-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
UniDA Protocol
This document describes the format of the UniDA Protocol messages managed by the UniDA library. This protocol is based on the Simple Message Protocol contained in Mytechia Commons which will be also explained.
Contents:
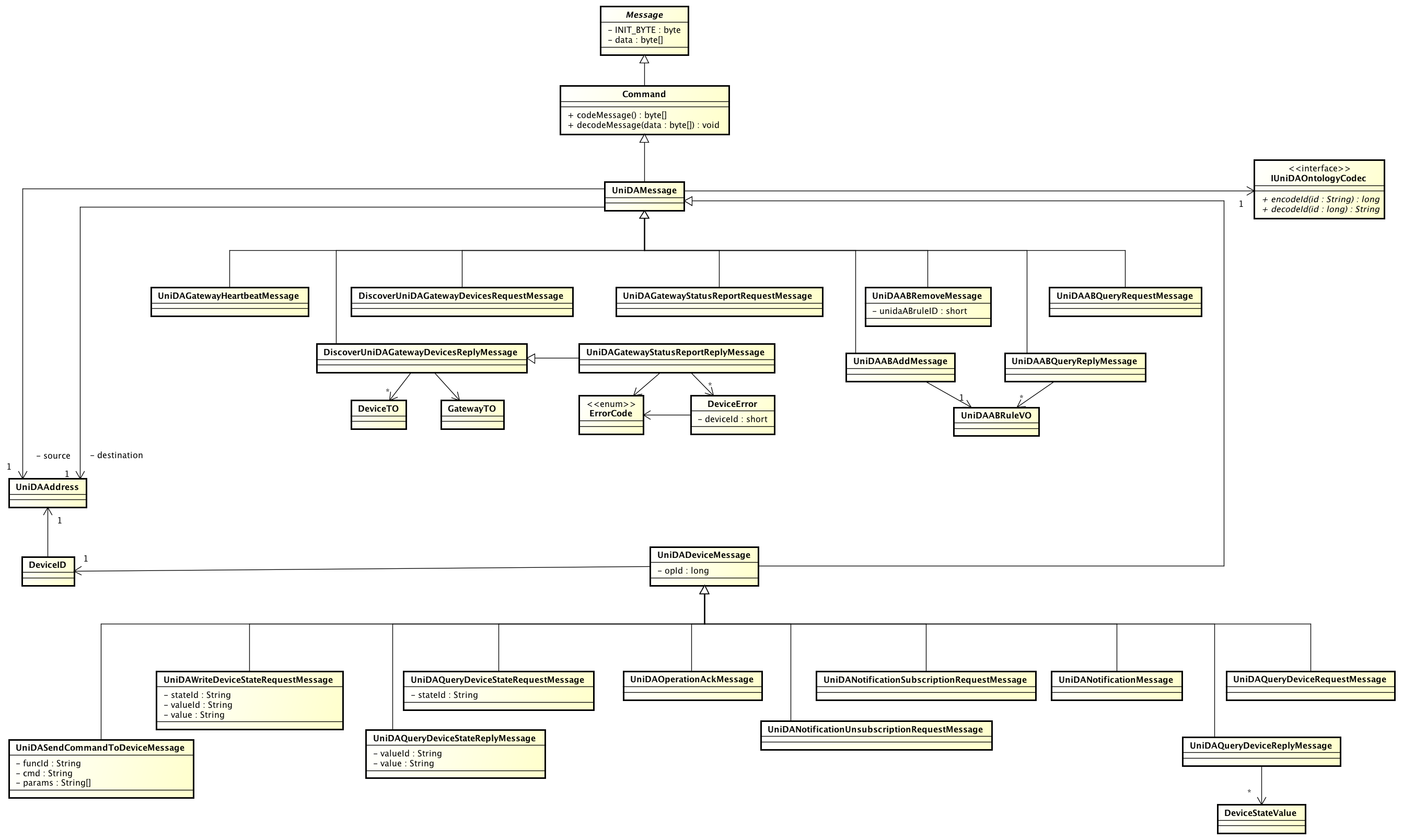
- Simple Message Protocol
- Message types
- Message relationships
-
UniDA Gateway Messages:
- Discover Gateway Devices, Request
- Discover Gateway Devices, Reply
- Heartbeat
- Gateway Status Report, Request
- Gateway Status Report, Reply
- Query Device States, Request
- Query Device States, Reply
- Autonomous Behaviour Add Rule
- Autonomous Behaviour Remove Rule
- Autonomous Behaviour Query, Request
- Autonomous Behaviour Query, Reply
- UniDA Device Messages:
Simple Message Protocol messages have always a fixed size header (8 bytes) and optionally a payload of variable length whose content structure is different for each kind of message.
Format:
| Init | Message type | Sequence number | Error code | Data size | Header checksum | Payload | Payload checksum | ||
| 1 byte | 1 byte | 1 byte | 1 byte | 2 bytes | 1 byte | variable | 1 byte | ||
Fields:
- Init byte: special byte that just marks the beginning of a message.
- Message type: identifies the type of the message.
- The sequence number is used to relate messages of the request/reply kind: the reply carries the same sequence number of the request message it is answering. It s auto-incremental, and cyclic.
- Error code: can be used to signal different states of error or non-normal execution.
- Data size: in number of bytes.
- Header checksum: calculated using a XOR with all the header bytes.
- Payload: actual content of the message, in case it s needed (some types of message don t use payload).
- Payload checksum: calculated using a XOR with all the payload bytes.
These are the types of messages handle by the UniDA Protocol:
| Generic ACK | 0x001 |
| Discover Gateway Devices, Request | 0x002 |
| Discover Gateway Devices- Reply | 0x003 |
| Gateway Heartbeat | 0x004 |
| Gateway Status Report, Request | 0x005 |
| Gateway Status Report, Reply | 0x006 |
| Query Device State, Request | 0x007 |
| Query Device State, Reply | 0x008 |
| Query Device States, Request | 0x009 |
| Query Device States, Reply | 0x010 |
| Send Command to Device | 0x011 |
| Subscribe, Request | 0x012 |
| Unsubscribe, Request | 0x013 |
| Notification | 0x014 |
| Write Device State, Request | 0x015 |
| Autonomous Behaviour: Add Rule | 0x017 |
| Autonomous Behaviour: Remove Rule | 0x018 |
| Autonomous Behaviour: Query, Request | 0x019 |
| Autonomous Behaviour: Query, Reply | 0x020 |
| Debug Init | 0x101 |
| Debug Data | 0x106 |
All UniDA messages share the need to hold the information about the source and destination of the message. So it can be considered like a second header, common to any UniDA message.
| Header | Src | Dest | Message payload | Cheksum |
| 7 bytes | 6 bytes | 6 bytes | Variable size | 1 byte |
Fields:
- The Simple Message Protocol header, already explained.
- UniDA address for the source.
- UniDA address for the destination.
- UniDA message payload, of variable size (some messages don t need payload at all).
- Simple Message Protocol checksum.
All gateway messages follow this format (the device messages do the same, but contain also a small additional "header").
This message is sent to ask an UniDA gateway for the information about the devices it handles.
| Header | Addresses | Cheksum |
| 7 bytes | 12 bytes | 1 byte |
This message needs no additional payload.
This message contains the full information about the gateway, its device IOs and the devices the gateway contains. Its size is variable: the gateway data and each device chunk include string fields and both the IOs and device lists have a number of elements.
| Header | Addresses | Gateway | N | Device IOs | N | Devices | Cheksum |
| 7 bytes | 12 bytes | Variable size | 2 bytes | Variable size | 2 bytes | Variable size | 1 byte |
The gateway chunk contains the following fields:
| Gateway data | |||
| Class | Model | Manufacturer | Op. State |
| 4 bytes | Variable size | Variable size | 2 bytes |
Each device IO contains the following fields:
| Device IO | ||
| IO id | N | Manufacturer |
| 2 bytes | 2 bytes | Variable size |
And each UniDA device contains the following fields:
| Device | |||||||
| Id | Class | Model | Manufacturer | Description | Op. State | N | IOs |
| 2 bytes | 4 bytes | Variable size | Variable size | Variable size | 2 bytes | 2 bytes | Variable size |

UniDA wiki by Mytech Ingenieria Aplicada is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.