We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation.
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
本来在看K-means (最最基础的聚类算法)和EM算法(具体看统计学习方法,此处就不列推导相关的了),在学习的过程中发现了Spectral Clustering的效果看起来更好。
从该图中不难看出其聚类效果并不是很好,未能准确的将中间部分完全分开。于是乎看到了教程中提到的Spectral Clustering的方法,也就是下图中所使用的算法,可以看到已经能够将数据准确的分开了。
以上两图来自Python Data Science Handbook 5.11 教程
关于Spectral Clustering 算法,这篇估计是经典中的经典,但是还没有看。只是尝试了下其用于对已知的webshell进行聚类的效果。因为如果直接在对未知样本进行分类的时候 采取多分类,显然会导致精度下降很多,但是当有需求判断这个webshell是哪一种时,这个方法就可以一试。以下代码采用sklearn编写。
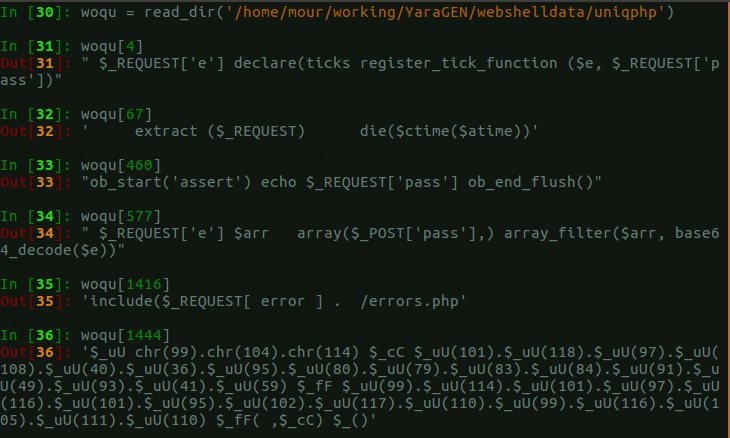
import os, sys, re import logging import pickle import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from sklearn.datasets import make_moons from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import HashingVectorizer, TfidfVectorizer from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformer from sklearn.preprocessing import Normalizer from sklearn.decomposition import TruncatedSVD from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline from sklearn.externals import joblib from sklearn.cluster import SpectralClustering,KMeans def read_dir(folder): res = [] for r, d, f, in os.walk(folder): for _ in f: file = os.path.join(r, _) res.append(" ".join(strings_file(file))) return res def strings_file(binfile): chars = r"A-Za-z0-9/\-:.,_$%'()[\]<> " shortestReturnChar = 4 regExp = '[%s]{%d,}' % (chars, shortestReturnChar) pattern = re.compile(regExp) with open(binfile, 'rb') as f: return pattern.findall(f.read().decode(errors='ignore')) def strings2ascii(strings): arr = [ord(c) for c in strings] return arr, len(arr) def clean_str(string): """ Tokenization/string cleaning for datasets. Original taken from https://github.com/yoonkim/CNN_sentence/blob/master/process_data.py """ string = re.sub(r"[^A-Za-z0-9(),!?\'\`]", " ", string) string = re.sub(r"\'s", " \'s", string) string = re.sub(r"\'ve", " \'ve", string) string = re.sub(r"n\'t", " n\'t", string) string = re.sub(r"\'re", " \'re", string) string = re.sub(r"\'d", " \'d", string) string = re.sub(r"\'ll", " \'ll", string) string = re.sub(r",", " , ", string) string = re.sub(r"!", " ! ", string) string = re.sub(r"\(", " \( ", string) string = re.sub(r"\)", " \) ", string) string = re.sub(r"\?", " \? ", string) string = re.sub(r"\s{2,}", " ", string) return string.strip().lower() logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s') n_features = 20000 n_components = 6 # Read dir file and single line in list files = read_dir('/home/mour/working/YaraGEN/webshelldata/uniqphp') # Convert To Vectorizer Transform With TFIDF based on Hashing Vectorizer hasher = HashingVectorizer(n_features=n_features, stop_words='english', alternate_sign=False, norm=None, binary=False) vectorizer = make_pipeline(hasher, TfidfTransformer()) X = vectorizer.fit_transform(files) # Dimensionality Reduction With LSA, also you can try with PCA svd = TruncatedSVD(n_components) normalizer = Normalizer(copy=False) lsa = make_pipeline(svd, normalizer) X = lsa.fit_transform(X) # Use SpectralClustering Clustering model = SpectralClustering(n_clusters=10, affinity='nearest_neighbors', assign_labels='kmeans') model.fit(X) labels = model.fit_predict(X) # from sklearn import manifold # X_embedded = manifold.TSNE(n_components=2).fit_transform(X) # plt.scatter(X_embedded[:,0],X_embedded[:,1],labels) # plt.show() # import hypertools as hyp # hyp.plot(X_embedded, '.', group=labels) # Save joblib.dump(model, 'spectral_clusering_webshell.pkl')
for i,x in enumerate(labels): if x == 1: print(i)
然后重新读一下文件,随便挑出来几个属于一类的看了下,效果还行。但是数据缺乏标签,如果有所有的数据都打了标签,想必能够得到一个更加精确的结果,更好的测试。
以下两篇有时间都要细读
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered:
No branches or pull requests
本来在看K-means (最最基础的聚类算法)和EM算法(具体看统计学习方法,此处就不列推导相关的了),在学习的过程中发现了Spectral Clustering的效果看起来更好。
从该图中不难看出其聚类效果并不是很好,未能准确的将中间部分完全分开。于是乎看到了教程中提到的Spectral Clustering的方法,也就是下图中所使用的算法,可以看到已经能够将数据准确的分开了。
关于Spectral Clustering 算法,这篇估计是经典中的经典,但是还没有看。只是尝试了下其用于对已知的webshell进行聚类的效果。因为如果直接在对未知样本进行分类的时候
采取多分类,显然会导致精度下降很多,但是当有需求判断这个webshell是哪一种时,这个方法就可以一试。以下代码采用sklearn编写。
然后重新读一下文件,随便挑出来几个属于一类的看了下,效果还行。但是数据缺乏标签,如果有所有的数据都打了标签,想必能够得到一个更加精确的结果,更好的测试。
References
以下两篇有时间都要细读
The text was updated successfully, but these errors were encountered: