- 802.1D for STP originally
- 802.1w RSTP
- 802.1s MSTP
- 802.1D-2004 now only RSTP
- 802.1s integrated into 802.1Q-2005
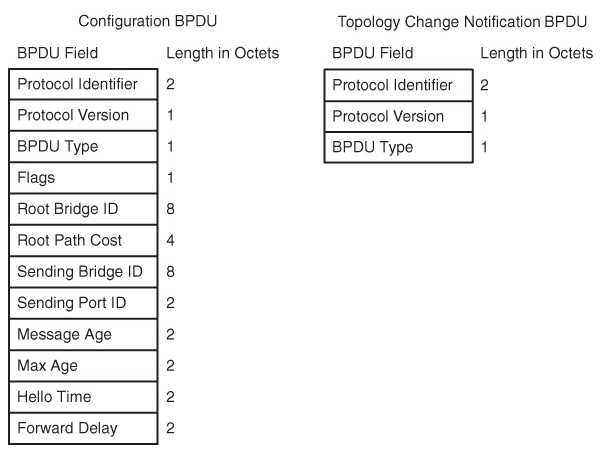
STP
- Protocol ID of 0x0000
- Protocol Ver - 0x00
- BPDU field shows config and tcn BPDUs
- Flags handles TC events (TC Ack flag and TC flag)
- Fields after show root bridge, distance of BPDU sender to root, sender bridge ID, sender port ID that BPDU traversed
- MessageAge - Set to 0 at root, others increment by 1 before forwarding
- Remaining lifetime of bpdu is MaxAge-MessageAge
- Timers reflect timers of root (MaxAge, HelloTime, ForwardDelay)
IDs of bridges and ports in BPDU. All have configurable priority.
Config BPDUs compared, superior based upon lowest: -
- RBID
- Root Path Cost
- Sender BID
- Sender PID
- Receiver PID (not in BPDU, local)
Above is order. Only config BPDUs compared. One RP on non-root, one DP per segment. TCNs not compared.
STP stores superior BPDU sent/received. Root and blocking ports store upstream BPDU, DP store own
BPDU lasts for MaxAge-MessageAge seconds
BID - 2 byte priority then MAC
- Elect root switch (lowest BID)
- Choose RP - Superior BPDU to root
- Choose DP - Swich that forwards superior BPDU from all forwarded BPDUs on segment
- All claim root until superior BPDU
- Once sup received, advertised on
802.1t amended BID for PVST+ and MST. Made priority 4 bits (multiples of 4096), 12 bits for Sys Ex ID (usually Vlan ID). Called MAC address reduction. VLAN IDs make ID unique (VLAN ID plus switch MAC). Configure with spanning-tree extend system-id, newer switches can't remove this command.
- Root sends hellos (default 2 seconds). Contains RBID and SBID (Root ID for both), RPC 0, SPID of egress
- Nonroot adds port cost to RPC in BPDU, superior becomes RP
- Hellos from RP sent out DP (updated RPC, SBID, SPID and MessageAge)
- No hellos on blocking ports
Least path cost to root. RPC on received port added to BPDU.
Port costs: -
| Standard | 10M | 100M | 1G | 10G |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-802.1D-1998 | 100 | 10 | 1 | 1 |
| 802.1D-1998 | 100 | 19 | 4 | 2 |
| 802.1D-2004 | 2000000 | 200000 | 20000 | 2000 |
1998 default on most CAT switches. 2004 for MST by default. Change with spanning-tree pathcost method long
- Hellos forwarded onto LAN segment by designated switch
- Port forwarding is DP
- ALl others root or blocked
- Superior hellos
Tiebreakers same as before
- Root Switch - Lowest BID
- RP - Least path cost to root
- DP - Sends best BPDUs to segment
- ALl other ports blocking
- Config BPDUs only from DP (would be inferior on other ports, including RP)
- Each port stores best BPDU sent/received. DP store best sent, RP and block store best rx'd
- RXd BPDUs expire - MaxAge-MessageAge
When stable, BPDUs unchanged, same results calculated.
TC event when: -
- TCN BPDU rx'd on DP
- Port moves to forwarding and switch has at least one DP
- Port moves from Learning or forwarding to block
- Switch becomes root
During TC, switch sends BPDUs with updated contents. Neighbours recalculate ports
- Switches instructed to age out unused CAM entries
- Forward Delay timer (default 15s) to time out CAM entries
TCNs go to Root, root informs switches. TCNs sent as config BPDUs cannot go upstream.
- TC occurs
- Switch sends TCN BPDUs out RP until acked
- Upstream switch acks with next hello, marks TCA bit
- Upstream repeats 1-3
- When TCN at root, BPDU with TCA sent through rx'd port
- For MaxAge+ForwardDelay seconds, root sends BPDUs with TC bit set, all switches time out CAM entries
No immediate change as loop potential.
Listening then learning, both ForwardDelay (default 15s)
Listening - No forwarding, no MAC learning Learning - No forwarding, MAC learning
PVST+ has STP per VLAN. Different roots, different ints for forwarding/blocking.
With 802.1Q and non-Cisco switches, only CST.
PVST+ runs on trunks as VLAN 1 STP instance. In CST regions, binding for all VLANs. In PVST+ region, only for 1 VLAN.
- CST treated as loop-free shared segment
- PVST+ BPDUs encapd with multicast dest mac of 0100.0CCC.CCCD, tagged with correct VLAN
- Using SNAP encap (ordinary BPDUs use LLC).
- TLV at end of BPDU with VLAN number of BPDU. Used to check for native VLAN mismatches
- VLAN1 on PVST+ uses standard BPDUs and PVST+ BPDU. PVST+ one only for mismatches
When sending BPDUs, access ports tx IEEE BPDUs to their access VLANs.
Trunks do: -
- IEEE BPDU for VLAN 1 (untagged)
- PVST+ BPDUs for all existing and allowed VLANs
If access port gets BPDU with wrong VLAN, Type Inconsistent.
On trunk:
- IEEE BPDUs processed by VLAN 1 STP instance
- PVST+ BPDUs go through: -
- Check VLAN tag, if tagged, BPDU in that VLAN. If no tag, native VLAN
- Check PVID TLV. If no match, PVIDInconsitent state, BPDU dropped
- If PVID TLV match, processed by VLAN STP. PVST+ VLAN 1 duplicate of IEEE.
show spanning-tree root - If on root, "This bridge is root"
spanning-tree vlan 1 priority 28672
int Fa0/1
spanning-tree vlan 1 cost 100
**spanning-tree vlan vlan-id root { primary | secondary } [diameter value] - Diameter lowers timers, sets pririty to 24756 if current root larger, or 4096 below root. Secondary set to 28672 always.
IEEE 802.1w
Discarding, Learning and Forwarding only. Can be Discarding or Forwarding unlimited time, learning transitions.
Discarding - No forwarding or MAC learning, processes rx BPDUs, sends BPDUs, tx/rx switch protocls (LLDP, VTP etc)
Four port roles: -
- RP - As before
- DP - As Before
- Alternate - Replacement of root
- Backup - replacement of DP
RP and DP can be in Disc or Learn states, or skipped with proposal agreement
AP
- Rx BPDUs, not meeting RP or DP rquirements
- Alt path to root
- If RP lost, AP with best BPDU promoted
BP
- RX BPDUs from same switch
- Attached to same link as another port on switch
- Takes over if DP fails, not rapid
AP protects against direct link failure.
BP not rapid as a shared link. Becomes Designated Discarding after three BPDUs lost on DP. One remains best, rest back to Backup Discarding. Moves through disc-learn-forwarding
Edge or Non-Edge ports. Edge port immediately forwarding. Expects no BPDUs, or will revert to non-edge
Default port type is non-edge
Link types of P2p and shared
- P2P - To anotehr RSTP switch
- Shared - To multiple switches
If link half duplex, assumed shared. Reverts to STP timers and operation.
Set with spanning-tree link-type {point-to-point | shared}
- Single BPDU for config and TCN
- Protocol verison 2
- Flags for all 8 bits
- Proposal bit
- Port role bits
- Learning bits
- Forwarding bit
- agreement bit
- Allows Proposal/Agreement, and originating port's role and state
BPDUs originated by all switches, based on info stored on RP. If RSTP BPDUs cease on port, problem contain on link between switch and nieghbour. RSTP ages out BPDUs after 3 hellos. MessageAge now only a hop count. If MessageAge higher than MaxAge, BPDU discarded
Inferior BPDUs immediately accepted and stored, as it implies a change.
- If RP would go onto new link, remaining ports can move from RP or AP to DP. Others may be DP, causing loop.
- Loops need preventing locally, could also be lower cost path
P/A is a port proposing to be DP, agreement saying it can.
On new link installation: -
- Both ends Designated Discarding
- DPs in discarding/learning state send BPDU with proposal bit set
- If one side sees BPDU now best resulting BPDU, goes from DP to RP (stays discarding)
- Proposal on RP makes all non-edge DPs int discarding (Sync state), no possible loops
- Once done, RP to forwarding, upstream allowed to change state to forwarding (agreement bit set after Sync)
This cascades down switches. Ports without portfast wont take part, so go back to STP timers. Use edge ports
Non-edge port going from non-forwarding to forwarding is TC event. Loss of forwarding means loss of MAC reachability.
- BPDUs flooded with TC flag set
- Switch seeing TCN sets tcWhile time to hello plus 1 sec on all non-edge DP and RP (if any) export if port where TC learned/detected
- Flush macs on these ports
- Sends TC flagged BPDUs on these ports until tcWhile expires
- RSTP per VLAN
- Same behaviour per instance as RSTP
- Backwards comaptible with RPVST+
- spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
- spanning-tree portfast or spanning-tree portfast default
- Non p2p switches revert to 802.1D or PVST to legacy switches
- Tune STP parameters per instance
- Less instances
- RSTP for convergence
- Limit on instances on certain platforms (128 on 2960, 3560 and 3750), true of RPVST+ and MST
All switches in region configed with same VLAN mappings, same instances etc
- System ID extension used
- 0-4095 for instances (2950 only support 0-15)
- Allows 65 active MST instances (0 plus 64 user)
- Single BPDU for all instance info, must fit in a frame (88 hypothetically, but 64 is limit)
- IST is Instance 0
- All VLANs default to IST
- IST interacts outside MST region
- All VLANs must inherit port state of IST on region boundary
- MST region seen as single switch outside it (CST blocks loops between regions)
- ISTs on region boundaries constitute an SPT between regions of links only on boundaries
- CST has no per vlan ability, is for loop free paths, and for interaction with non-MST swithes.
- CST costs only cost of links between regions (external costs)
- CST on region boundary merges with IST inside it (known as CIST)
- Multiple roots due to those in each region. One for entire region, rest per region (CIST Region Root)
CIST Root elected by lowest BID from all switches in CIST. IST BID formed from IST priority, instance number 0 and base MAC. Also all STP and RSTP switches form this (using their only BIDs)
Non-CIST root regions can have only switches at region boundary in IST root switch election.
IST root elected by lowest external RPC to CIST root. Sum of all inter-region links to reach region from root. In a tie, lowest IST BID
CIST Regional RP sitting on Region Root Switch is Master Port, provides connectivity to CIST root for all instances inside region.
STP and RSTP
- Switches speak exclusively instance 0 to boundary ports with IEEE BPDUs. All port roles on this instance apply to all on boundary port
MSTP and PVST+
- Single representative chosen on behalf of entire region
- Interaction determines port roles and states for all VLANs
- MST side works (due to port roles on boundary port rule)
- MST instance must deliver info tp PVST+ switches so every PVST+ instance gets same info to make same choice
PVST Simulation - Same info for all instances despite interop only between one instance per side
MST --> PVST+ - IST info replicated to PVST BPDUs on all active VLANs
PVST+ --> MST - MST takes VLAN 1 instance for entire region, processes info in IST.
MST Boundary becomes RP if BPDUs superior to boundary ports own BPDUs, but best VLAN 1 PVST+ BPDUs on Boundary. Implies CIST root located in PVST+ region and VLAN 1 root. All VLANs in forwarding. PVST+ BPDUs coming in verified to see if identical or superior to those in VLAN 1
If sys ID extension in PVST+, PVST BPDUs per VLAN cannot be identical (as VLAN part of it). So switches not in VLAN 1 must be lower by at least 4096 of PVST+ VLAN 1 root priotity.
If not met, PVST simulation consistency, port blocking.
MST boundary becomes non-DP if incoming VLAN 1 PVST+ BPDU superior, but not enough to be root. Must monitor all PVST+ BPDUs. Cisco optimisation says if true, port blocked according to Non-designated role. If not met, PVST simulation declared and port kept blocked.
Recommended to make MST region as root to all PVST+ instances.
RPVST+ treated as PVST+ operation to cut down on complexity. STP and RSTP operate normally
Name, rev number and VLAN-to-instance mappings must match, MD5 hashed and compared. Show has with spanning-tree configuration digest. Changes mean switch is own region.
Prestandard version of MST on older switches, digest command shows only 1 has. Two for new. Config to pre-standard with spanning-tree mst pre-standard
spanning-tree mst configuration
name REGION
revision 1
instance 1 vlan 2
spanning-tee mode mst
spanning-tee mst 0 priority 0
spanning-tree mst 1 priority 4096
int Fa0/1
spanning-tere cost mst
Use vtp mode servet mst and vtp primary mst, distributes MST config across VTPv3 domain.
- Edge port
- Forwarding immediately
- Not part of Sync, P/A
- Send BPDUs, none expected back
- If rx BPDUs, Portfast disabled until port goes down and up
- No issues to DHCP for hosts
- Ports don't go discarding during P/A phase
spanning-tree portfast spanning-tree portfast default spanning-tree disable spanning-tree portfast trunk - Brings trunk up immediately
BPDU Guard
- Per port or globally per portfast port
- Err disables port on BPDU rx
- spanning-tree bpduguard enable
- spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
- spanning-tree bpduguard disable
- err-disable not receovered unless additional config added
Root Guard
- Per port
- Ignores superior BPDUs
- root inconsisent blocking
- All frames cease until BPDUs cease
- spanning-tree guard root
- Recovers when BPDUs expire (MaxAge-MessageAge in STP, 3xhello in RSTP)
BPDU Filter
- Stops tx
- Optionally stops rx
- If global configged, applies only to edge ports
- 10 Hellos sent to start, then stops sending BPDUs
- Can still rx BPDUs, would disable BPDU filter (back to 10 hellos)
- spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
- spanning-tree bpdufilter disable
- If per port, unconditional stopping of rx and tx
Global BPDU filter with BPDU guard works, received BPDU will automatically errdisable. Per port doesnt as no BPDUs ever get to BPDU guard
UDLD, STP Loop Guard, Bridge Assuarance, RSTP/MST Dispute
UDLD
- Cisco proprietary
- Echo mechanism between device pair
- Switch ID and port ID in message
- Message lists all neighbouring switch/port pairs on same segment
Detected like so: -
- Switch/Port pair does not appear in other switches list of detected neighbours
- Same originator Switch Port/Pair in message, looped port
- Single neighbour detected, but UDLD message contains more than one, shared media issue
Err-dsiabled if above found.
Two operational modes
- Normal - Attempts to reconnect 8 times if messages lost, no action taken if attempts failed
- Aggressive - As above, but err-disables port
udld { enable | aggressive } - Global, only fibre ports
udld port [ aggressive ] - Per port, any media
show udld neighbors
udld reset - resets state
STP Loop Guard
If receiving BPDUs on Root/Alternate ports, unidirectional link could move to DP. Loop Guard assumes after BPDUs rx'd, not poss in working network to stop rx'ing them without physical failure. Ports can't be DP.
Loop inconsisent state, starts on loss of BPDU, stops on rx BPDU
spanning-tree loopguard default - Global, automatically added to RP and AP, not shared link
spanning-tree guard loop - Per port, can go on shared
Bridge Assurance
- RPVST+ and MST only, on p2p links.
- BPDUs sent on port at each hello always, on RP, DP, AP or BP
- BPDUs become hello mechanism
- If loss of BPDUs, BA-inconsistent
- Support on Cat 6500 and Nexus 7000
spanning-tree bridge assurance spanning-tree portfast network
Dispute Mechanism
Info in RSTP and MST BPDUs (role and state of port)
- If inferior BPDU from a port claiming Designated Learning or FOrwarding, moves to discarding
- Also exists in RPVST+
- No config required
- PortChannels
- STP sees as one link
- Bandwidth only parameter changed on link failure
- Hashing over frame address fields
- Matching fields across frames form flow/conversation
- Flow produces same has, so same link
- LB on L2, L3 and/or L4 headers
- XOR if more than one field
Over L2 port channel, might have multiple dest macs, one source mac, and vice versa in other direction. Use different hashing
port-channel load-balance type - Global command
- Max active links is 8
- On CAT switches LB mechanism produces 3 bit result in 0-7, values assign ed to links
- Fewer links means 2 results could be on same link
- Traffic tends to be equal across 8, 4 or 2 links
- Other switch platforms use 8 bit hash, 1/256 of traffic, more granular
Must have same: -
- Speed and duplex settings
- Same mode (trunk, access, dynamic)
- Same access VLAN
- Same allowed and native VLANs
- No SPAN ports
- int Port-Channel added when Port Channel created
- Inherits config of first int added, all others compared
- Port suspended if no config match
- Config changes on Port-Channel only on non-suspended members
Following guidelines: -
- Don't create PC manually
- Remove port channel from config so no issues when adding ports later
- Identical phy port config
- Correct physical port config first, not PC
- Can be L2 or L3, not possible to change after PC created. Can combine L2 and L3 in a PC
- Shut down phy interfaces and port channel when fixing err-disable
channel-group mode on - static Port-Channel
Only single BPDU sent per port channel, also subject to hash. May not turn up on ports that go forwarding, hence dispute mechanism.
Etherchannel Misconfig Guard - BPDUs should be rx'd over etherchannel with same source MAC in ehternet header. If not, ports treated as individual links. Doesnt help if only one BPDU rx'd over one link/ Enabled by default, disable with no spanning-tree etherchannel guard misconfig
802.1AX (formerly 802.3ad) LACP or PAgP
PAgP
- Max 8 links, no more in PC, ca only change timers (normal: 30s, fast: 1s)
- channel-group 1 mode auto/desirable
LACP
- Max 16 links
- 8 active, rest in Hot Standby
- One switch in charged of standby, lowest LACP system ID, set with lacp system-priority,
- If multiple standby links, switch in control chooses with lowest port ID< change with lacp port-priority, 0-65535
- channel-group 1 mode active/passive
Helper commands limit to LACP or PAgP commands channel-protocol pagp/lacp
- Messages include System IDs, ID of physical ports and group
- No detail port info beyond this
- Verify if links to be bundled connected to same neighbouring device and same group
- Name of device, hostname
- IOS version
- Hardware capabilities (routing, switching and/or bridging)
- Platform
- L3 address
- Interface
- Duplex
- VTP domain
- Native VLAN
- May be off on VT or Multipoint FR
- Holddown 180s
- no cdp run - Global
- no cdp enable - Per port (can't disable globally and enable per port)
- show cdp timers
- cdp timer seconds
- cdp holdtime seconds
- 802.1AB
- TLVs
- Mandatory TLVs are
- Port Description
- System Name
- System Description
- System capabilities
- Management Address
- lldp run
- lldp transmit
- lldp receive
- lldp holdtime
- lldp reinit
- lldp timer
- Runts - <64 byte frame
- CRC errors - FCS doesn't match calculation
- Frames - CRC error and noninteger octets
- Alignment - CRCs and odd octets
- Collision - Duplex mismatch
- Late collision - Collision occurs after first 64 bytes
show controllers
show int status err-disabled
show spanning-tree inconsistent ports
show spanning-tree [ vlan number ] root [ detail | priority [ system-id ] ]