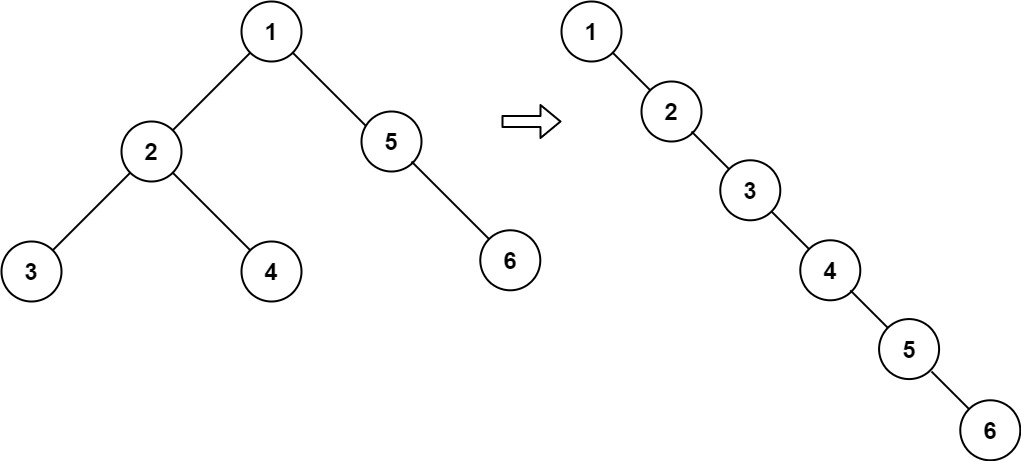
Given the root of a binary tree, flatten the tree into a "linked list":
- The "linked list" should use the same
TreeNodeclass where therightchild pointer points to the next node in the list and theleftchild pointer is alwaysnull. - The "linked list" should be in the same order as a pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,2,5,3,4,null,6] Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
Example 2:
Input: root = [] Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [0] Output: [0]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 2000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Can you flatten the tree in-place (with
O(1) extra space)?
Companies:
Facebook, Microsoft, Bloomberg, Amazon
Related Topics:
Linked List, Stack, Tree, Depth-First Search, Binary Tree
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
TreeNode* dfs(TreeNode* root) { // returns a pointer to the last node after flattening
if (!root || (!root->left && !root->right)) return root;
auto leftLast = dfs(root->left), rightLast = dfs(root->right), left = root->left, right = root->right;
root->left = nullptr;
root->right = left ? left : right;
if (left) leftLast->right = right;
return right ? rightLast : leftLast;
}
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
stack<TreeNode*> s{{root}};
TreeNode *prev = nullptr;
while (s.size()) {
auto node = s.top();
s.pop();
if (prev) prev->right = node;
prev = node;
if (node->right) s.push(node->right);
if (node->left) s.push(node->left);
node->left = node->right = nullptr;
}
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
TreeNode *prev = nullptr;
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
auto right = root->right;
if (prev) prev->right = root;
prev = root;
flatten(root->left);
root->left = nullptr;
flatten(right);
}
};Note: Left-to-right pre-order traversal has the reverse result of right-to-left post-order traversal.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-binary-tree-to-linked-list/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(H)
class Solution {
TreeNode *prev = nullptr;
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) return;
flatten(root->right);
flatten(root->left);
root->right = prev;
root->left = nullptr;
prev = root;
}
};