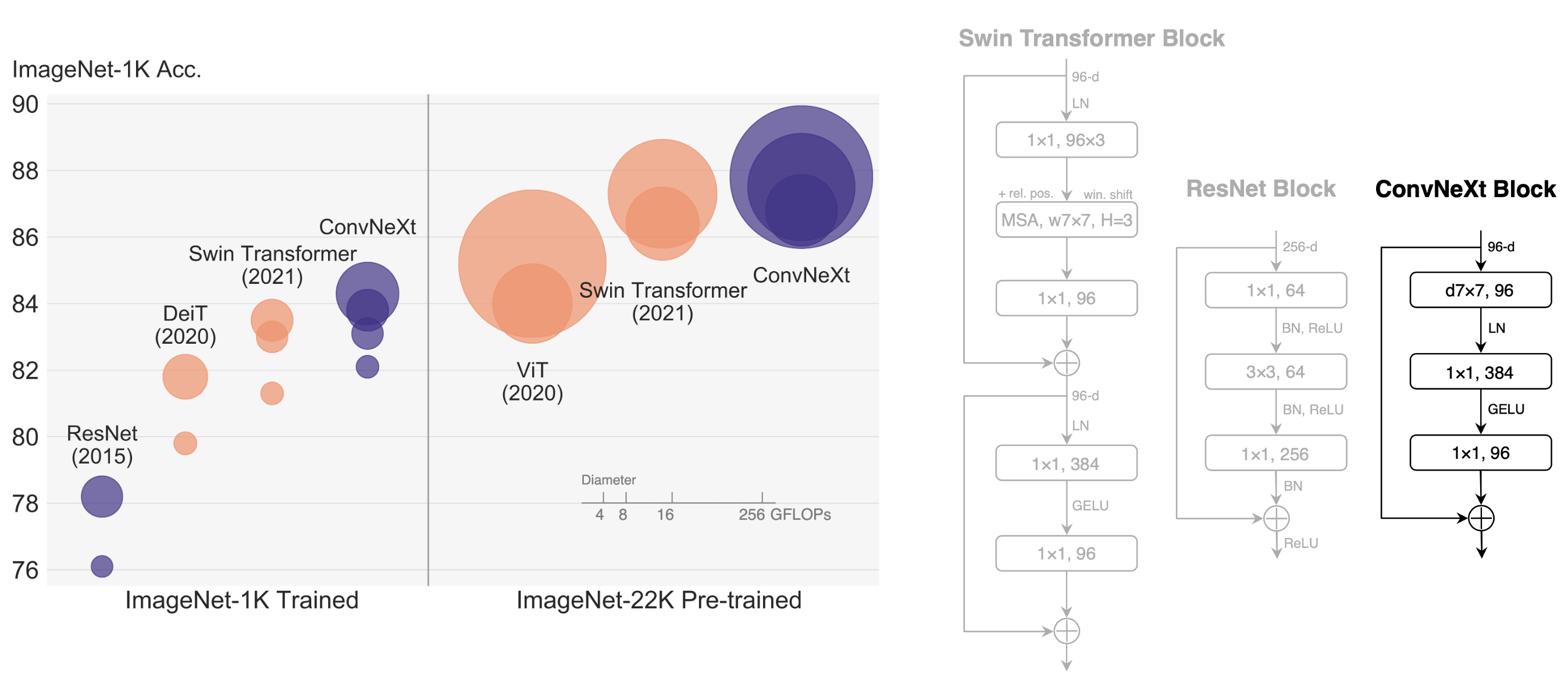
ConvNeXt is initially described in A ConvNet for the 2020s, which is a pure convolutional model (ConvNet), inspired by the design of Vision Transformers. The ConvNeXt has the pyramid structure and achieve competitive performance on various vision tasks, with simplicity and efficiency.
Show the paper's abstract
The "Roaring 20s" of visual recognition began with the introduction of Vision Transformers (ViTs), which quickly superseded ConvNets as the state-of-the-art image classification model. A vanilla ViT, on the other hand, faces difficulties when applied to general computer vision tasks such as object detection and semantic segmentation. It is the hierarchical Transformers (e.g., Swin Transformers) that reintroduced several ConvNet priors, making Transformers practically viable as a generic vision backbone and demonstrating remarkable performance on a wide variety of vision tasks. However, the effectiveness of such hybrid approaches is still largely credited to the intrinsic superiority of Transformers, rather than the inherent inductive biases of convolutions. In this work, we reexamine the design spaces and test the limits of what a pure ConvNet can achieve. We gradually "modernize" a standard ResNet toward the design of a vision Transformer, and discover several key components that contribute to the performance difference along the way. The outcome of this exploration is a family of pure ConvNet models dubbed ConvNeXt. Constructed entirely from standard ConvNet modules, ConvNeXts compete favorably with Transformers in terms of accuracy and scalability, achieving 87.8% ImageNet top-1 accuracy and outperforming Swin Transformers on COCO detection and ADE20K segmentation, while maintaining the simplicity and efficiency of standard ConvNets.
Predict image
>>> import torch
>>> from mmcls.apis import get_model, inference_model
>>>
>>> model = get_model('convnext-tiny_32xb128_in1k', pretrained=True)
>>> predict = inference_model(model, 'demo/demo.JPEG')
>>> print(predict['pred_class'])
sea snake
>>> print(predict['pred_score'])
0.8915778398513794Use the model
>>> import torch
>>> from mmcls.apis import get_model
>>>
>>> model = get_model('convnext-tiny_32xb128_in1k', pretrained=True)
>>> inputs = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224))
>>> # To get classification scores.
>>> out = model(inputs)
>>> print(out.shape)
torch.Size([1, 1000])
>>> # To extract features.
>>> outs = model.extract_feat(inputs)
>>> print(outs[0].shape)
torch.Size([1, 768])Train/Test Command
Place the ImageNet dataset to the data/imagenet/ directory, or prepare datasets according to the docs.
Train:
python tools/train.py configs/convnext/convnext-tiny_32xb128_in1k.py
Test:
```shell
python tools/test.py configs/convnext/convnext-tiny_32xb128_in1k.py https://download.openmmlab.com/mmclassification/v0/convnext/convnext-tiny_3rdparty_32xb128-noema_in1k_20220222-2908964a.pthFor more configurable parameters, please refer to the API.
The pre-trained models on ImageNet-1k or ImageNet-21k are used to fine-tune on the downstream tasks.
| Model | Training Data | Params(M) | Flops(G) | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ConvNeXt-T (convnext-tiny_32xb128-noema_in1k) |
ImageNet-1k | 28.59 | 4.46 | 81.95 | 95.89 | model |
ConvNeXt-S (convnext-small_32xb128-noema_in1k) |
ImageNet-1k | 50.22 | 8.69 | 83.21 | 96.48 | model |
ConvNeXt-B (convnext-base_32xb128-noema_in1k) |
ImageNet-1k | 88.59 | 15.36 | 83.64 | 96.61 | model |
ConvNeXt-B* (convnext-base_3rdparty-noema_in1k) |
ImageNet-1k | 88.59 | 15.36 | 83.71 | 96.60 | model |
ConvNeXt-B* (convnext-base_3rdparty_in21k) |
ImageNet-21k | 88.59 | 15.36 | N/A | N/A | model |
ConvNeXt-L* (convnext-large_3rdparty_in21k) |
ImageNet-21k | 197.77 | 34.37 | N/A | N/A | model |
ConvNeXt-XL* (convnext-xlarge_3rdparty_in21k) |
ImageNet-21k | 350.20 | 60.93 | N/A | N/A | model |
Models with * are converted from the official repo.
| Model | Pretrain | resolution | Params(M) | Flops(G) | Top-1 (%) | Top-5 (%) | Config | Download |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ConvNeXt-T (convnext-tiny_32xb128_in1k) |
From scratch | 224x224 | 28.59 | 4.46 | 82.14 | 96.06 | config | model | log |
ConvNeXt-T* (convnext-tiny_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k) |
ImageNet-21k | 224x224 | 28.59 | 4.46 | 82.90 | 96.62 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-T* (convnext-tiny_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k-384px) |
ImageNet-21k | 384x384 | 28.59 | 13.13 | 84.11 | 97.14 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-S (convnext-small_32xb128_in1k) |
From scratch | 224x224 | 50.22 | 8.69 | 83.16 | 96.56 | config | model | log |
ConvNeXt-S* (convnext-small_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k) |
ImageNet-21k | 224x224 | 50.22 | 8.69 | 84.59 | 97.41 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-S* (convnext-small_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k-384px) |
ImageNet-21k | 384x384 | 50.22 | 25.58 | 85.75 | 97.88 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-B (convnext-base_32xb128_in1k) |
From scratch | 224x224 | 88.59 | 15.36 | 83.66 | 96.74 | config | model | log |
ConvNeXt-B* (convnext-base_3rdparty_in1k) |
From scratch | 224x224 | 88.59 | 15.36 | 83.85 | 96.74 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-B (convnext-base_3rdparty_in1k-384px)* |
From scratch | 384x384 | 88.59 | 45.21 | 85.10 | 97.34 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-B* (convnext-base_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k) |
ImageNet 21k | 224x224 | 88.59 | 15.36 | 85.81 | 97.86 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-B* (convnext-base_in21k-pre-3rdparty_in1k-384px) |
ImageNet-21k | 384x384 | 88.59 | 45.21 | 86.82 | 98.25 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-L* (convnext-large_3rdparty_in1k) |
From scratch | 224x224 | 197.77 | 34.37 | 84.30 | 96.89 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-L* (convnext-large_3rdparty_in1k-384px) |
From scratch | 384x384 | 197.77 | 101.10 | 85.50 | 97.59 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-L* (convnext-large_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k) |
ImageNet 21k | 224x224 | 197.77 | 34.37 | 86.61 | 98.04 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-L (convnext-large_in21k-pre-3rdparty_in1k-384px)* |
ImageNet-21k | 384x384 | 197.77 | 101.10 | 87.46 | 98.37 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-XL* (convnext-xlarge_in21k-pre_3rdparty_in1k) |
ImageNet 21k | 224x224 | 350.20 | 60.93 | 86.97 | 98.20 | config | model |
ConvNeXt-XL* (convnext-xlarge_in21k-pre-3rdparty_in1k-384px) |
ImageNet-21k | 384x384 | 350.20 | 179.20 | 87.76 | 98.55 | config | model |
Models with * are converted from the official repo. The config files of these models are only for inference. We don't ensure these config files' training accuracy and welcome you to contribute your reproduction results.
@Article{liu2022convnet,
author = {Zhuang Liu and Hanzi Mao and Chao-Yuan Wu and Christoph Feichtenhofer and Trevor Darrell and Saining Xie},
title = {A ConvNet for the 2020s},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.03545},
year = {2022},
}