-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 573
Commit
This commit does not belong to any branch on this repository, and may belong to a fork outside of the repository.
docs: add chinese translation for Python docs (#455)
* docs: add chinese translation
- Loading branch information
Showing
2 changed files
with
115 additions
and
4 deletions.
There are no files selected for viewing
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| Original file line number | Diff line number | Diff line change |
|---|---|---|
| @@ -0,0 +1,109 @@ | ||
| ### Pyroscope Rideshare 示例 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| #### _用其他语言阅读此文。_ | ||
| <kbd>[English](README.md)</kbd> | ||
|
|
||
| 注意:关于Pyroscope pip包的文档,请访问[我们的网站](https://pyroscope.io/docs/python/) | ||
| ## 背景介绍 | ||
|
|
||
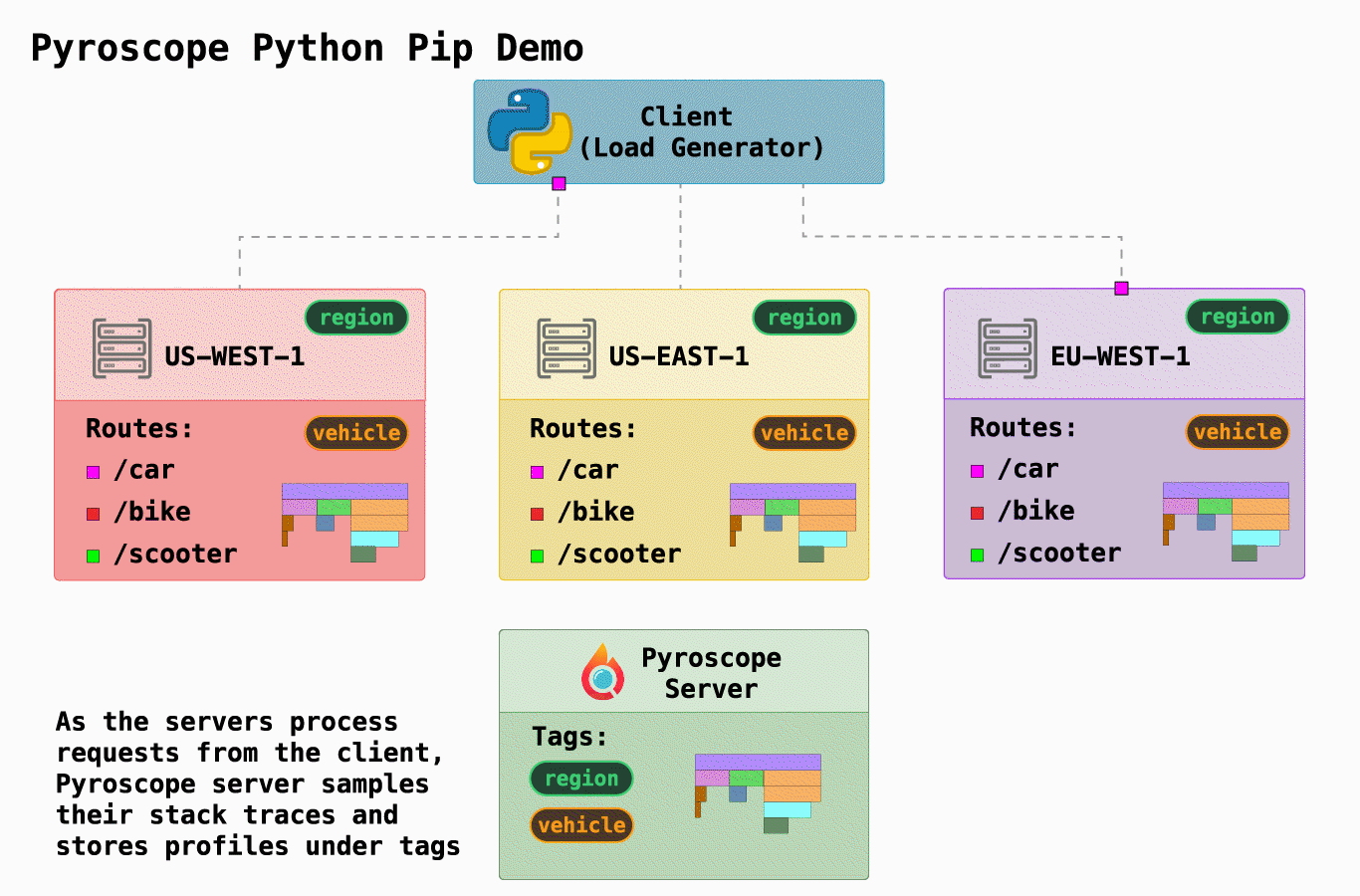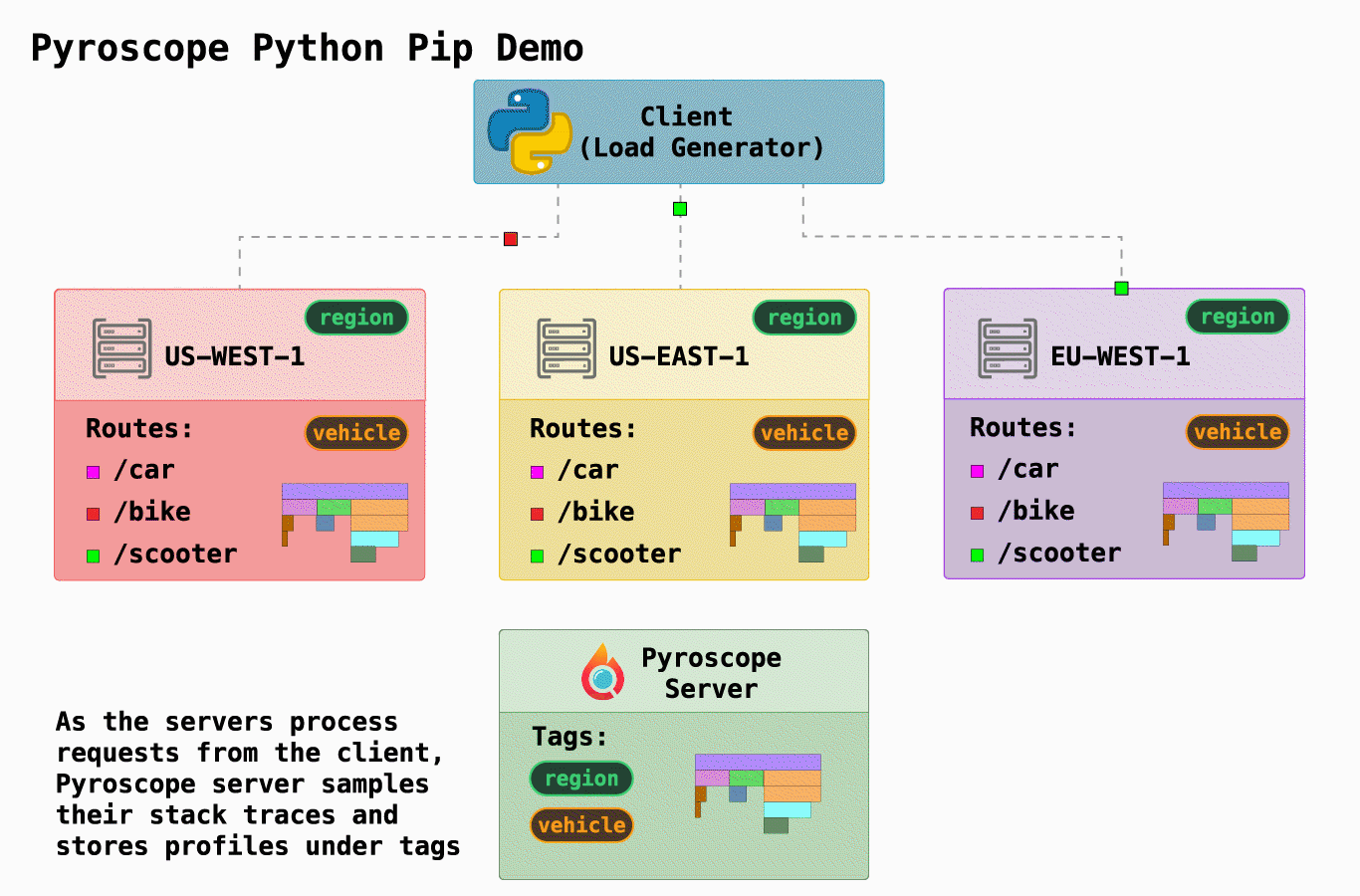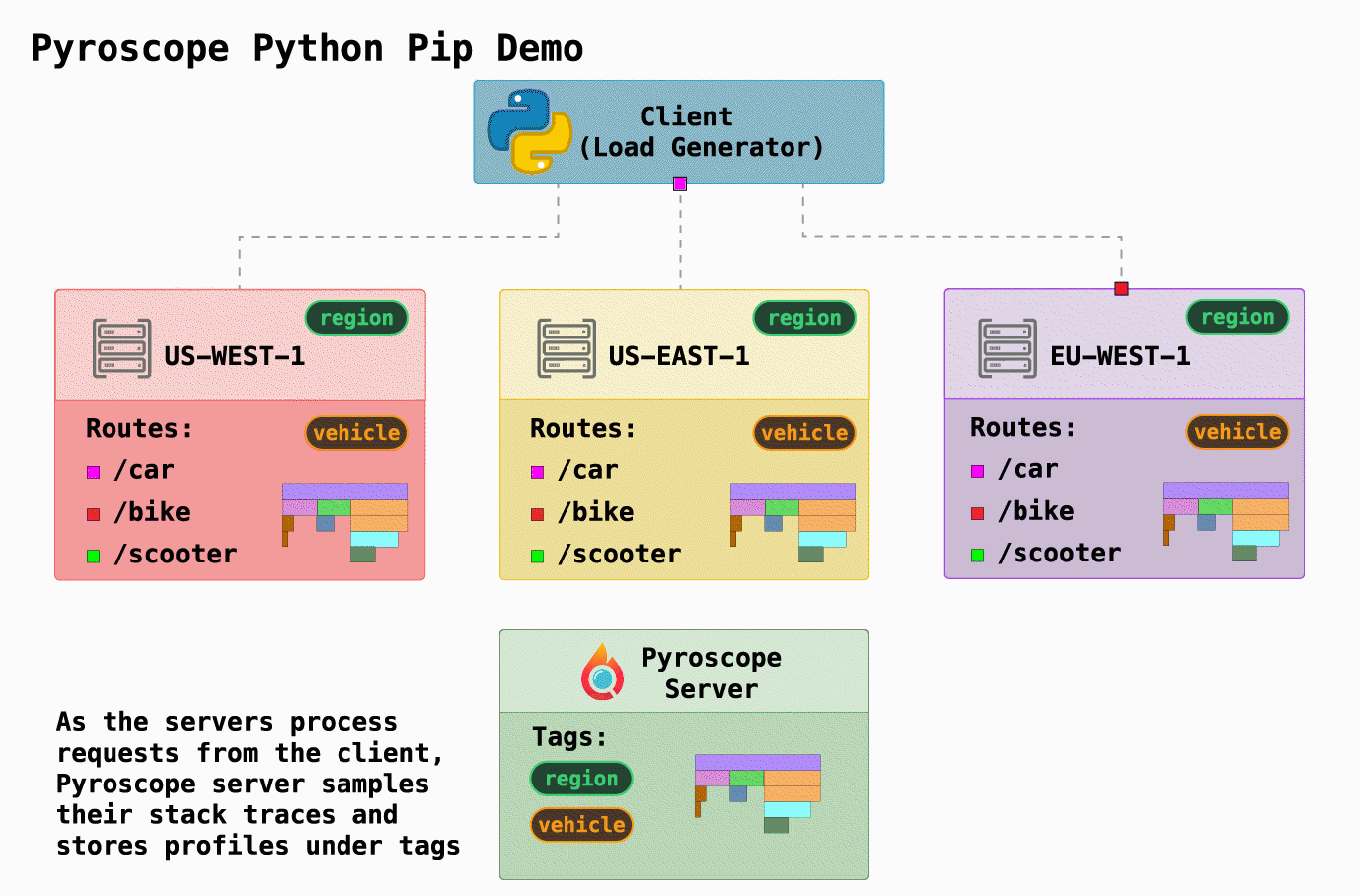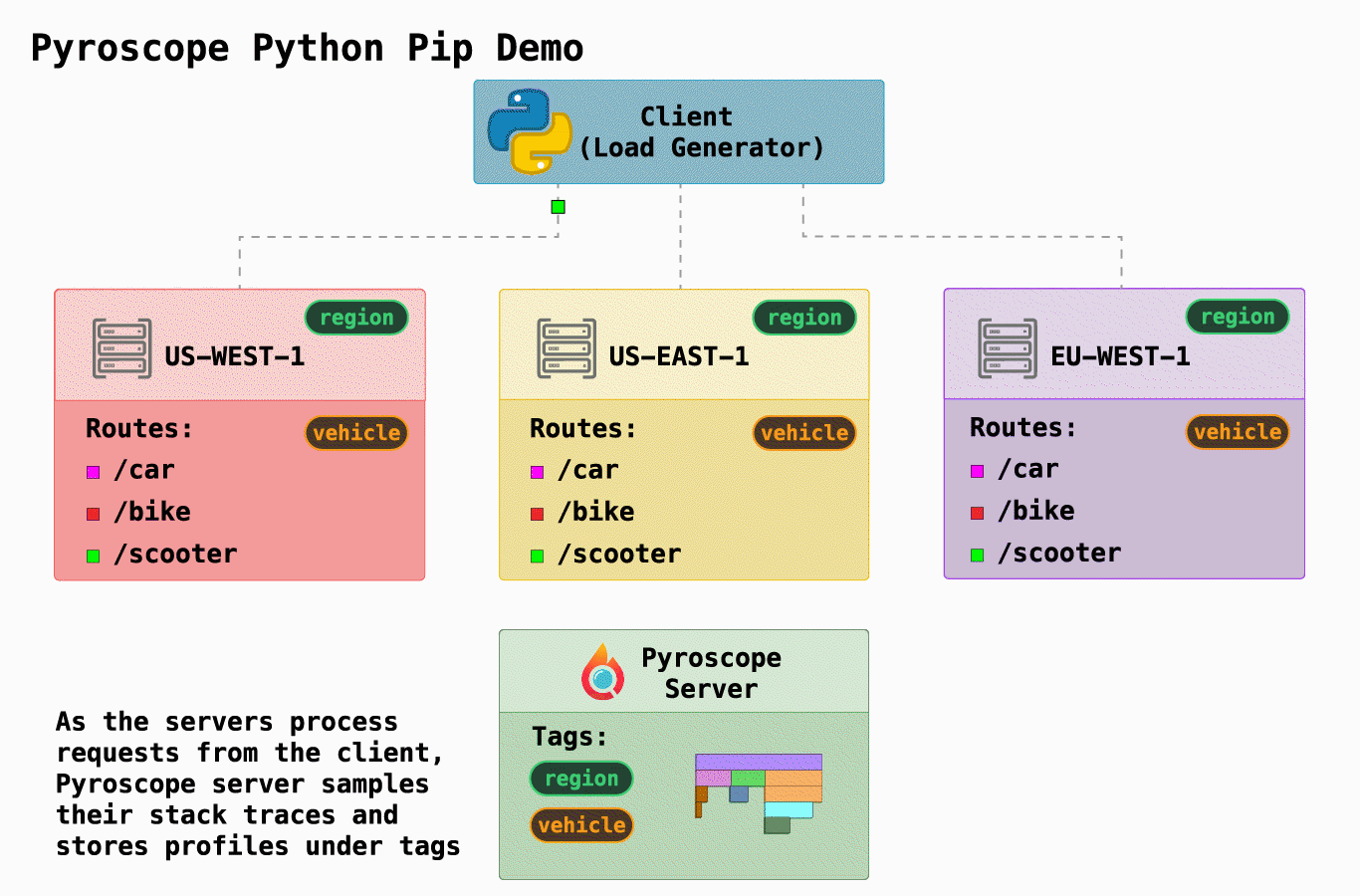
| 在这个例子中,我们展示了 Pyroscope 的一个简化的基本用例。我们模拟了一个 "骑行共享" 公司,它有三个请求端点,可以在`server.py`中找到: | ||
| - `/bike`:调用`order_bike(search_radius)`函数来订购一辆自行车。 | ||
| - `/car` : 调用`order_car(search_radius)`函数来订购汽车。 | ||
| - `/scooter` : 调用`order_scooter(search_radius)'函数来订购摩托车。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们还模拟了在3个不同地区运行3个不同的服务器(通过[docker-compose.yml](https://github.com/pyroscope-io/pyroscope/blob/main/examples/python/docker-compose.yml)) | ||
| - us-east-1 | ||
| - us-west-1 | ||
| - eu-west-1 | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Pyroscope最有用的功能之一是能够以对你有意义的方式来标记你的数据。在这种情况下,我们有两个自然划分,因此我们 "标记(tag)" 我们的数据以表示这些: | ||
| - `region`:静态地标记运行代码的服务器的区域 | ||
| - `vehicle`: 动态标记端点(类似于标记控制器轨道的方式) | ||
|
|
||
| ## 标记静态区域 | ||
| 标记一些静态的东西,如`区域`,可以在初始化代码中的`config.tags`变量中完成: | ||
| ``` | ||
| pyroscope.configure( | ||
| app_name = "ride-sharing-app", | ||
| server_address = "http://pyroscope:4040", | ||
| tags = { | ||
| "region": f'{os.getenv("REGION")}', # 根据环境变量标记该区域 | ||
| } | ||
| ) | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
| ## 在函数中动态地添加标签 | ||
| 像我们对 `vehicle` 标签所做的那样,可以在我们的实用程序 `find_nearest_vehicle()` 函数中使用 `with pyroscope.tag_wrapper()` 上下文区块来完成更动态的标记 | ||
| ``` | ||
| def find_nearest_vehicle(n, vehicle): | ||
| with pyroscope.tag_wrapper({ "vehicle": vehicle}): | ||
| i = 0 | ||
| start_time = time.time() | ||
| while time.time() - start_time < n: | ||
| i += 1 | ||
| ``` | ||
| 这个上下文区块的作用是: | ||
| 1. 添加标签 `{ "vehicle" => "car" }` | ||
| 2. 执行`find_nearest_vehicle()`函数 | ||
| 3. 在该块结束之前,它将(在后台)从应用程序中删除`{ "vehicle" => "car" }`,因为该上下文区块已经完成 | ||
|
|
||
| ## 例子中产生的火焰图/性能结果 | ||
| ### 运行这个例子 | ||
| 要运行该例子,请运行以下命令: | ||
| ``` | ||
| # 拉取最新的 pyroscope 镜像: | ||
| docker pull pyroscope/pyroscope:latest | ||
| # 运行示例项目: | ||
| docker-compose up --build | ||
| # 重置数据库(非必需): | ||
| # docker-compose down | ||
| ``` | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
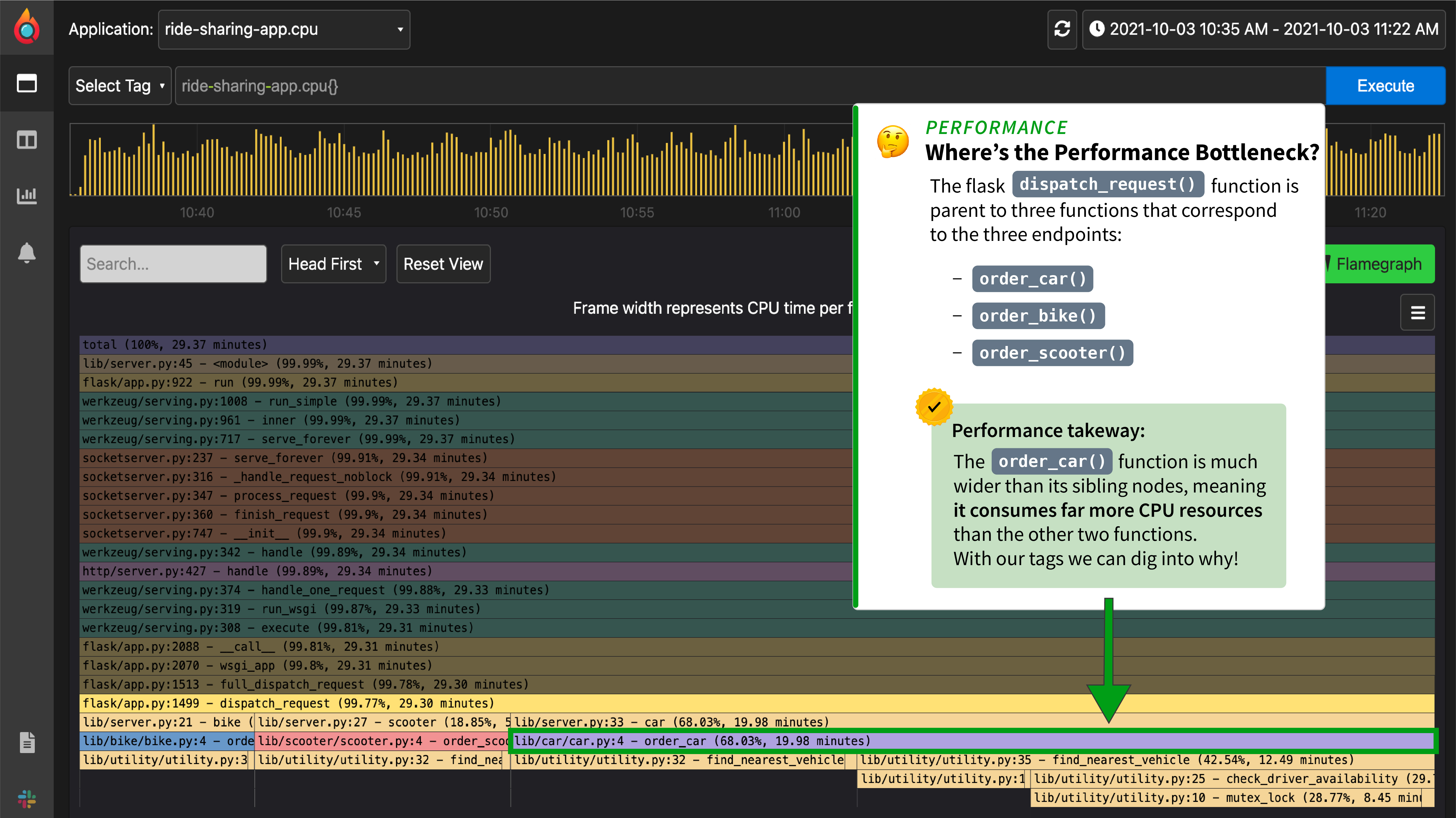
| 这个例子要做的是运行上面提到的所有代码,同时向3个服务器以及它们各自的3个端点发送一些模拟负载。如果你从下拉菜单中选择我们的应用程序:`rid-sharing-app.cpu`,你应该看到一个看起来像这样的火焰图(见下文)。在我们给予20-30秒的时间来更新火焰图之后,点击刷新按钮,我们看到火焰图底部的3个函数占用的CPU资源与它们各自的`search_radius`参数 _大小成正比_。 | ||
| ## 性能瓶颈在哪里? | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| 当分析从你的应用程序输出的剖析文件时,第一步是注意 _最大的节点_,这是你的应用程序花费最多资源的地方。在这个例子中,它恰好是 `order_car` 函数。 | ||
|
|
||
| 使用 Pyroscope 包的好处是,现在我们可以进一步调查为什么 `order_car()` 函数有问题。同时标记 `region`和 `vehicle`使我们能够测试两个好的假设: | ||
| - `/car` 端点的代码出了问题 | ||
| - 我们的一个区域出了问题 | ||
|
|
||
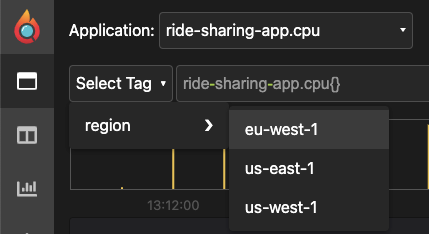
| 为了分析这一点,我们可以从 "Select Tag" 下拉菜单中选择一个或多个标签: | ||
|
|
||
|  | ||
|
|
||
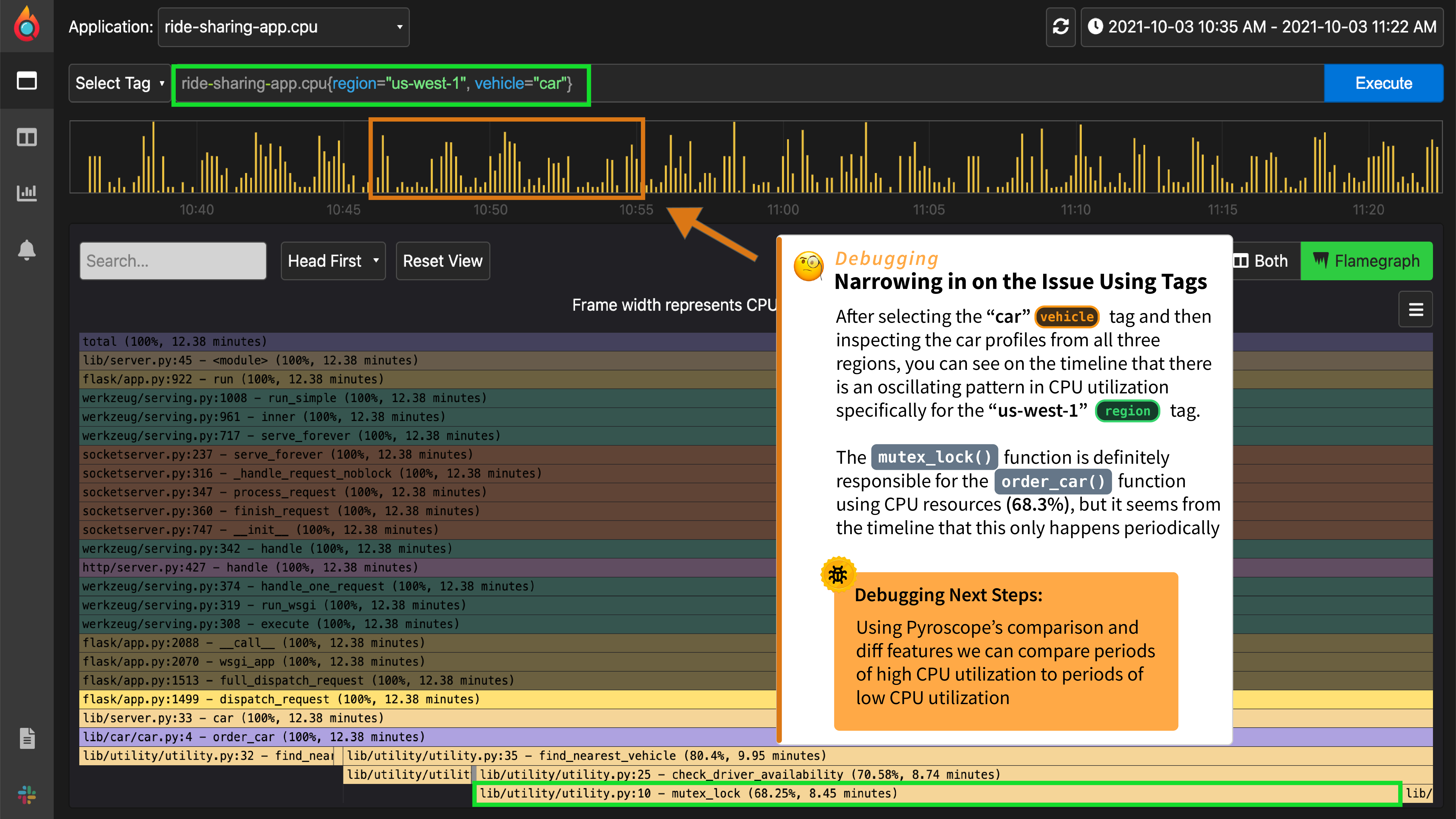
| ## 使用标签缩小问题的范围 | ||
| 知道`order_car()`函数有问题,我们就自动选择该标签。然后,在检查了多个 `region` 标签后,通过查看时间线,可以清楚地看到 `us-west-1`区域存在问题,它在高cpu时间和低cpu时间之间交替出现。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们还可以看到,`mutex_lock()`函数在这段时间内几乎消耗了70%的CPU资源。 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
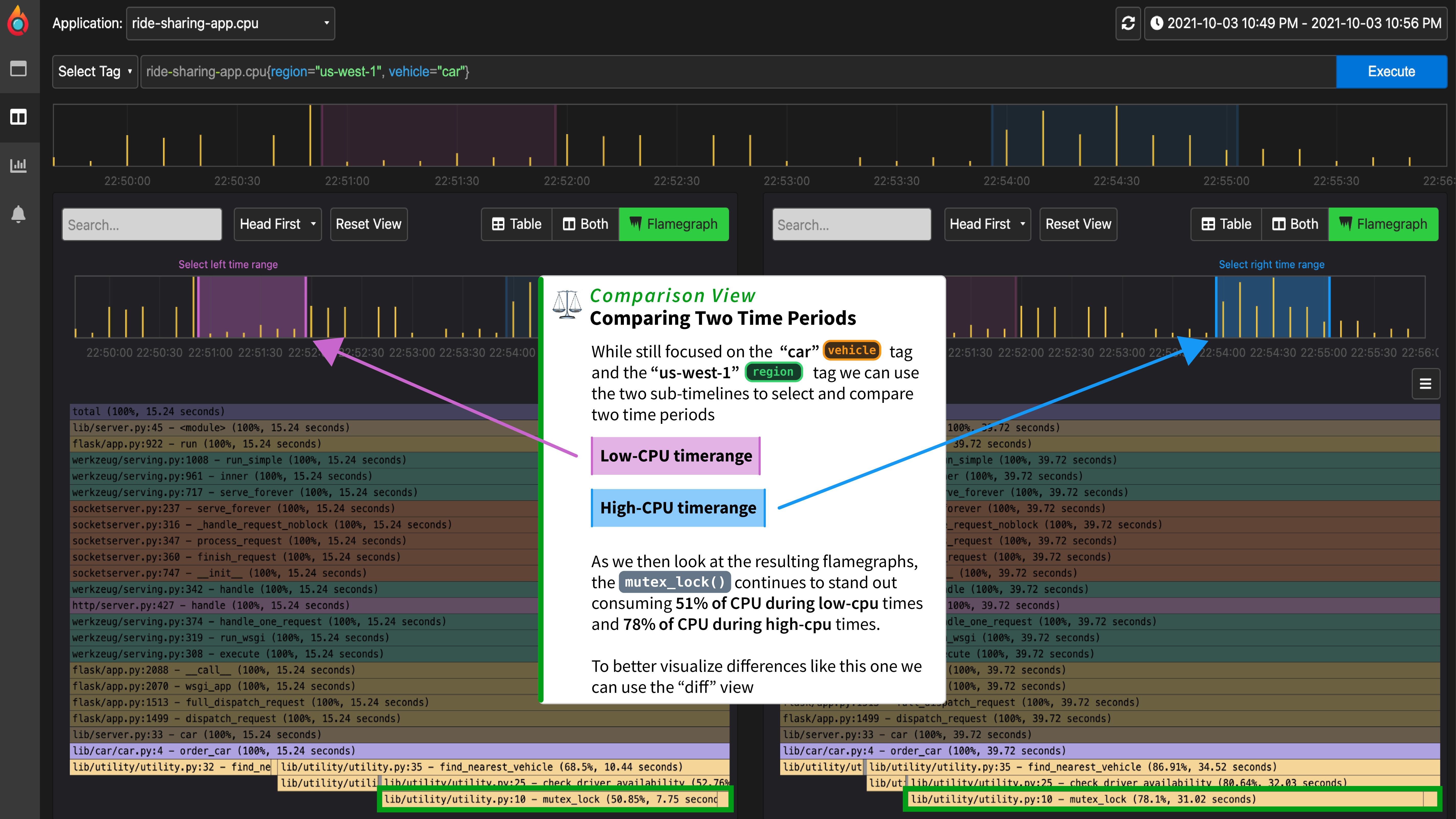
| ## 比较两个时间段的情况 | ||
| 使用 Pyroscope 的 "比较视图",我们实际上可以从时间线上选择两个不同的时间范围来比较所产生的火焰图。左边时间线上的粉红色部分结果是左边的火焰图,右边的蓝色部分代表右边的火焰图。 | ||
| 当我们选择一个低CPU利用率的时期和一个高CPU利用率的时期时,我们可以看到`mutex_lock()`函数有明显不同的行为,它在低CPU时期占用**51%的CPU**,在高CPU时期占用**78%的CPU**。 | ||
|  | ||
|
|
||
| ## 可视化两个火焰图之间的差异 | ||
| 虽然在 _这个例子_ 中,差异足以在比较视图中看到,但有时两个火焰图之间的差异在相互叠加的情况下会更直观。在不改变任何参数的情况下,我们可以简单地选择差异视图选项卡,看到用彩色编码的差异火焰图表示的差异。 | ||
| 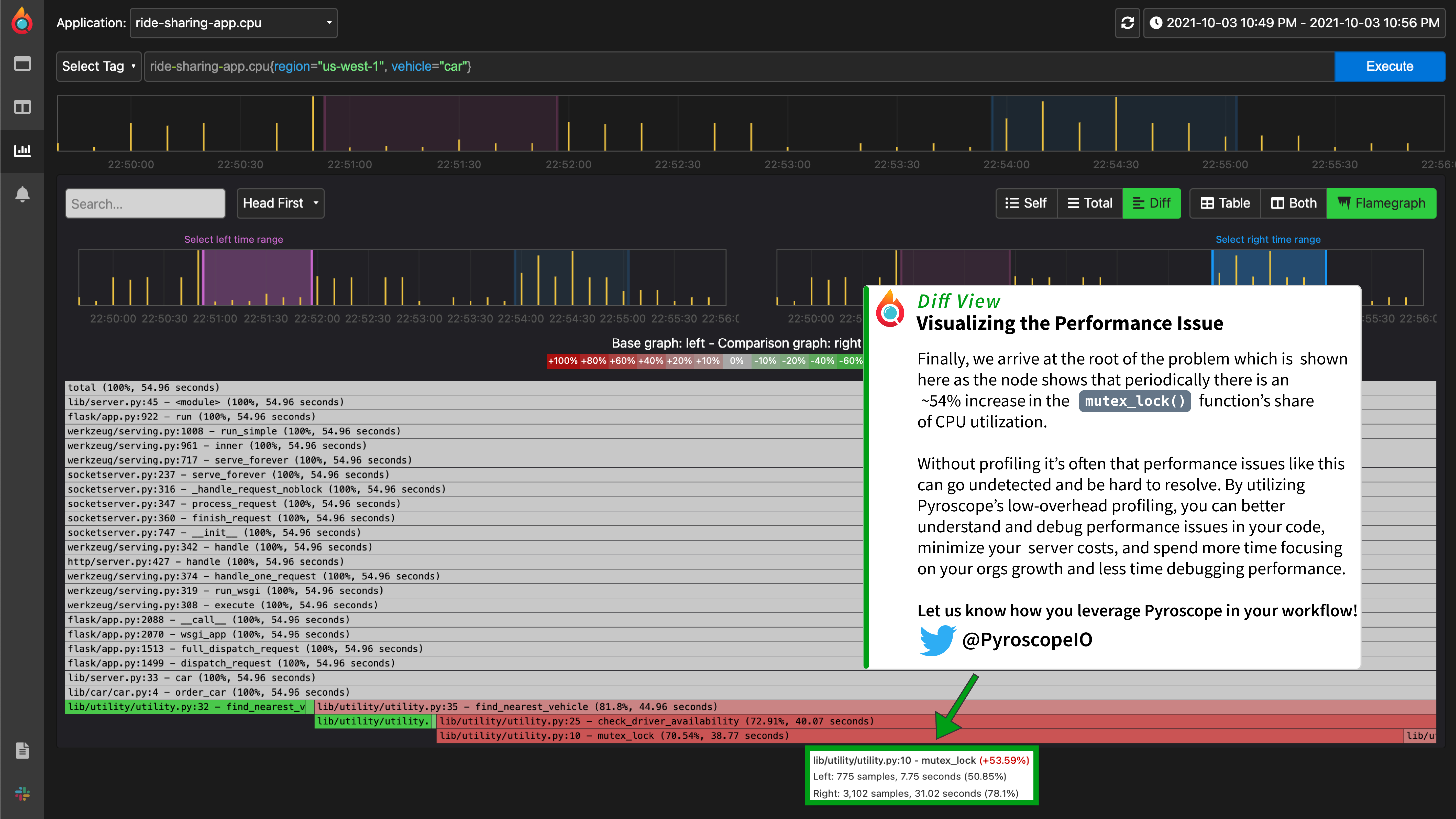 | ||
|
|
||
| ### 更多用例 | ||
| 我们一直在与几个不同的公司测试这一功能,我们看到一些公司标记其业务数据的方式: | ||
| - 标记控制器 | ||
| - 标记区域 | ||
| - 从redis / sidekiq / rabbitmq队列中标记作业 | ||
| - 标记提交 | ||
| - 标记预发/生产环境 | ||
| - 标记其测试套件的不同部分 | ||
| - 等等... | ||
|
|
||
| ### 未来路线图 | ||
| 我们希望你能尝试一下这个例子,看看你能用什么方式来适配你的 python 应用。持续剖析已经成为监测和调试性能问题的一个越来越流行的工具(可以说是可观察性的第四个支柱)。 | ||
|
|
||
| 我们希望通过增加与流行工具的集成、内存分析等内容来继续改进这个pip包,我们很想听听 _你希望看到的功能_。 |