We have n jobs, where every job is scheduled to be done from startTime[i] to endTime[i], obtaining a profit of profit[i].
You're given the startTime, endTime and profit arrays, return the maximum profit you can take such that there are no two jobs in the subset with overlapping time range.
If you choose a job that ends at time X you will be able to start another job that starts at time X.
Example 1:
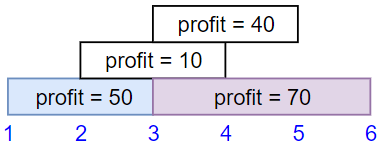
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,3], endTime = [3,4,5,6], profit = [50,10,40,70] Output: 120 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first and fourth job. Time range [1-3]+[3-6] , we get profit of 120 = 50 + 70.
Example 2:
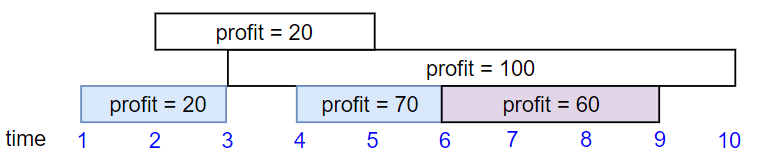
Input: startTime = [1,2,3,4,6], endTime = [3,5,10,6,9], profit = [20,20,100,70,60] Output: 150 Explanation: The subset chosen is the first, fourth and fifth job. Profit obtained 150 = 20 + 70 + 60.
Example 3:
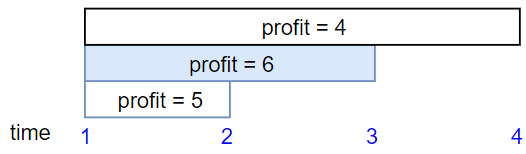
Input: startTime = [1,1,1], endTime = [2,3,4], profit = [5,6,4] Output: 6
Constraints:
1 <= startTime.length == endTime.length == profit.length <= 5 * 1041 <= startTime[i] < endTime[i] <= 1091 <= profit[i] <= 104
Companies:
DoorDash, Amazon, Swiggy, Databricks, Airbnb, Microsoft, LinkedIn, Adobe
Related Topics:
Array, Binary Search, Dynamic Programming, Sorting
Let dp[time] be the maximum profit we can get within time [time, Infinity). We need to get the dp values in descending order of start time.
dp[startTime[i]] = max( maxProfit, profit[i] + dp[endTime[i]] )
where `maxProfit` is the maximumProfit we've seen thus far
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<array<int, 3>> jobs;
for (int i = 0; i < startTime.size(); ++i) jobs.push_back({ startTime[i], endTime[i], profit[i] });
sort(begin(jobs), end(jobs), greater<>()); // sort jobs in descending order of start time
map<int, int> dp{{INT_MAX, 0}}; // startTime to max profit
int ans = 0;
for (auto &[s, e, p] : jobs) {
dp[s] = max(ans, p + dp.lower_bound(e)->second);
ans = max(ans, dp[s]);
}
return ans;
}
};The other way around. Let dp[time] be the maximum profit we can get within time [0, time]. We need to get the dp values in ascending order of end time.
dp[endTime[i]] = max( maxProfit, profit[i] + dp[startTime[i]] )
where `maxProfit` is the maximumProfit we've seen thus far
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
vector<array<int, 3>> jobs;
for (int i = 0; i < startTime.size(); ++i) jobs.push_back({ endTime[i], startTime[i], profit[i] });
sort(begin(jobs), end(jobs));
map<int, int> dp{{0, 0}}; // endTime to max profit
int ans = 0;
for (auto &[e, s, p] : jobs) {
dp[e] = max(ans, p + prev(dp.upper_bound(s))->second);
ans = max(ans, dp[e]);
}
return ans;
}
};We can use an auxiliary index array id to do the sorting which saves some space.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-profit-in-job-scheduling/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(NlogN)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
int jobScheduling(vector<int>& startTime, vector<int>& endTime, vector<int>& profit) {
int N = startTime.size(), ans = 0;
vector<int> id(N);
iota(begin(id), end(id), 0);
sort(begin(id), end(id), [&](int a, int b) { return startTime[a] > startTime[b]; }); // sort jobs in descending order of start time
map<int, int> m{{INT_MAX,0}}; // time -> maxProfit
for (int i : id) {
m[startTime[i]] = max(ans, profit[i] + m.lower_bound(endTime[i])->second);
ans = m[startTime[i]];
}
return ans;
}
};