'HPE CTY Program Project'
In this we were asked to make a Security Dashboard for vatious Kubernetes Services.
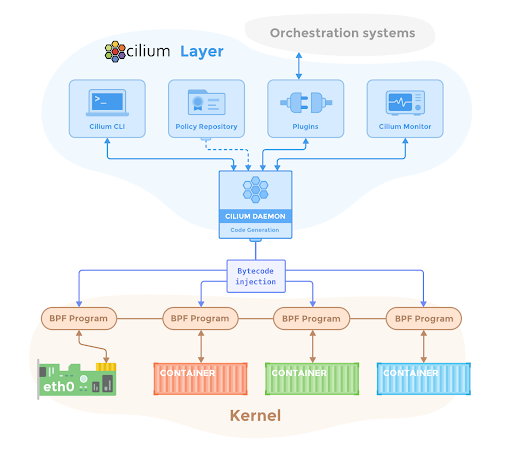
In this project I have installed Docker, Kubernetes and Cilium using Virtual Machines.
- Used Docker Desktop for running containers.
- Installed K8s on openSUSE and Windows.
- Created Cluster Mesh using Microsoft Azure Services.
- Installed Cilium on K8s.
- Created Network Policies and implemented them.
- Created a Grafana Dashboard to visualise the results of the policies implemented.
Before installing Docker, ensure that your system meets the following prerequisites
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows
- Architecture: x86_64 (64-bit) for Linux or macOS, or x86_64 or arm64 for Windows
- Kernel version: 3.10 or higher (Linux)
- RAM: At least 2GB
Follow the steps below to install Docker on your system:
-
Linux: Open a terminal and execute the following commands:
$ curl -fsSL https://get.docker.com -o get-docker.sh $ sudo sh get-docker.sh
-
macOS: Install Docker Desktop for macOS by following the instructions on the Docker Webise.
-
Windows: Install Docker Desktop for Windows by following the instructions on the Docker Website.
After the installation is complete, you can verify the Docker installation by running the following command in a terminal:
```shell
$ docker --version
```
Before installing Kubernetes, ensure that your system meets the following prerequisites:
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows
- Processor Architecture: x86_64 (64-bit)
- RAM: Minimum 2GB
Follow the steps below to install Kubernetes with Minikube on your system:
-
Linux:
- For Linux, you can install Minikube using a package manager like apt, yum, or dnf. Open a terminal and execute the following commands:
$ curl -LO https://storage.googleapis.com/minikube/releases/latest/minikube-linux-amd64 $ sudo install minikube-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/minikube
- For Linux, you can install Minikube using a package manager like apt, yum, or dnf. Open a terminal and execute the following commands:
-
macOS:
- On macOS, you can use Homebrew to install Minikube. Open a terminal and execute the following command:
$ brew install minikube
- On macOS, you can use Homebrew to install Minikube. Open a terminal and execute the following command:
-
Windows:
- On Windows, you can use Chocolatey to install Minikube. Open an elevated PowerShell or Command Prompt and execute the following command:
$ choco install minikube
- On Windows, you can use Chocolatey to install Minikube. Open an elevated PowerShell or Command Prompt and execute the following command:
After the installation is complete, you can start Minikube by running the following command in a terminal or command prompt:
```shell
$ minikube start
```
To verify the Minikube installation and check the status of the cluster, run the following command:
```shell
$ kubectl cluster-info
```
For more information on using Minikube and Kubernetes, refer to the official Minikube documentation and official Kubernetes documentation.
Before setting up Grafana, ensure that you have the following prerequisites:
- Operating System: Linux, macOS, or Windows
- Docker: Grafana can be run as a Docker container, so make sure Docker is installed on your system.
Follow the steps below to set up Grafana dashboard:
-
Step 1: Start Grafana Container:
Run the following command in a terminal or command prompt to start a Grafana container:
$ docker run -d -p 3000:3000 --name grafana grafana/grafana
This command will download the Grafana Docker image (if not already available) and start a Grafana container on port 3000.
-
Step 2: Access Grafana Dashboard:
Open a web browser and navigate to http://localhost:3000 to access the Grafana dashboard.
-
Step 3: Log in to Grafana:
Use the default login credentials to log in to Grafana:
Username: admin Password: admin
-
Step 4: Configure Data Source:
- Once logged in, click on the "Configuration" gear icon on the left sidebar, then select "Data Sources". Click on "Add data source" and choose the type of data source you want to configure (e.g., Prometheus, InfluxDB, etc.).
- Fill in the necessary details for your data source, such as the URL, authentication, and other settings.
- Click "Save & Test" to verify the connection to your data source.
- Step 5: Create a Dashboard:
- After configuring the data source, click on the "+" icon on the left sidebar, then select "Dashboard" > "New Dashboard".
- Customize your dashboard by adding panels, visualizations, and queries based on your data source.
- Save your dashboard and give it a meaningful name.
For more information and advanced usage of Grafana, refer to the official Grafana documentation.
Before installing Cilium with Hubble, ensure that your system meets the following prerequisites:
- Operating System: Linux (Kernel version 4.9 or higher)
- Kubernetes: Cilium requires a Kubernetes cluster
Follow the steps below to install Cilium with Hubble on your system:
-
Step 1: Install Cilium:
- Install Cilium on your Kubernetes cluster using the following command:
$ kubectl create -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/cilium/v1.10/install/kubernetes/quick-hubble-install.yaml
- Install Cilium on your Kubernetes cluster using the following command:
-
Step 2: Verify Cilium Installation:
-
Wait for the Cilium installation to complete. You can check the status by running the following command:
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system --selector=k8s-app=cilium
-
Ensure that all the Cilium pods are running and ready before proceeding.
-
-
Step 3: Install Hubble:
- Install Hubble using the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cilium/hubble/master/install/kubernetes-hubble.yaml
- Install Hubble using the following command:
-
Step 4: Verify Hubble Installation:
-
Wait for the Hubble installation to complete. You can check the status by running the following command:
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system --selector=k8s-app=hubble
-
Ensure that all the Hubble pods are running and ready before proceeding.
-
-
Step 5: Access Hubble UI:
-
To access the Hubble UI, run the following command to start a port-forward to the Hubble UI service:
$ kubectl port-forward -n kube-system service/hubble-ui 8080:80
-
Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:8080to access the Hubble UI.
-
For more information on Cilium and Hubble, refer to the official Cilium documentation and official Hubble documentation.
Cilium provides powerful network security and policy enforcement capabilities within Kubernetes. This guide will walk you through the process of creating and applying network policies using Cilium.
Before creating policies in Cilium, ensure that you have:
- Installed and configured Cilium on your Kubernetes cluster.
- Basic knowledge of Kubernetes concepts and networking.
Follow the steps below to create network policies in Cilium:
-
Step 1: Define Policy Rules:
-
Determine the communication rules you want to enforce within your Kubernetes cluster. For example, you may want to allow traffic from a specific set of pods to a particular service, while blocking all other traffic.
-
Network policies in Cilium use the Kubernetes NetworkPolicy resource. Define the desired policy rules in a YAML file, specifying the source and destination selectors, ports, and protocols.
-
Here's an example of a simple network policy YAML file:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: NetworkPolicy metadata: name: allow-frontend-to-backend spec: podSelector: matchLabels: app: frontend ingress: - from: - podSelector: matchLabels: app: backend ports: - protocol: TCP port: 80
-
-
Step 2: Apply the Network Policy:
-
Apply the network policy by running the following command:
$ kubectl apply -f network-policy.yaml
-
Replace
network-policy.yamlwith the actual filename or path to your network policy YAML file.
-
-
Step 3: Verify the Policy:
-
To verify that the network policy has been applied successfully, run the following command:
$ kubectl get networkpolicies
-
This command will display the list of network policies in your Kubernetes cluster.
-
You can also check the Cilium status to ensure that the policies are correctly enforced:
$ cilium status
-
If the policies are applied and enforced without errors, the status output will confirm their successful implementation.
-
To update or delete a network policy in Cilium, follow these steps:
-
Updating a Network Policy:
- Make the necessary changes to the network policy YAML file.
- Run the following command to update the policy:
$ kubectl apply -f network-policy.yaml
-
Deleting a Network Policy:
-
To delete a network policy, run the following command:
$ kubectl delete networkpolicy <policy-name>
-
Replace
<policy-name>with the name of the network policy you want to delete.
-
For more advanced usage and configuration options, refer to the official Cilium documentation.
Have Successfully installed all requirements and applied all network policies