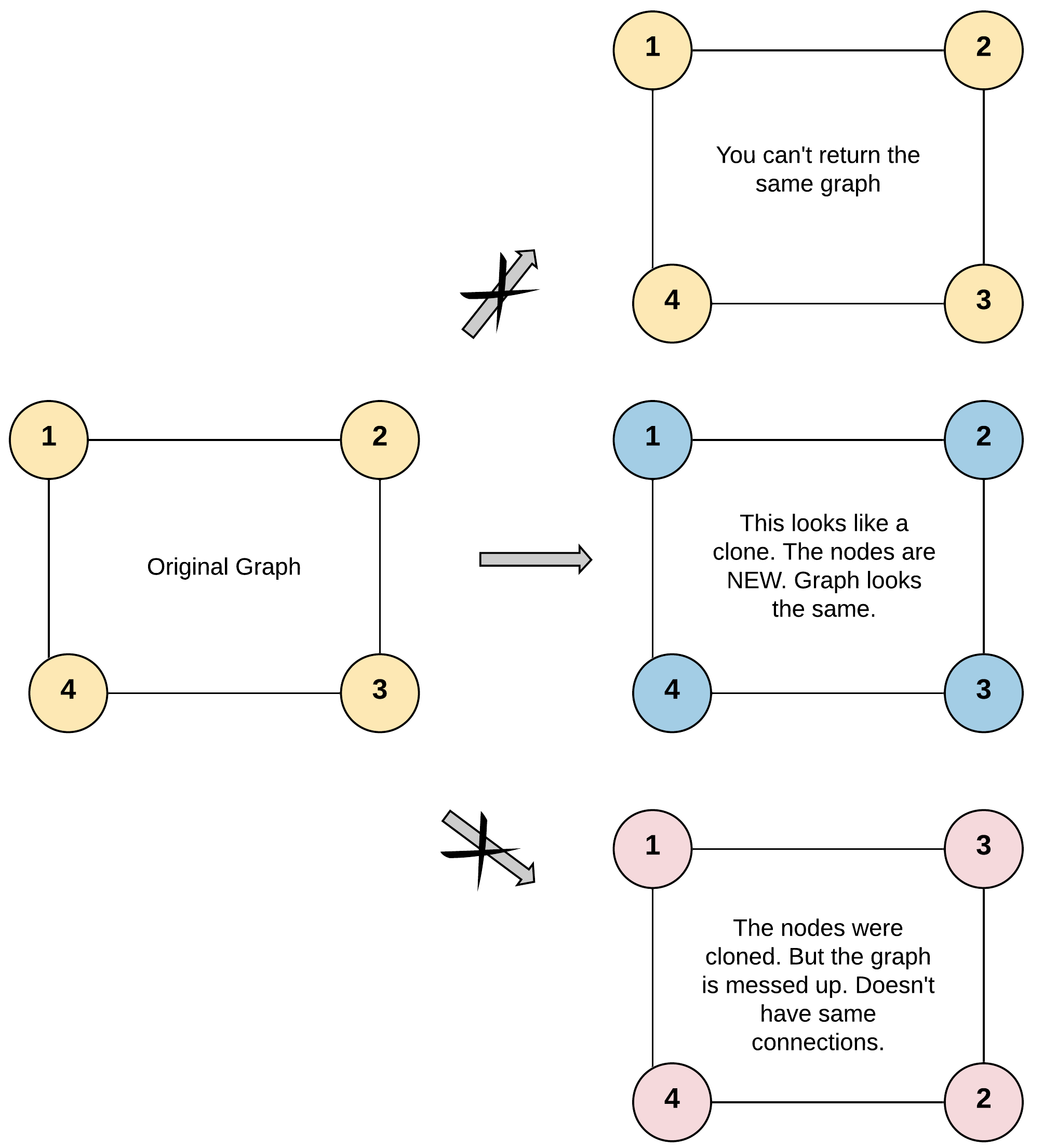
Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node's value is the same as the node's index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example 1:
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]] Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph. 1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3). 3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4). 4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Example 2:
Input: adjList = [[]] Output: [[]] Explanation: Note that the input contains one empty list. The graph consists of only one node with val = 1 and it does not have any neighbors.
Example 3:
Input: adjList = [] Output: [] Explanation: This an empty graph, it does not have any nodes.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the graph is in the range
[0, 100]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100Node.valis unique for each node.- There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph.
- The Graph is connected and all nodes can be visited starting from the given node.
Companies:
Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft, Google, Bloomberg, Salesforce, Twitter, Oracle
Related Topics:
Hash Table, Depth-First Search, Breadth-First Search, Graph
Similar Questions:
- Copy List with Random Pointer (Medium)
- Clone Binary Tree With Random Pointer (Medium)
- Clone N-ary Tree (Medium)
An unordered_map is used to record the mapping between the original and copied nodes, and to ensure each node is only copied once.
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
if (m.count(node)) return m[node];
auto cpy = new Node(node->val);
m[node] = cpy;
for (auto &n : node->neighbors) cpy->neighbors.push_back(cloneGraph(n));
return cpy;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/clone-graph/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(N)
// Space: O(N)
class Solution {
public:
Node* cloneGraph(Node* node) {
if (!node) return nullptr;
queue<Node*> q;
unordered_map<Node*, Node*> m;
m[node] = new Node(node->val);
q.push(node);
while (q.size()) {
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
auto copy = m[p];
for (auto nei : p->neighbors) {
if (!m.count(nei)) {
m[nei] = new Node(nei->val);
q.push(nei);
}
copy->neighbors.push_back(m[nei]);
}
}
return m[node];
}
};