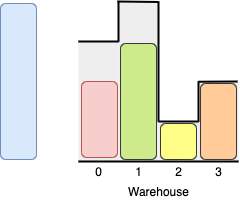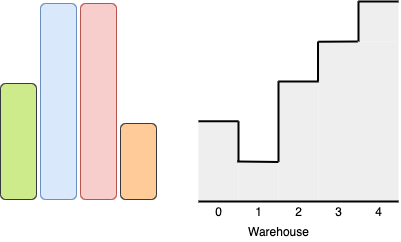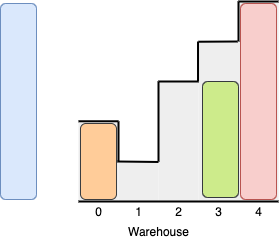You are given two arrays of positive integers, boxes and warehouse, representing the heights of some boxes of unit width and the heights of n rooms in a warehouse respectively. The warehouse's rooms are labeled from 0 to n - 1 from left to right where warehouse[i] (0-indexed) is the height of the ith room.
Boxes are put into the warehouse by the following rules:
- Boxes cannot be stacked.
- You can rearrange the insertion order of the boxes.
- Boxes can be pushed into the warehouse from either side (left or right)
- If the height of some room in the warehouse is less than the height of a box, then that box and all other boxes behind it will be stopped before that room.
Return the maximum number of boxes you can put into the warehouse.
Example 1:
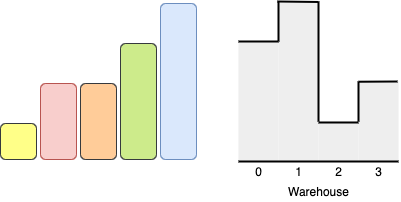
Input: boxes = [1,2,2,3,4], warehouse = [3,4,1,2] Output: 4 Explanation:We can store the boxes in the following order: 1- Put the yellow box in room 2 from either the left or right side. 2- Put the orange box in room 3 from the right side. 3- Put the green box in room 1 from the left side. 4- Put the red box in room 0 from the left side. Notice that there are other valid ways to put 4 boxes such as swapping the red and green boxes or the red and orange boxes.
Example 2:
Input: boxes = [3,5,5,2], warehouse = [2,1,3,4,5] Output: 3 Explanation:It's not possible to put the two boxes of height 5 in the warehouse since there's only 1 room of height >= 5. Other valid solutions are to put the green box in room 2 or to put the orange box first in room 2 before putting the green and red boxes.
Example 3:
Input: boxes = [1,2,3], warehouse = [1,2,3,4] Output: 3
Example 4:
Input: boxes = [4,5,6], warehouse = [3,3,3,3,3] Output: 0
Constraints:
n == warehouse.length1 <= boxes.length, warehouse.length <= 1051 <= boxes[i], warehouse[i] <= 109
Companies:
Google
Related Topics:
Greedy
Similar Questions:
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/put-boxes-into-the-warehouse-ii/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(WlogW + BlogB)
// Space: O(W)
class Solution {
public:
int maxBoxesInWarehouse(vector<int>& B, vector<int>& W) {
vector<int> left(W.size(), INT_MAX);
left[0] = W[0];
for (int i = 1; i < W.size(); ++i) {
left[i] = min(left[i - 1], W[i]);
}
int right = W.back();
for (int i = W.size() - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
right = min(right, W[i]);
W[i] = max(left[i], right);
}
sort(begin(W), end(W));
sort(begin(B), end(B));
int ans = 0;
for (int w : W) {
ans += ans < B.size() && B[ans] <= w;
}
return ans;
}
};// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/put-boxes-into-the-warehouse-ii/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(BlogB + min(B, W))
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int maxBoxesInWarehouse(vector<int>& B, vector<int>& W) {
int L = 0, R = W.size() - 1, ans = 0;
sort(begin(B), end(B), greater());
for (int i = 0; i < B.size() && L <= R; ++i) {
int tall = W[L] >= W[R] ? L : R;
if (W[tall] < B[i]) continue;
++ans;
if (tall == L) ++L;
else --R;
}
return ans;
}
};Or
// OJ: https://leetcode.com/problems/put-boxes-into-the-warehouse-ii/
// Author: github.com/lzl124631x
// Time: O(BlogB + min(B, W))
// Space: O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int maxBoxesInWarehouse(vector<int>& B, vector<int>& W) {
int L = 0, R = W.size() - 1, ans = 0;
sort(begin(B), end(B), greater());
for (int i = 0; i < B.size() && L <= R; ++i) {
if (B[i] <= W[L]) {
++ans;
++L;
} else if (B[i] <= W[R]) {
++ans;
--R;
}
}
return ans;
}
};