In this chapter we'll be using 2 new pieces of the |ProductName|, dialogs and settings. By the end of this chapter you'll be configuring settings in the dashboard as well as opening popup windows outside of Tableau.
Get started by downloading the starter workbook :download:`here <https://extension-documentation.s3.amazonaws.com/tutorials/value-override/Value+Override+Starter+Workbook.twbx>` and creating a new Tableau Extension in Anvil with the trexjacket dependency. The Chat tutorial describes these steps if you need a refresher. Click here view the steps: :doc:`/tutorials/chat-extension/1-setting-up`.
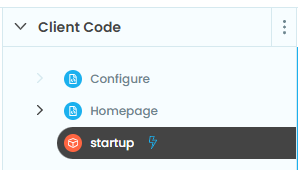
Once you've created your Anvil app, you'll need to create 3 things in the Client Code section:
- A
Homepageform: This will be the main page of our extension - A
Configureform: This will be the configure page of our extension - A module named
startup(set as the startup module): We'll use this page to define our default settings and open theHomepageform
Once you're done, the "Client Code" section should look like this (note that the startup module has a lightning bolt next to it):
In the startup module, let's set some default values for our settings by adding the following code:
from trexjacket import api, dialogs
from .Configure import Configure
api.get_dashboard().settings.setdefaults({
"worksheet": None,
"id_field": None,
"override_field": None,
"username": None
})
dialogs.open_start_form('Homepage')Here we define our default values for the workbook settings as well as open our Homepage form. In order to open dialogs using Tableau Extensions, you must open your main form using dialogs.open_start_form.
In the Homepage form, add a button component named btn_configure with its "click" event handler registered to a method named btn_configure_click.
.. dropdown:: Anvil tip: Adding buttons
:open:
To add a button with Anvil, simply drag and drop the component from the Toolbox right into the form's design pane:
.. image:: https://extension-documentation.s3.amazonaws.com/tutorials/value-override/button_event_click.gif
When adding buttons, don't forget to give the component a descriptive name (``btn_configure`` above), as well as register the event handling function in the Toolbox view:
.. image:: https://extension-documentation.s3.amazonaws.com/tutorials/value-override/container_properties.PNG
In the above example we bind the ``btn_configure_click`` method to the button's click event. Now each time a user clicks our button, the ``btn_configure_click`` method of our form will run!
Then add the following code to Homepage (note that the btn_configure_click method here is the same method we added in the "Container properties" section of the button component!):
from ._anvil_designer import HomepageTemplate
import anvil
from trexjacket.api import get_dashboard
from trexjacket import dialogs
class Homepage(HomepageTemplate):
def __init__(self, **properties):
self.dashboard = get_dashboard()
self.init_components(**properties)
# When a user clicks the configure button, we'll use the dialogs
# module to open our configure form in a new window
def btn_configure_click(self, **event_args):
dialogs.show_form('configure_form', width=900, height=900)
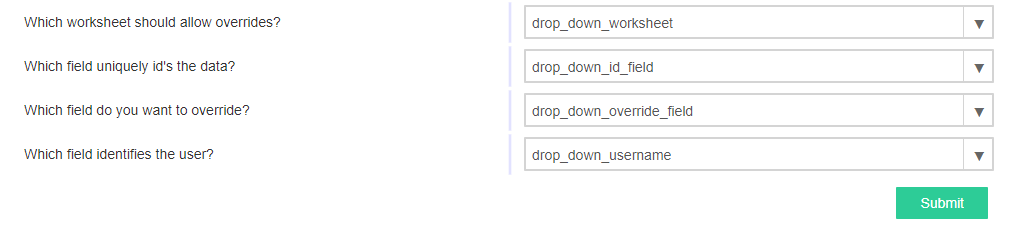
self.refresh_data_bindings()Finally, let's set up our configure form. Start by adding 4 labels, 4 drop down components, and a button to the Configure form. Once you're done, the UI of the Configure form should look like this:
Use the table below to configure the data bindings for the drop down components (be sure to check the "writeback" option for each drop down component's data binding):
Drop down data bindings| Component name | Data binding |
|---|---|
drop_down_worksheet |
selected_value to self.dashboard.settings['worksheet'] |
drop_down_id_field |
selected_value to self.dashboard.settings['id_field'] |
drop_down_override_field |
selected_value to self.dashboard.settings['override_field'] |
drop_down_username |
selected_value to self.dashboard.settings['username'] |
btn_submit |
click event to self.btn_submit_click |
Important!
By binding a drop down's selected value to the keys in our dashboard settings, we can provide a quick and easy way to configure settings. Now whenever a user chooses from the drop down menu, our settings are saved! These values can be retrieved anywhere in our application using their name, just like how dictionaries work: dashboard.settings[keyname]. Settings can make your extensions configurable and extensible, allowing you to reuse extensions in different dashboards.
Now that we have our UI elements, let's add our code to Configure:
from ._anvil_designer import ConfigureTemplate
import anvil
from trexjacket import api, dialogs
# In order for our Configure form to be able to be opened in
# a popup window we need to register it using the @dialogs.dialog_form decorator.
@dialogs.dialog_form('configure_form')
class Configure(ConfigureTemplate):
def __init__(self, **properties):
self.dashboard = api.get_dashboard()
self.drop_down_worksheet.items = [ws.name for ws in self.dashboard.worksheets]
self.show_fields()
self.init_components(**properties)
# Here we call self.raise_event('x-close-alert')
# to close the dialog window once we're done
def btn_submit_click(self, **event_args):
self.raise_event('x-close-alert')
def show_fields(self):
fields = []
if self.dashboard.settings['worksheet']:
# This is our first time accessing settings, reading the value of the 'worksheet' key to
# to dynamically get a worksheet from our dashboard.
ws = self.dashboard.get_worksheet(self.dashboard.settings['worksheet'])
records = ws.get_summary_data()
if not records:
ph = "No summary fields in worksheet!"
else:
ph = "Pick a field"
fields = [f for f in records[0]]
else:
ph = "Pick a worksheet first"
for dropdown in [
self.drop_down_id_field,
self.drop_down_override_field,
self.drop_down_username,
]:
dropdown.placeholder = ph
dropdown.items = fields
def drop_down_sheet_change(self, **event_args):
self.show_fields()Important!
Notice that the string we passed to @dialogs.dialog_form is the string we used in our Homepage form to open our dialog box.
Now that we've configured our forms, clicking the "Configure" inside our extension should open a popup window like the one below:
.. dropdown::
:open:
.. image:: https://extension-documentation.s3.amazonaws.com/tutorials/value-override/configure_settings.gif
Go ahead and open the configure form of your extension and select the fields above for each drop down.
In the next chapter we'll enable users to add an override from the Homepage form.