Collection of PowerShell functions and scripts a Blue Teamer might use
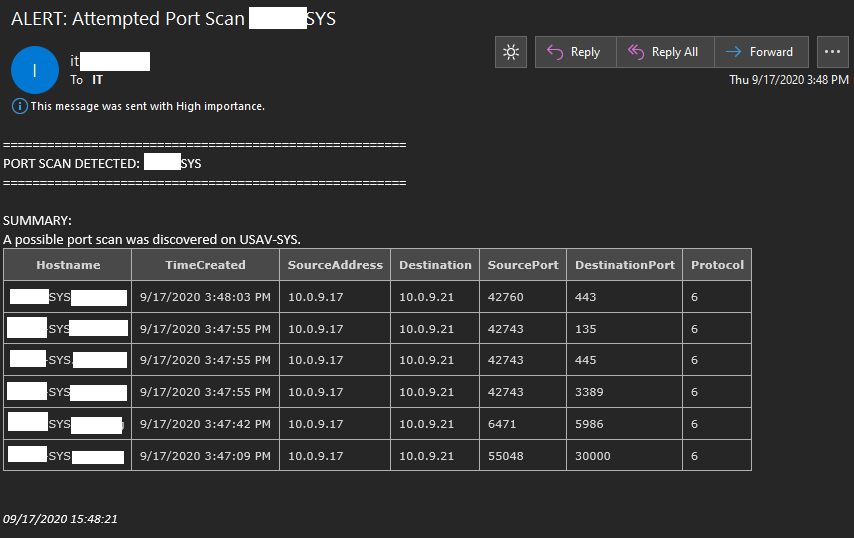
This cmdlet is used to discover attemtped port scans on a device. It runs on an infinite loop. This cmdlet can be used to send an email alert containing the log information, it can automatically added a source IP addresses accused of port scanning to the Windows Firewall on a block list. The default uninitiated connection limit that sets off the alert is 5. This means that when 5 ports are successfully connected to on a device in under two minutes an alert or blacklist IP action is triggered. You can of course have nothing occur as well. This cmdlet obtains IP Addresses from the firewall log. It then uses those IP's to the Windows Filtering Connection event logs. This script does everything needed to configure permissions and logging on the local device. The firewall log location is the CIS Benchmark recommended and will require a restart after the firewall log files are created and permissions are set. You can also exclude IP addresses to prevent legitimate port scanners from vulnerability scanning servers from being blocked by this funciton. There are servers such as File Servers and VoIP servers that will have connections from a lot of different IP addresses. In these cases you will want to use the -IgnorePort parameter to define ports such as 445 preventing this port from being added to the connection count for an IP. I am still working on a way to filter things out for those higher traffic servers. Currently this port scan monitor is only useful on servers that do not receive a hunderd separate connections a minute.
PS> Watch-PortScan -LogFile C:\Windows\System32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall.log -Limit 7 -Tail 8000 -ActiveBlockList -ExcludeAddresses '10.10.10.10', '10.10.10.11' -EmailAlert
# The above example checks the last 8000 newest entries in the pfirewall.log file and extracts individual IP addresses. The detection limit is set to 10 so when 7 open ports are connected to by the same IP in the last 2 minutes, an email alert is triggered and the IP is added to the Windows Firewall and prevented from being communicated with thanks to the -EmailAlert and -ActiveBlockList switch parameters. The Block List is set to active which means that any discovered port scanners, excluding IP addresses 10.10.10.10 and 10.10.10.11 will have a firewall rule added, blocking inbound and outbound connections to the IP. The -EmailAlert parameter will send an email alert using the info you provide. Rather than make 50 parameters you are expected to define your email information in the script. You will then receive an email alert with a small log file containing a table with info on the port connections that occured to let you know what the attacker knows. This function is used for changing the registry values for RC4 and AES Ciphers as well as SSL2.0, SSL3.0, TLS1.0, TLS1.1, and TLS1.2. Enabling all of the switches will set the recommended SCAP disabled and enabled values for these for IIS 10. REFERENCE CIS Benchmarks
PS> Disable-WeakSSL [ -WeakCiphers ] [ -StrongAES ] [ -WeakSSLandTLS ]This script is used to delete ransomware notes saved to a large number of locations on multiple servers using SMB mapped drives
PS> Remove-RansomwareNote -ComputerName "dc01","files","desktop1" -FileName "Ransom.txt" -Credential $LiveCredThis script is used to encrypt the autologin password. If autologin is currently set up it will encrypt the clear text password. If it is not set up already you will be prompted for credentials to use
PS> .\Setup-Secure-Autologon.ps1This cmdlet is meant to be run to patch the CVE-2017-8529 vulnerability on Windows computers for 64 or 32 bit architectures. This does not take any parameters other them common parameters.
PS> Resolve-CVE-2017-8529 -VerboseThis cmdlet is used for discovering evidence of compromise as a result of CVE-2020-0601
PS> Find-CVE-2020-0601 -VerboseThis cmdlet is meant to be run to patch the CVE-2020-0796 vulnerability on Windows version 1903 and 1909 if they are vulnerable
PS> Resolve-CVE-2020-0796 -ComputerName "DESK01", "DESK02" -Verbose
PS> Get-ADComputer -Filter 'Name -like "DESK*"' | Resolve-CVE-2020-0796
# Use below command to undo changes made
PS> Resolve-CVE-2020-0796 -ComputerName "DESK01", "DESK02" -Undo -VerboseThis cmdlet is meant to mitigate CVE-2020-1350 using a registry setting in cases that prevent a server from being restarted with the newest patch KB4569509.
PS> Resolve-CVE-2020-1350This script is meant to be run using task scheduler in response to DNS Server Event ID 6001. Whenever a DNS zone transfer occurs this event is set off in the event logs. Triggering this script to run will send an email to the IT Administrator or whomever you define informing them the DNS zone transfer occurred as well as the IP address that initiated it. Some Windows DNS servers may need zone transfers to be enabled in order to work correctly. This alert helps turn that into an advantage for us defenders.
PS> .\DNSZoneTransferAlert.ps1This function is used to check the TLS protocols and algorithms a device is capable of using. It also returns certificate information
PS> Test-SslOptions -UrlDomain "osbornepro.com" -Port 443
PS> "osbornepro.com","btpssecpack.osbornepro.com","encrypit.osbornepro.com","writeups.osbornepro.com" | Test-SslOptions -Port 443This function is meant to be used as a scheduled task on servers. PowerShell command logging will need to be enabled for this to work. There are arguments on whether or not this should be done. I am a believer that the input should be logged. Anyway, this checks the event log for maliciously used powershell commands. This includes commands such as vssadmin (watches for NTDS.dit password extraction on domain controllers), IEX (watches for remotely issued commands), and bitsadmin/Start-BitsTransfer and certutil -urlcache -split -f (watches for donwloading to a device through the command line).
PS> Get-DubiousPowerShellCommand -VerboseThis function is meant to be run by Task Scheduler on servers whenever Event IDs 7009 or 7045 are triggered. This will inform the Administrator whenever a new service is installed on a server. I have excluded Windows Defender updates. If you have any other false positives just add an -and to Where-Object or add If statement near line 58. The BTOBTO I mentioned in the email body is referring to a python exploit that can be used if admin credentials are compromised. Most other payloads I have seen have random service names in Base64 format.
PS> Get-NewlyInstalledService -SmtpServer mail.smtp2go.com -To rosborne@osbornepro.com -From rosborne@osbornepro.com -VerboseThis script is meant to be run by Task Scheduler. Any unique connections made with a server are documented and placed into a log file. Any IPv4 addresses that are able to be resolved are resolved and placed in a document C:/Users/Public/Documents/ConnectionDNSHistory.csv. Any server Internet connections are logged into a separate file C:/Users/Public/Documents/ConnectionHistroy.csv. You are able to configure alerts by receiving an email anytime a new port has been opened as a listener on a device. I do not use the alerts as I have not worked on perfecting that part as this is one of my first written scripts. Stil very useful.
PS> .\NewOpenPortMonitor.ps1This cmdlet is used for discovering possibly malicious changes on a machine. It will require a reference copy of the hosts file in Windows. It also requires a list of known applications and known Current User Applications as a reference. I have it set up to update these files if they are located in a network share which is what I use.
It checks the following items
- Sorts the heaviest processes. Make sure they are all legit.
- If the hosts file has been altered the IP Addresses are displayed. The function then requires the admin to enter the IP Addresses manually. This will close any open connections and prevent any more connections to the discovered IP Addresses.
- If an altered start page is configured it will be shown to the admin who will need to remove the setting.
- Checks local machine and current user registry for any previously unknown applications and shows the unknown apps to the admin. The admin should verify these applications are safe.
- Make sure no proxy settings have been configured/altered.
- Lastly any Alternate Data Streams are looked for and identified
PS> Search-ForCompromise -VerboseThis is another script I am very proud of. This script is useful in an environment where users can log into any computer but are assigned maybe 1, 2, or 3+. What this script does is query the event log for the last 24 hours. Anywhere a successful logon happens (Event ID 4624), the IP Address is noted and compared to the assigned IP Address list located in a CSV File you create. You can then have it notify you of the sign in by email. This is a little niche to a smaller environment. IMPORTANT: For this to work you will need a CSV file containing the user and their assigned devices. That info is imported from the CSV before it can be worked with.
PS> .\UnusualUserSignInAlert.ps1This is a very simple operation that was meant to make comparing a file's hash value to the checksum through PowerShell simplified. Instead of using Get-FileHash in powershell and then comparing the value to the site you downloaded a file from, this cmdlet caluclates the hash of the file and compares that value to the checksum which is one of the parameter values. All the same hashes are available as in the Get-FileHash cmdlet. "SHA1","SHA256","SHA384","SHA512","MD5","RIPEMD160","MACTripleDES" The default algorithm if no algorithm is defined is SHA256.
Compare-FileHash -FilePath C:\Path\To\File.exe -Hash 'e399fa5f4aa087218701aff513cc4cfda332e1fbd0d7c895df57c24cd5510be3' -Algorithm SHA256
Compare-FileHash C:\Path\To\File.exe 'e399fa5f4aa087218701aff513cc4cfda332e1fbd0d7c895df57c24cd5510be3'This cmdlet is for enabling DNS over HTTPS on a Windows machine. It can also be used to disable DNS over HTTPS on a Windows machine.
# This example enables DNS over HTTPS but requires a restart to apply
PS> Enable-DoH
# This example enables DNS over HTTPS and prompts the runner to restart
PS> Enable-DoH -Restart
# This example disables DNS over HTTPS but requires a restart
PS> Enable-DoH -Undo
# This example disables DNS over HTTPS and prompts the runner to restart
PS> Enable-DoH -Undo -Restart