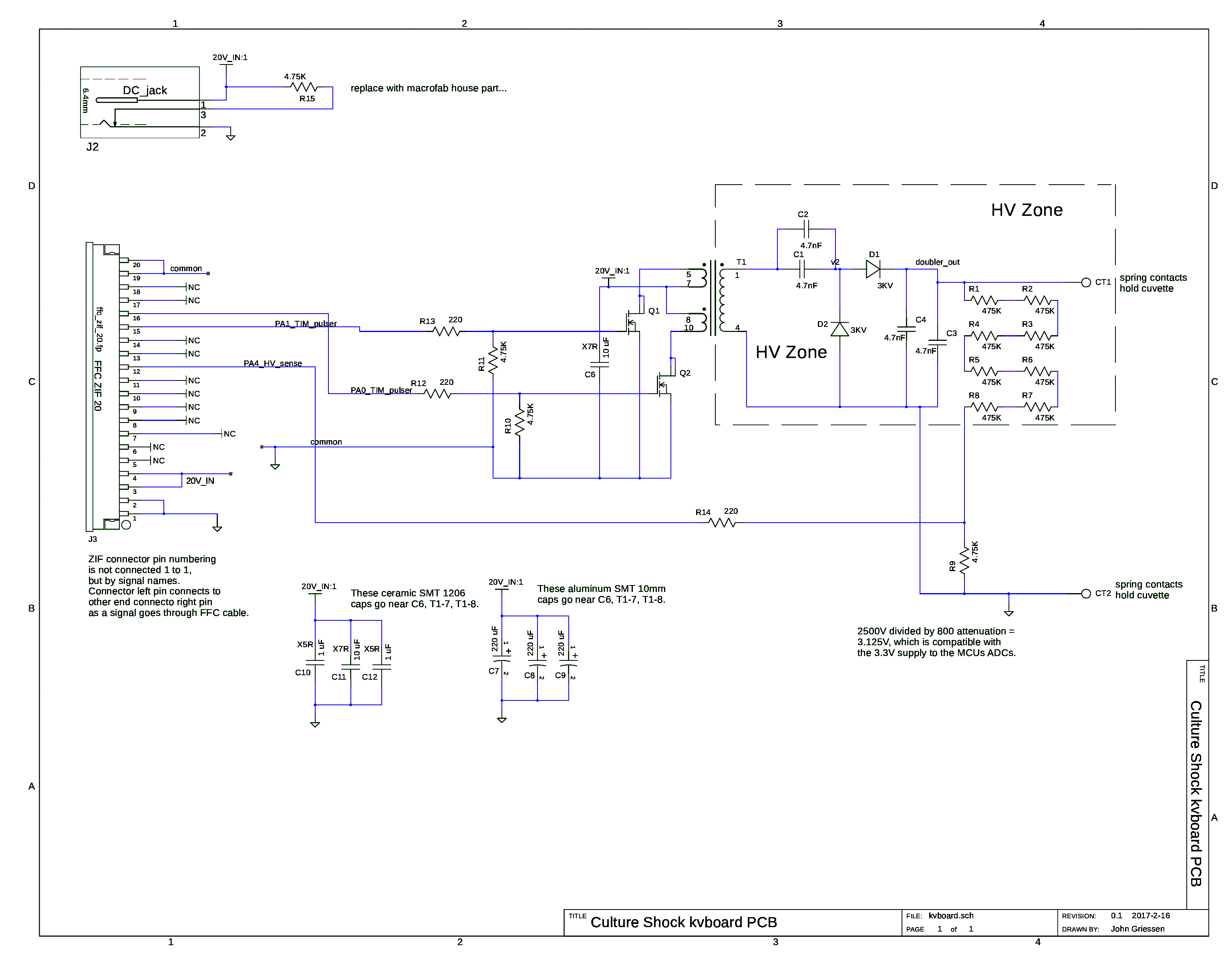
- Connect your oscilloscope to these pins to watch the pulse widths and periods of each digital operation from the microcontroller
- These are useful to trigger on
- you can then watch the analog/choppier high-voltage develop on another oscilloscope input
- These are useful to trigger on
- With Culture_Shock v0.1, the G30TH module was used for the STM microcontroller it was built with
- Connecting the first oscilloscope probe to PA1 and GND (red minigrabber)

- Connecting the second oscilloscope probe to PA0

- Connecting the third oscilloscope probe and 1GOhm resistor to the high-voltage (HV) output
- Overall setup

-
requires pexpect
pip install pexpectand tk (comes with Python out-of-box in most cases)- pexpect is a terminal interaction library
- you can send lines to a terminal
- you setup what you expect the terminal to reply with
- these act like triggers to tell your program your output was seen
- pexpect is a terminal interaction library
-
I used
picocomfor test and development- thus what I programmed the expectations to be might need adjusted for other terminal programs
-
the terminal interaction is logged to the command-line where you start the GUI
- use this to debug why your expectations aren't being met
-
every time the pulse button is clicked, the a() function is called using the 3 input boxes for args
- reduce the Num Pulse Pairs for a first-try adjustment
- you should see the waveform get shorter in length
- reduce the Num Pulse Pairs for a first-try adjustment
-
NOTE: this is still work-in-progress, dependent on the ADC working, which is still WIP
- has not been rigourously debugged, understood, or tested with conditions other than the default (starting) conditions for period, width, num-pulses
-
see demo pics here
-
https://github.com/micropython/micropython/blob/master/drivers/display/ssd1306.py
-
Graphing the ADC values will require scaling the data to fit.
-
Currently with the DMA transfer the ADC reads into a buffer of length 2048.
-
The OLED is only 128 wide
- 64 tall
-
scaling in the X direction may be done with averaging every (2048/128)==16 values
- or a median filter
- or a max-val filter
-
scaling in the Y will use the ADC max-val and the height of the OLED (64)
- val / 1024.0 * 64.0
-
see demo pics here
In case we really need to customize or reduce overhead
- See here for background
git clone https://github.com/micropython/micropython.gitcd micropythongit checkout v1.9.3- patch with ADC DMA sampling changes
patch -p1 ./ports/stm32/adc.c < ../culture_shock/FOR_ADC_DMA__adc.c.patch- assumes culture_shock and micropython repos are in the same directory
- hacks the read_timed method, and adds a new method read_timed_stop
cd ports/stm32/boards/git clone https://github.com/dhylands/G30TH.gitcd ..- connect 3.3V to pin B0
make BOARD=G30TH- if you need to erase the program area, i.e. if you wrote bad MicroPython code that "bricked" the MCU
dfu-util -v -s :mass-erase:force -a 0 -d 0483:df11 -D build-G30TH/firmware.dfu
make BOARD=G30TH deploy
- 11.8.1 Using the DMA When the DMA mode is enabled (DMA bit set to 1 in the ADC_CR2 register), after each conversion of a regular channel, a DMA request is generated. This allows the transfer of the converted data from the ADC_DR register to the destination location selected by the software. Despite this, if data are lost (overrun), the OVR bit in the ADC_SR register is set and an interrupt is generated (if the OVRIE enable bit is set). DMA transfers are then disabled and DMA requests are no longer accepted. In this case, if a DMA request is made, the regular conversion in progress is aborted and further regular triggers are ignored. It is then necessary to clear the OVR flag and the DMAEN bit in the used DMA stream, and to re- initialize both the DMA and the ADC to have the wanted converted channel data transferred to the right memory location. Only then can the conversion be resumed and the data transfer, enabled again.
5 4 3 2 1 0 OVR STRT JSTRT JEOC EOC AWD rc_w0 rc_w0 rc_w0 rc_w0 rc_w0 rc_w0
- Bits 31:6 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
- Bit 5 OVR: Overrun
- This bit is set by hardware when data are lost . It is cleared by software. Overrun detection is enabled only when DMA = 1 or EOCS = 1.
- 0: No overrun occurred
- 1: Overrun has occurred
- This bit is set by hardware when data are lost . It is cleared by software. Overrun detection is enabled only when DMA = 1 or EOCS = 1.
- Bit 4 STRT: Regular channel start flag
- This bit is set by hardware when regular channel conversion starts. It is cleared by software.
- 0: No regular channel conversion started
- 1: Regular channel conversion has started
- This bit is set by hardware when regular channel conversion starts. It is cleared by software.
- Bit 3 JSTRT: Injected channel start flag
- This bit is set by hardware when injected group conversion starts. It is cleared by software.
- 0: No injected group conversion started
- 1: Injected group conversion has started
- This bit is set by hardware when injected group conversion starts. It is cleared by software.
- Bit 2 JEOC: Injected channel end of conversion
- This bit is set by hardware at the end of the conversion of all injected channels in the group. It is cleared by software.
- 0: Conversion is not complete
- 1: Conversion complete
- This bit is set by hardware at the end of the conversion of all injected channels in the group. It is cleared by software.
- Bit 1 EOC: Regular channel end of conversion
- This bit is set by hardware at the end of the conversion of a regular group of channels. It is cleared by software or by reading the ADC_DR register.
- 0: Conversion not complete (EOCS=0), or sequence of conversions not complete (EOCS=1)
- 1: Conversion complete (EOCS=0), or sequence of conversions complete (EOCS=1)
- This bit is set by hardware at the end of the conversion of a regular group of channels. It is cleared by software or by reading the ADC_DR register.
- Bit 0 AWD: Analog watchdog flag
- This bit is set by hardware when the converted voltage crosses the values programmed in the ADC_LTR and ADC_HTR registers. It is cleared by software.
- 0: No analog watchdog event occurred
- 1: Analog watchdog event occurred
- This bit is set by hardware when the converted voltage crosses the values programmed in the ADC_LTR and ADC_HTR registers. It is cleared by software.
-
Address offset: 0x04
-
Reset value: 0x0000 0000
-
Bit 31 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
-
Bit 30 SWSTART: Start conversion of regular channels
- This bit is set by software to start conversion and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- 0: Reset state
- 1: Starts conversion of regular channels
- Note: This bit can be set only when ADON = 1 otherwise no conversion is launched.
- This bit is set by software to start conversion and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
-
Bits 29:28 EXTEN: External trigger enable for regular channels
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of a regular group.
- 00: Trigger detection disabled
- 01: Trigger detection on the rising edge
- 10: Trigger detection on the falling edge
- 11: Trigger detection on both the rising and falling edges
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of a regular group.
-
Bits 27:24 EXTSEL[3:0]: External event select for regular group
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of a regular group:
- 0000: Timer 1 CC1 event
- 0001: Timer 1 CC2 event
- 0010: Timer 1 CC3 event
- 0011: Timer 2 CC2 event
- 0100: Timer 2 CC3 event
- 0101: Timer 2 CC4 event
- 0110: Timer 2 TRGO event
- 0111: Timer 3 CC1 event
- 1000: Timer 3 TRGO event
- 1001: Timer 4 CC4 event
- 1010: Timer 5 CC1 event
- 1011: Timer 5 CC2 event
- 1100: Timer 5 CC3 event
- 1101: Reserved
- 1110: Reserved
- 1111: EXTI line11
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of a regular group:
-
Bit 23 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
-
Bit 22 JSWSTART: Start conversion of injected channels
- This bit is set by software and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- 0: Reset state
- 1: Starts conversion of injected channels
- Note: This bit can be set only when ADON = 1 otherwise no conversion is launched.
- This bit is set by software and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
-
Bits 21:20 JEXTEN: External trigger enable for injected channels
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of an injected group.
- 00: Trigger detection disabled
- 01: Trigger detection on the rising edge
- 10: Trigger detection on the falling edge
- 11: Trigger detection on both the rising and falling edges
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of an injected group.
-
Bits 19:16 JEXTSEL[3:0]: External event select for injected group
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of an injected group.
- 0000: Timer 1 CC4 event
- 0001: Timer 1 TRGO event
- 0010: Timer 2 CC1 event
- 0011: Timer 2 TRGO event
- 0100: Timer 3 CC2 event
- 0101: Timer 3 CC4 event
- 0110: Timer 4 CC1 event
- 0111: Timer 4 CC2 event
- 1000: Timer 4 CC3 event
- 1001: Timer 4 TRGO event
- 1010: Timer 5 CC4 event
- 1011: Timer 5 TRGO event
- 1100: Reserved
- 1101: Reserved
- 1110: Reserved
- 1111: EXTI line15
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of an injected group.
-
Bits 15:12 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
-
Bit 11 ALIGN: Data alignment
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to Figure 35 and Figure 36.
- 0: Right alignment
- 1: Left alignment
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to Figure 35 and Figure 36.
-
Bit 10 EOCS: End of conversion selection
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- 0: The EOC bit is set at the end of each sequence of regular conversions. Overrun detection is enabled only if DMA=1.
- 1: The EOC bit is set at the end of each regular conversion. Overrun detection is enabled.
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
-
Bit 9 DDS: DMA disable selection (for single ADC mode)
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- 0: No new DMA request is issued after the last transfer (as configured in the DMA controller)
- 1: DMA requests are issued as long as data are converted and DMA=1
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
-
Bit 8 DMA: Direct memory access mode (for single ADC mode)
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to the DMA controller chapter for more details.
- 0: DMA mode disabled
- 1: DMA mode enabled
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to the DMA controller chapter for more details.
-
Bits 7:2 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
-
Bit 1 CONT: Continuous conversion
- This bit is set and cleared by software. If it is set, conversion takes place continuously until it is cleared.
- 0: Single conversion mode
- 1: Continuous conversion mode
- This bit is set and cleared by software. If it is set, conversion takes place continuously until it is cleared.
-
Bit 0 ADON: A/D Converter ON / OFF
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- Note:
- 0: Disable ADC conversion and go to power down mode
- 1: Enable ADC
- Address offset: 0x08
- Reset value: 0x0000 0000
- Bit 31 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
- Bit 30 SWSTART: Start conversion of regular channels
- This bit is set by software to start conversion and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- 0: Reset state
- 1: Starts conversion of regular channels
- Note: This bit can be set only when ADON = 1 otherwise no conversion is launched.
- This bit is set by software to start conversion and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- Bits 29:28 EXTEN: External trigger enable for regular channels
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of a regular group.
- 00: Trigger detection disabled
- 01: Trigger detection on the rising edge
- 10: Trigger detection on the falling edge
- 11: Trigger detection on both the rising and falling edges
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of a regular group.
- Bits 27:24 EXTSEL[3:0]: External event select for regular group
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of a regular group:
- 0000: Timer 1 CC1 event
- 0001: Timer 1 CC2 event
- 0010: Timer 1 CC3 event
- 0011: Timer 2 CC2 event
- 0100: Timer 2 CC3 event
- 0101: Timer 2 CC4 event
- 0110: Timer 2 TRGO event
- 0111: Timer 3 CC1 event
- 1000: Timer 3 TRGO event
- 1001: Timer 4 CC4 event
- 1010: Timer 5 CC1 event
- 1011: Timer 5 CC2 event
- 1100: Timer 5 CC3 event
- 1101: Reserved
- 1110: Reserved
- 1111: EXTI line11
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of a regular group:
- Bit 23 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
- Bit 22 JSWSTART: Start conversion of injected channels
- This bit is set by software and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- 0: Reset state
- 1: Starts conversion of injected channels
- Note: This bit can be set only when ADON = 1 otherwise no conversion is launched.
- This bit is set by software and cleared by hardware as soon as the conversion starts.
- Bits 21:20 JEXTEN: External trigger enable for injected channels
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of an injected group.
- 00: Trigger detection disabled
- 01: Trigger detection on the rising edge
- 10: Trigger detection on the falling edge
- 11: Trigger detection on both the rising and falling edges
- These bits are set and cleared by software to select the external trigger polarity and enable the trigger of an injected group.
- Bits 19:16 JEXTSEL[3:0]: External event select for injected group
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of an injected group.
- 0000: Timer 1 CC4 event
- 0001: Timer 1 TRGO event
- 0010: Timer 2 CC1 event
- 0011: Timer 2 TRGO event
- 0100: Timer 3 CC2 event
- 0101: Timer 3 CC4 event
- 0110: Timer 4 CC1 event
- 0111: Timer 4 CC2 event
- 1000: Timer 4 CC3 event
- 1001: Timer 4 TRGO event
- 1010: Timer 5 CC4 event
- 1011: Timer 5 TRGO event
- 1100: Reserved
- 1101: Reserved
- 1110: Reserved
- 1111: EXTI line15
- These bits select the external event used to trigger the start of conversion of an injected group.
- Bits 15:12 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
- Bit 11 ALIGN: Data alignment
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to Figure 35 and Figure 36.
- 0: Right alignment
- 1: Left alignment
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to Figure 35 and Figure 36.
- Bit 10 EOCS: End of conversion selection
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- 0: The EOC bit is set at the end of each sequence of regular conversions. Overrun detection is enabled only if DMA=1.
- 1: The EOC bit is set at the end of each regular conversion. Overrun detection is enabled.
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- Bit 9 DDS: DMA disable selection (for single ADC mode)
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- 0: No new DMA request is issued after the last transfer (as configured in the DMA controller)
- 1: DMA requests are issued as long as data are converted and DMA=1
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- Bit 8 DMA: Direct memory access mode (for single ADC mode)
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to the DMA controller chapter for more details.
- 0: DMA mode disabled
- 1: DMA mode enabled
- This bit is set and cleared by software. Refer to the DMA controller chapter for more details.
- Bits 7:2 Reserved, must be kept at reset value.
- Bit 1 CONT: Continuous conversion
- This bit is set and cleared by software. If it is set, conversion takes place continuously until it is cleared.
- 0: Single conversion mode
- 1: Continuous conversion mode
- This bit is set and cleared by software. If it is set, conversion takes place continuously until it is cleared.
- Bit 0 ADON: A/D Converter ON / OFF
- This bit is set and cleared by software.
- Note:
- 0: Disable ADC conversion and go to power down mode
- 1: Enable ADC


