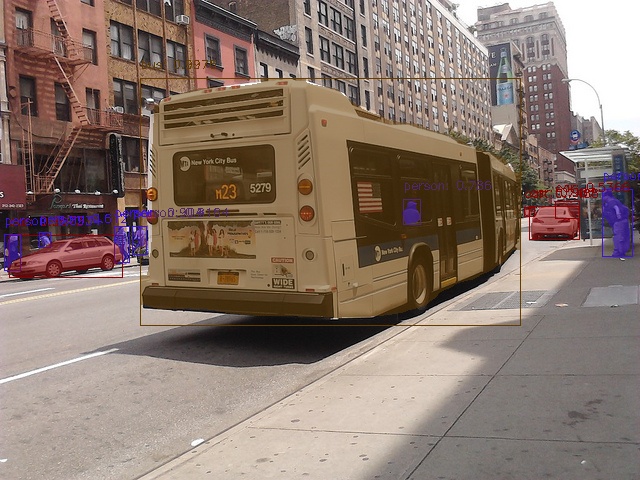
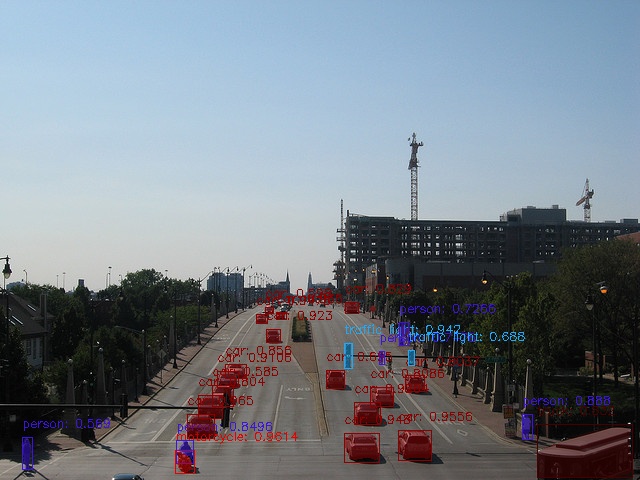
This document describes the usage of AIT for detectron2 vision models such as mask RCNN and faster RCNN.
For an end-to-end example with the API, see prepare_and_run_rcnn.sh which covers how to prepare and run inference with mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.
-
Pick a model and its config file from
configs, for example,mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.yaml. -
Build the AIT Model by running
compile_model.pywith the config file, for example,
cfg=examples/02_detectron2/configs/mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.yaml
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7 python3 examples/02_detectron2/compile_model.py \
--config $cfg \
--batch 1
All parameters in the built AIT model are not initialized, and therefore are filled with random values. We will initialize these parameters in the following step (i.e., exporting the weights of the pre-trained model to the AIT model). Check tmp/mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN/params.json for the list of parameters in the AIT model and their shapes.
- For example, download Detectron2
mask_rcnn_R_50_FPNpre-trained model and save it totmp/pt_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pkl:
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/COCO-InstanceSegmentation/mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x/137849600/model_final_f10217.pkl -O tmp/pt_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pkl
- Export the weights from the pre-trained model to AIT model by running
tools/convert_pt2ait.py:
python3 examples/02_detectron2/tools/convert_pt2ait.py \
--d2-weight tmp/pt_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pkl \
--ait-weight tmp/ait_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pt \
--model-name mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN
The weights are exported to AIT and saved as tmp/ait_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pt for inference run.
- For example, download the COCO 2017 Dataset:
mkdir -p ~/.torch/datasets/coco
wget https://dl.fbaipublicfiles.com/detectron2/annotations/coco/val2017_100.tgz -O ~/.torch/datasets/coco/val2017_100.tgz
tar xzf ~/.torch/datasets/coco/val2017_100.tgz -C ~/.torch/datasets/coco && rm -f ~/.torch/datasets/coco/val2017_100.tgz
- Run inference of the AIT model on the inputs with
demo.py:
python3 examples/02_detectron2/demo.py \
--weight tmp/ait_mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.pt \
--config examples/02_detectron2/configs/mask_rcnn_R_50_FPN.yaml \
--batch 1 --input "~/.torch/datasets/coco/val2017/*.jpg" \
--confidence-threshold 0.5 \
--display \
--cudagraph
AIT requires to do profiling to decide best algorithms for CUTLASS and CK.
To enable multiple GPUs profiling, set the environment variable CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES on NVIDIA platform and HIP_VISIBLE_DEVICES on AMD platform with available GPU ids.
PT = PyTorch 1.12 Eager
- Input size: 448x608
| Batch size | PT Latency (ms) | PT FPS | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21.70 | 46.09 | 4.40 | 227.27 |
| 2 | 29.71 | 67.32 | 6.68 | 299.40 |
| 4 | 35.67 | 112.13 | 11.12 | 359.71 |
| 8 | 59.71 | 133.98 | 22.24 | 359.71 |
| 16 | 112.91 | 141.70 | 36.64 | 436.68 |
| 32 | 224.24 | 142.70 | 71.04 | 450.45 |
| 64 | 448.84 | 142.59 | 140.16 | 456.62 |
- Input size: 800x1344
| Batch size | PT Latency (ms) | PT FPS | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.99 | 43.50 | 8.50 | 117.65 |
| 2 | 34.48 | 58.01 | 13.42 | 149.03 |
| 4 | 65.00 | 61.54 | 22.88 | 174.83 |
| 8 | 125.25 | 63.87 | 41.44 | 193.05 |
| 16 | 246.49 | 64.91 | 78.56 | 203.67 |
| 32 | 503.21 | 63.59 | 154.56 | 207.04 |
| 64 | OOM | OOM | 304.64 | 210.08 |
PT = PyTorch 1.12 Eager
- Input size: 448x608
| Batch size | PT Latency (ms) | PT FPS | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 24.75 | 40.41 | 10.63 | 94.07 |
| 2 | 29.28 | 68.30 | 15.96 | 125.31 |
| 4 | 42.45 | 94.24 | 26.24 | 152.44 |
| 8 | 79.73 | 100.34 | 51.04 | 156.74 |
| 16 | 141.84 | 112.81 | 89.12 | 179.53 |
| 32 | 284.39 | 112.52 | 161.92 | 197.63 |
| 64 | 600.84 | 106.52 | Error | Error |
- Input size: 800x1344
| Batch size | PT Latency (ms) | PT FPS | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26.80 | 37.31 | 19.23 | 52.00 |
| 2 | 43.61 | 45.86 | 30.28 | 66.05 |
| 4 | 98.88 | 40.45 | 51.56 | 77.58 |
| 8 | 189.45 | 42.23 | 98.80 | 80.97 |
| 16 | 389.94 | 41.03 | 177.28 | 90.25 |
| 32 | 807.22 | 39.64 | 333.44 | 95.97 |
| 64 | 1768.66 | 36.19 | Error | Error |
- Input size: 448x608
| Batch size | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | 12.78 | 156.49 |
| 4 | 20.66 | 193.61 |
| 8 | 32.16 | 248.76 |
| 16 | 61.52 | 260.08 |
| 32 | 106.08 | 301.66 |
| 64 | 194.24 | 329.49 |
- Input size: 800x1344
| Batch size | AIT Latency (ms) | AIT FPS |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||
| 2 | 22 | 90.91 |
| 4 | 34 | 117.65 |
| 8 | 55.52 | 144.09 |
| 16 | 104.48 | 153.14 |
| 32 | 190.24 | 168.21 |
| 64 | 362.88 | 176.37 |
- For NVIDIA A100, our test cluster doesn't allow to lock frequency. We make warm up longer to collect more stable results, but it is expected to have small variance to the results with locked frequency.
- To benchmark MI-250, the first step is to run
python3 benchmark_ait.pyto generate all necessary model dynamic library files with single GCD. Then run./benchmark_mi250.sh {batch_size}to simulate data parallel execution on 2 GCDs, each GCD is processing half of the batch. - To benchmark MI-250 1 GCD, we lock the frequency with command
rocm-smi -d x --setperfdeterminism 1700, wherexis the GPU id. - To benchmark MI-250 2 GCDs, we observed performance regression with rocm perf-determ mode. The 2 GCDs number is running without perf-determ mode set with command
rocm-smi -d x --resetperfdeterminism, wherexis the GPU id. - Performance results are what we can reproduced. It should not be used for other purposes.