UADA3D: Unsupervised Adversarial Domain Adaptation for 3D Object Detection with Sparse LiDAR and Large Domain Gaps
In this study, we address a gap in existing unsupervised domain adaptation approaches on LiDAR-based 3D object detection, which have predominantly concentrated on adapting between established, high-density autonomous driving datasets. We focus on sparser point clouds, capturing scenarios from different perspectives: not just from vehicles on the road but also from mobile robots on sidewalks, which encounter significantly different environmental conditions and sensor configurations. We introduce Unsupervised Adversarial Domain Adaptation for 3D Object Detection (UADA3D). UADA3D does not depend on pre-trained source models or teacher-student architectures. Instead, it uses an adversarial approach to directly learn domain-invariant features. We demonstrate its efficacy in various adaptation scenarios, showing significant improvements in both self-driving car and mobile robot domains.
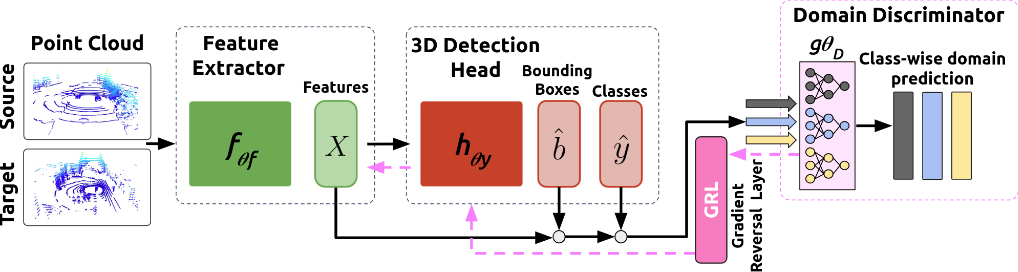
provides a schematic overview of our method UADA3D. In each iteration, a batch of samples
Code coming soon 😁
@article{wozniak2024uada3d,
title={UADA3D: Unsupervised Adversarial Domain Adaptation for 3D Object Detection with Sparse LiDAR and Large Domain Gaps},
author={Wozniak, K Maciej, and Hansson, Mattias and Thiel, Marko and Jensfelt, Patric},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.17633},
year={2024}
}