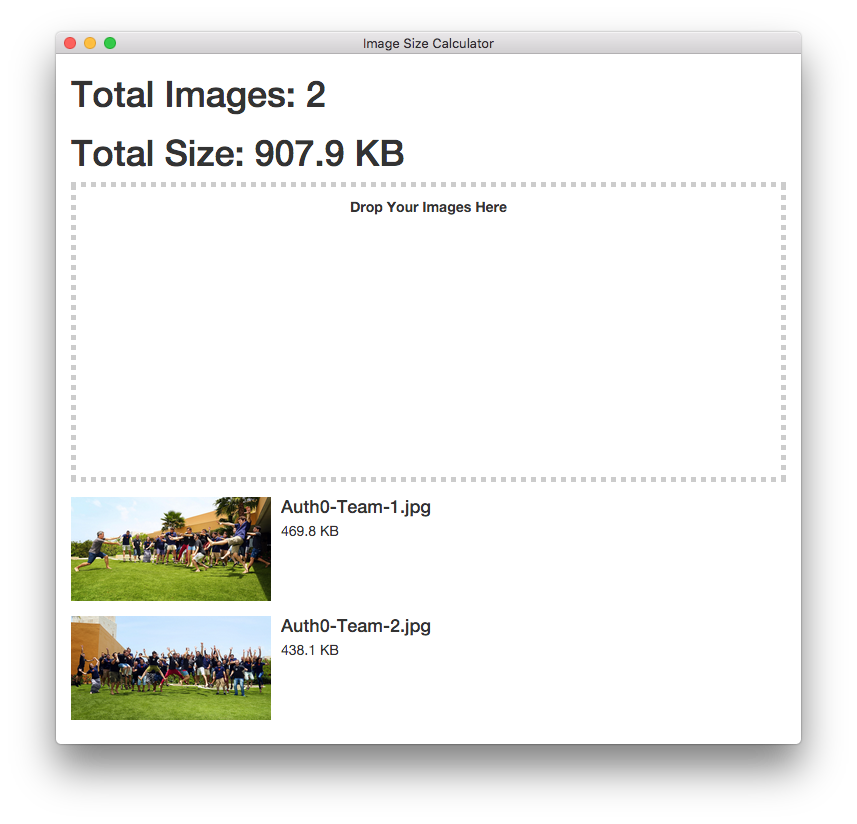
This Angular 2 and Electron sample app is a simple image calculator that lets users drop images in and find their total size.
To get started, clone the repo to your target directory. This app uses Webpack, and a few commands have been provided as scripts in package.json.
npm install
# To build only
npm run build
# To watch for changes
npm run watch
# Start the Electron app
npm run electronElectron can be used with any framework, so once all of the code needed to make Electron work is in place, we simply create the Angular 2 app as we would for the web.
The Electron configuration is contained in app/main.js.
// app/main.js
var app = require('app');
// browser-window creates a native window
var BrowserWindow = require('browser-window');
var mainWindow = null;
app.on('window-all-closed', function () {
if (process.platform != 'darwin') {
app.quit();
}
});
app.on('ready', function () {
// Initialize the window to our specified dimensions
mainWindow = new BrowserWindow({ width: 1200, height: 900 });
// Tell Electron where to load the entry point from
mainWindow.loadURL('file://' + __dirname + '/index.html');
// Clear out the main window when the app is closed
mainWindow.on('closed', function () {
mainWindow = null;
});
});The entry point for the app is the index.html file within the app directory.
<!-- app/index.html -->
<body>
<div class="container">
<app></app>
</div>
<script src="../build/common.js"></script>
<script src="../build/angular2.js"></script>
<script src="../build/app.js"></script>
</body>The Angular 2 app uses TypeScript and the Webpack configuration is set up to place the transpiled JavaScipt in the build directory.
// app/app.ts
import {bootstrap} from 'angular2/platform/browser';
import {Component, Pipe, PipeTransform} from 'angular2/core';
import {NgFor} from 'angular2/common';
@Pipe({ name: 'byteFormat'})
class ByteFormatPipe implements PipeTransform {
// Credit: http://stackoverflow.com/a/18650828
transform(bytes, args) {
if(bytes == 0) return '0 Bytes';
var k = 1000;
var sizes = ['Bytes', 'KB', 'MB', 'GB'];
var i = Math.floor(Math.log(bytes) / Math.log(k));
return (bytes / Math.pow(k, i)).toFixed(1) + ' ' + sizes[i];
}
}
@Component({
selector: 'app',
pipes: [ByteFormatPipe],
template: `
<h1>Total Images: {{ imageStats().count }}</h1>
<h1>Total Size: {{ imageStats().size | byteFormat}}</h1>
<div
(dragover)="false"
(dragend)="false"
(drop)="handleDrop($event)"
style="height: 300px; border: 5px dotted #ccc;">
<p style="margin: 10px; text-align: center">
<strong>Drop Your Images Here</strong>
</p>
</div>
<div class="media" *ngFor="#image of images">
<div class="media-left">
<a href="#">
<img class="media-object" src="{{image.path}}" style="max-width:200px">
</a>
</div>
<div class="media-body">
<h4 class="media-heading">{{image.name}}</h4>
<p>{{image.size | byteFormat}}</p>
</div>
</div>
`
})
export class App {
images:Array<Object> = [];
constructor() {}
handleDrop(e) {
var files:File = e.dataTransfer.files;
var self = this;
Object.keys(files).forEach((key) => {
if(files[key].type === "image/png" || files[key].type === "image/jpeg") {
self.images.push(files[key]);
}
else {
alert("File must be a PNG or JPEG!");
}
});
return false;
}
imageStats() {
let sizes:Array<Number> = [];
let totalSize:number = 0;
this
.images
.forEach((image:File) => sizes.push(image.size));
sizes
.forEach((size:number) => totalSize += size);
return {
size: totalSize,
count: this.images.length
}
}
}
bootstrap(App);Auth0 helps you to:
- Add authentication with multiple authentication sources, either social like Google, Facebook, Microsoft Account, LinkedIn, GitHub, Twitter, Box, Salesforce, amont others, or enterprise identity systems like Windows Azure AD, Google Apps, Active Directory, ADFS or any SAML Identity Provider.
- Add authentication through more traditional username/password databases.
- Add support for linking different user accounts with the same user.
- Support for generating signed Json Web Tokens to call your APIs and flow the user identity securely.
- Analytics of how, when and where users are logging in.
- Pull data from other sources and add it to the user profile, through JavaScript rules.
- Go to Auth0 and click Sign Up.
- Use Google, GitHub or Microsoft Account to login.
If you have found a bug or if you have a feature request, please report them at this repository issues section. Please do not report security vulnerabilities on the public GitHub issue tracker. The Responsible Disclosure Program details the procedure for disclosing security issues.
This project is licensed under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.