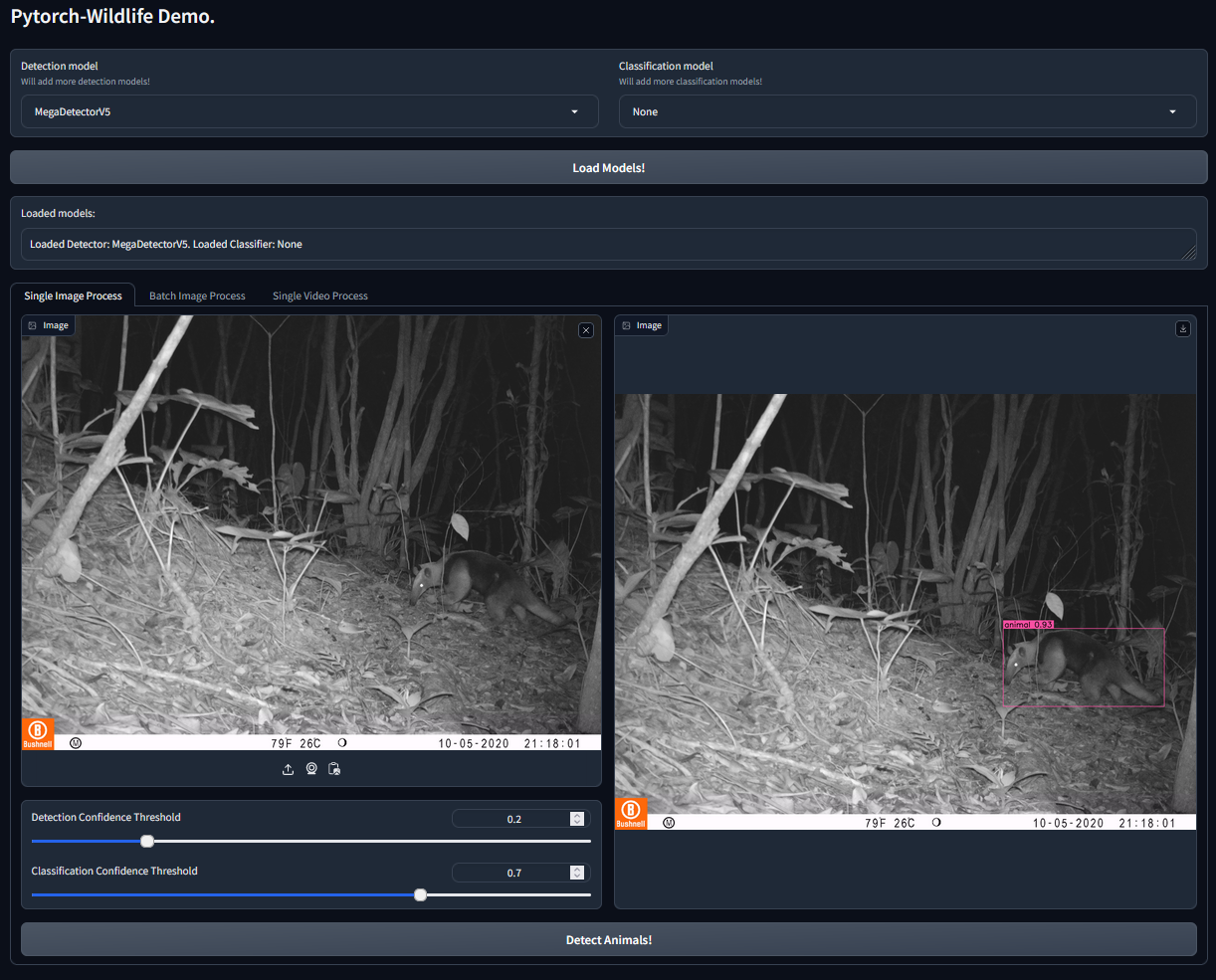
We are thrilled to announce our collaboration with EcoAssist---a powerful user interface software that enables users to directly load models from the PyTorch-Wildlife model zoo for image analysis on local computers. With EcoAssist, you can now utilize MegaDetectorV5 and the classification models---AI4GAmazonRainforest and AI4GOpossum---for automatic animal detection and identification, alongside a comprehensive suite of pre- and post-processing tools. This partnership aims to enhance the overall user experience with PyTorch-Wildlife models for a general audience. We will work closely to bring more features together for more efficient and effective wildlife analysis in the future.
The public beta testing for MegaDetectorV6 has officially started! In the next generation of MegaDetector, we are focusing on computational efficiency and performance. We have trained multiple new models using the latest YOLO-v9 architecture, and in the public beta testing, we will allow people to test the compact version of MegaDetectorV6 (MDv6-c). We want to make sure these models work as expected on real-world datasets.
This MDv6-c model has only one-sixth (SMALLER) of the parameters of the current MegaDetectorV5 and exhibits 12% higher recall (BETTER) on animal detection in our validation datasets. In other words, MDv6-c has significantly fewer false negatives when detecting animals, making it a more robust animal detection model than MegaDetectorV5. Furthermore, one of our testers reported that the speed of MDv6-c is at least 5 times FASTER than MegaDetectorV5 on their datasets.
| Models | Parameters | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|
| MegaDetectorV5 | 121M | 0.96 | 0.73 |
| MegaDetectroV6-c | 22M | 0.92 | 0.85 |
We are also working on an extra-large version of MegaDetectorV6 for optimal performance and a transformer-based model using the RT-Detr architecture to prepare ourselves for the future of transformers. These models will be available in the official release of MegaDetectorV6.
If you want to join the beta testing, please come to our discord channel and DM the admins there:
In addition, we have recently published a summary paper on Pytorch-Wildlife. The paper has been accepted as an oral presentation at the CV4Animals workshop at this year's CVPR. Please feel free to cite us!
The new version of PytorchWildlife uses the latest version of Pytorch (currently 2.3.1), which is compatible with CUDA 12.x.
- Added a file separation function. You can now automatically separate your files between animals and non-animals into different folders using our
detection_folder_separationfunction. Please see the Python demo file and Jupyter demo! - 🥳 Added Timelapse compatibility! Check the Gradio interface or notebooks.
👉 Click for more
- MegaDetectorV6 with multiple model sizes for both optimized performance and low-budget devices like camera systems (Public beta testing has started!!).
- Supervision 0.19+ and Python 3.10+ compatibility.
- A detection model fine-tuning module to fine-tune your own detection model for Pytorch-Wildlife.
- Direct LILA connection for more training/validation data.
- More pretrained detection and classification models to expand the current model zoo.
To check the full version of the roadmap with completed tasks and long term goals, please click here!.
At the core of our mission is the desire to create a harmonious space where conservation scientists from all over the globe can unite. Where they're able to share, grow, use datasets and deep learning architectures for wildlife conservation. We've been inspired by the potential and capabilities of Megadetector, and we deeply value its contributions to the community. As we forge ahead with Pytorch-Wildlife, under which Megadetector now resides, please know that we remain committed to supporting, maintaining, and developing Megadetector, ensuring its continued relevance, expansion, and utility.
Pytorch-Wildlife is pip installable:
pip install PytorchWildlife
To use the newest version of MegaDetector with all the existing functionalities, you can use our Hugging Face interface or simply load the model with Pytorch-Wildlife. The weights will be automatically downloaded:
from PytorchWildlife.models import detection as pw_detection
detection_model = pw_detection.MegaDetectorV5()For those interested in accessing the previous MegaDetector repository, which utilizes the same MegaDetector v5 model weights and was primarily developed by Dan Morris during his time at Microsoft, please visit the archive directory, or you can visit this forked repository that Dan Morris is actively maintaining.
Tip
If you have any questions regarding MegaDetector and Pytorch-Wildlife, please email us or join us in our discord channel:
PyTorch-Wildlife is a platform to create, modify, and share powerful AI conservation models. These models can be used for a variety of applications, including camera trap images, overhead images, underwater images, or bioacoustics. Your engagement with our work is greatly appreciated, and we eagerly await any feedback you may have.
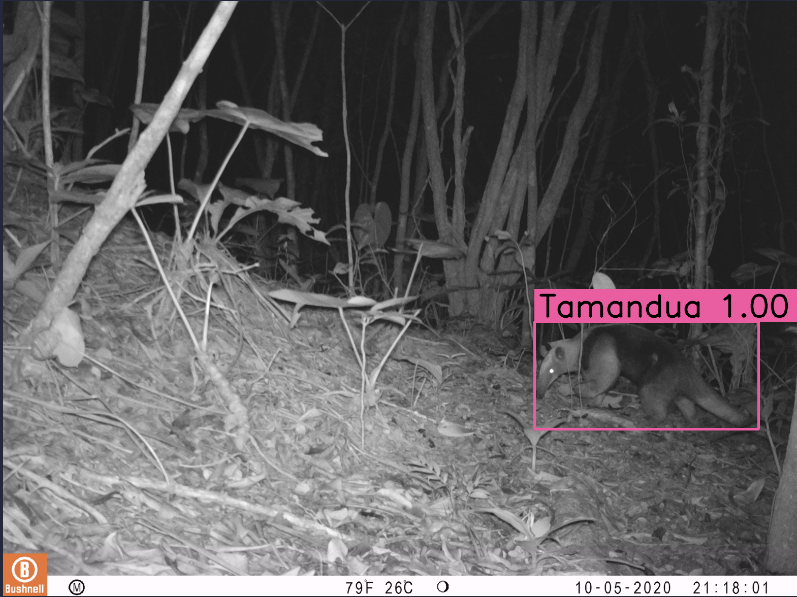
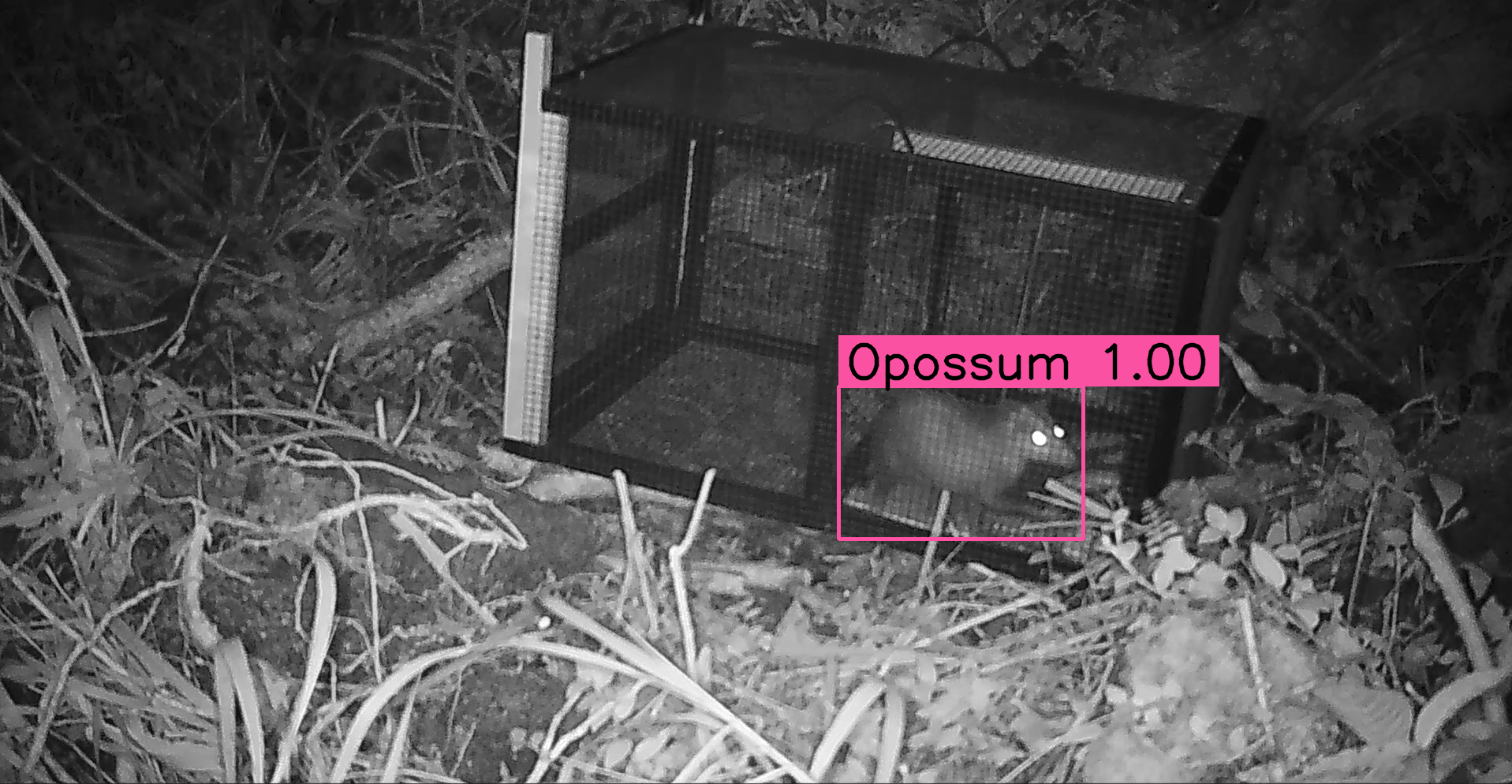
The Pytorch-Wildlife library allows users to directly load the MegaDetector v5 model weights for animal detection. We've fully refactored our codebase, prioritizing ease of use in model deployment and expansion. In addition to MegaDetector v5, Pytorch-Wildlife also accommodates a range of classification weights, such as those derived from the Amazon Rainforest dataset and the Opossum classification dataset. Explore the codebase and functionalities of Pytorch-Wildlife through our interactive HuggingFace web app or local demos and notebooks, designed to showcase the practical applications of our enhancements at PyTorchWildlife. You can find more information in our documentation.
👇 Here is a brief example on how to perform detection and classification on a single image using PyTorch-wildlife
import torch
from PytorchWildlife.models import detection as pw_detection
from PytorchWildlife.models import classification as pw_classification
img = torch.randn((3, 1280, 1280))
# Detection
detection_model = pw_detection.MegaDetectorV5() # Model weights are automatically downloaded.
detection_result = detection_model.single_image_detection(img)
#Classification
classification_model = pw_classification.AI4GAmazonRainforest() # Model weights are automatically downloaded.
classification_results = classification_model.single_image_classification(img)pip install PytorchWildlife
Please refer to our installation guide for more installation information.
If you want to directly try Pytorch-Wildlife with the AI models available, including MegaDetector v5, you can use our Gradio interface. This interface allows users to directly load the MegaDetector v5 model weights for animal detection. In addition, Pytorch-Wildlife also has two classification models in our initial version. One is trained from an Amazon Rainforest camera trap dataset and the other from a Galapagos opossum classification dataset (more details of these datasets will be published soon). To start, please follow the installation instructions on how to run the Gradio interface! We also provide multiple Jupyter notebooks for demonstration.
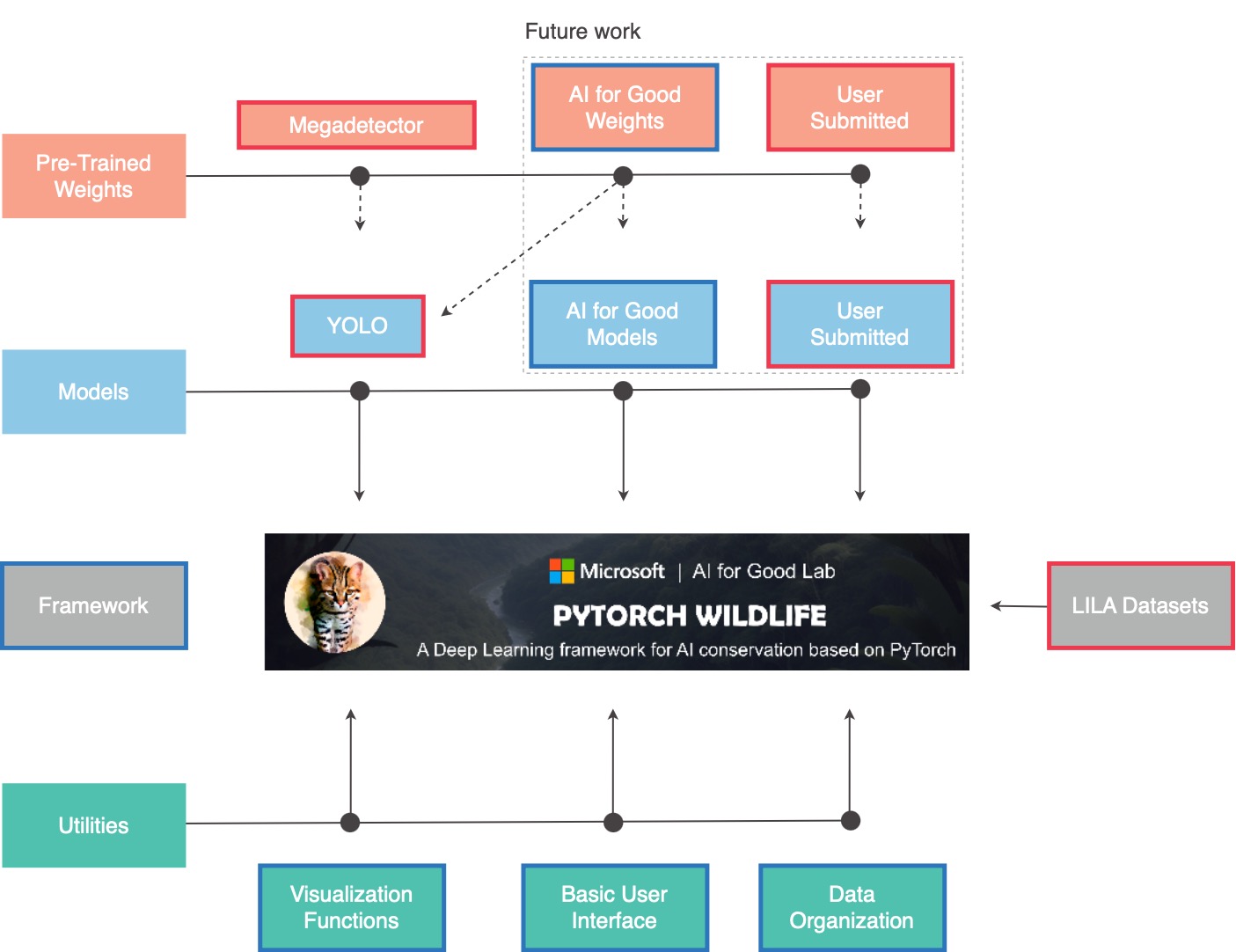
What are the core components of Pytorch-Wildlife?
Pytorch-Wildlife integrates four pivotal elements:
▪ Machine Learning Models
▪ Pre-trained Weights
▪ Datasets
▪ Utilities
In the provided graph, boxes outlined in red represent elements that will be added and remained fixed, while those in blue will be part of our development.
We're kickstarting with YOLO as our first available model, complemented by pre-trained weights from MegaDetector v5. This is the same MegaDetector v5 model from the previous repository.
As we move forward, our platform will welcome new models and pre-trained weights for camera traps and bioacoustic analysis. We're excited to host contributions from global researchers through a dedicated submission platform.
Pytorch-Wildlife will also incorporate the vast datasets hosted on LILA, making it a treasure trove for conservation research.
Our set of utilities spans from visualization tools to task-specific utilities, many inherited from Megadetector.
While we provide a foundational user interface, our platform is designed to inspire. We encourage researchers to craft and share their unique interfaces, and we'll list both existing and new UIs from other collaborators for the community's benefit.
Let's shape the future of wildlife research, together! 🙌
▪️ Packaging
- Animal detection fine-tuning
- MegaDetectorV5 integration
- MegaDetectorV6 integration
- User submitted weights
- Animal classification fine-tuning
- Amazon Rainforest classification
- Amazon Opossum classification
- User submitted weights
▪️ Utility Toolkit
- Visualization tools
- MegaDetector utils
- User submitted utils
▪️ Datasets
- Animal Datasets
- LILA datasets
▪️ Accessibility
- Basic user interface for demonstration
- UI Dev tools
- List of available UIs
Credits to Universidad de los Andes, Colombia.
Credits to Universidad de los Andes, Colombia.
Credits to the Agency for Regulation and Control of Biosecurity and Quarantine for Galápagos (ABG), Ecuador.
@misc{hernandez2024pytorchwildlife,
title={Pytorch-Wildlife: A Collaborative Deep Learning Framework for Conservation},
author={Andres Hernandez and Zhongqi Miao and Luisa Vargas and Rahul Dodhia and Juan Lavista},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.12930},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
This project is open to your ideas and contributions. If you want to submit a pull request, we'll have some guidelines available soon.
We have adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact us with any additional questions or comments.
This repository is licensed with the MIT license.
The extensive collaborative efforts of Megadetector have genuinely inspired us, and we deeply value its significant contributions to the community. As we continue to advance with Pytorch-Wildlife, our commitment to delivering technical support to our existing partners on MegaDetector remains the same.
Here we list a few of the organizations that have used MegaDetector. We're only listing organizations who have given us permission to refer to them here or have posted publicly about their use of MegaDetector.
👉 Full list of organizations
(Newly Added) TerrOïko (OCAPI platform)
Arizona Department of Environmental Quality
Canadian Parks and Wilderness Society (CPAWS) Northern Alberta Chapter
Czech University of Life Sciences Prague
Idaho Department of Fish and Game
SPEA (Portuguese Society for the Study of Birds)
The Nature Conservancy in Wyoming
Upper Yellowstone Watershed Group
Applied Conservation Macro Ecology Lab, University of Victoria
Banff National Park Resource Conservation, Parks Canada(https://www.pc.gc.ca/en/pn-np/ab/banff/nature/conservation)
Blumstein Lab, UCLA
Borderlands Research Institute, Sul Ross State University
Capitol Reef National Park / Utah Valley University
Center for Biodiversity and Conservation, American Museum of Natural History
Centre for Ecosystem Science, UNSW Sydney
Cross-Cultural Ecology Lab, Macquarie University
DC Cat Count, led by the Humane Rescue Alliance
Department of Fish and Wildlife Sciences, University of Idaho
Department of Wildlife Ecology and Conservation, University of Florida
Ecology and Conservation of Amazonian Vertebrates Research Group, Federal University of Amapá
Gola Forest Programma, Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB)
Graeme Shannon's Research Group, Bangor University
Hamaarag, The Steinhardt Museum of Natural History, Tel Aviv University
Institut des Science de la Forêt Tempérée (ISFORT), Université du Québec en Outaouais
Lab of Dr. Bilal Habib, the Wildlife Institute of India
Mammal Spatial Ecology and Conservation Lab, Washington State University
McLoughlin Lab in Population Ecology, University of Saskatchewan
National Wildlife Refuge System, Southwest Region, U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service
Northern Great Plains Program, Smithsonian
Quantitative Ecology Lab, University of Washington
Santa Monica Mountains Recreation Area, National Park Service
Seattle Urban Carnivore Project, Woodland Park Zoo
Serra dos Órgãos National Park, ICMBio
Snapshot USA, Smithsonian
Wildlife Coexistence Lab, University of British Columbia
Wildlife Research, Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife
Wildlife Division, Michigan Department of Natural Resources
Department of Ecology, TU Berlin
Ghost Cat Analytics
Protected Areas Unit, Canadian Wildlife Service
School of Natural Sciences, University of Tasmania (story)
Kenai National Wildlife Refuge, U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service (story)
Australian Wildlife Conservancy (blog, blog)
Felidae Conservation Fund (WildePod platform) (blog post)
Alberta Biodiversity Monitoring Institute (ABMI) (WildTrax platform) (blog post)
Shan Shui Conservation Center (blog post) (translated blog post)
Irvine Ranch Conservancy (story)
Wildlife Protection Solutions (story, story)
Road Ecology Center, University of California, Davis (Wildlife Observer Network platform)
Important
If you would like to be added to this list or have any questions regarding MegaDetector and Pytorch-Wildlife, please email us or join us in our Discord channel: