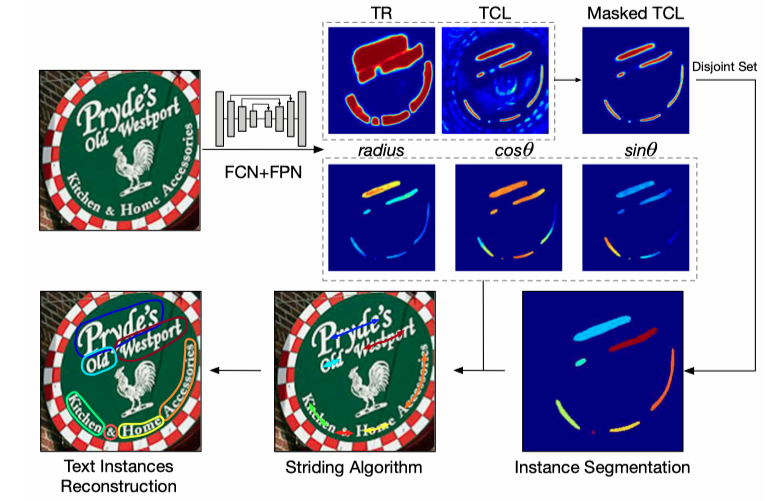
TextSnake: A Flexible Representation for Detecting Text of Arbitrary Shapes (ECCV 2018) by Megvii with 2 versions of my pretrained weights.
- Paper link: arXiv:1807.01544
- Original author's github: princewang1994/TextSnake.pytorch
import cv2
import numpy as np
from inference_utils import load_image, load_detector_and_transforms, visualize_detection, predict_single_image
model_path = './weights/textsnake_my_train_v1_30.pth'
device = 'cuda'
size = 1024
tr_thresh=0.7
tcl_thresh=0.4
detector, transforms = load_detector_and_transforms(model_path, size, tr_thresh, tcl_thresh, device)
source_img = load_image('./demo/chester_minsk_20.07.2019.jpg')
transformed_img = transforms(source_img)
tcl_contours, tr_pred, tcl_pred = predict_single_image(detector, transformed_img, device)
visualize_detection(cv2.resize(source_img, (size, size)), tr_pred, tcl_pred[0], tcl_contours, tr_thresh=tr_thresh, tcl_thresh=tcl_thresh, figsize=(30,12))Comparison of different representations for text instances. (a) Axis-aligned rectangle. (b) Rotated rectangle. (c) Quadrangle. (d) TextSnake. Obviously, the proposed TextSnake representation is able to effectively and precisely describe the geometric properties, such as location, scale, and bending of curved text with perspective distortion, while the other representations (axis-aligned rectangle, rotated rectangle or quadrangle) struggle with giving accurate predictions in such cases.
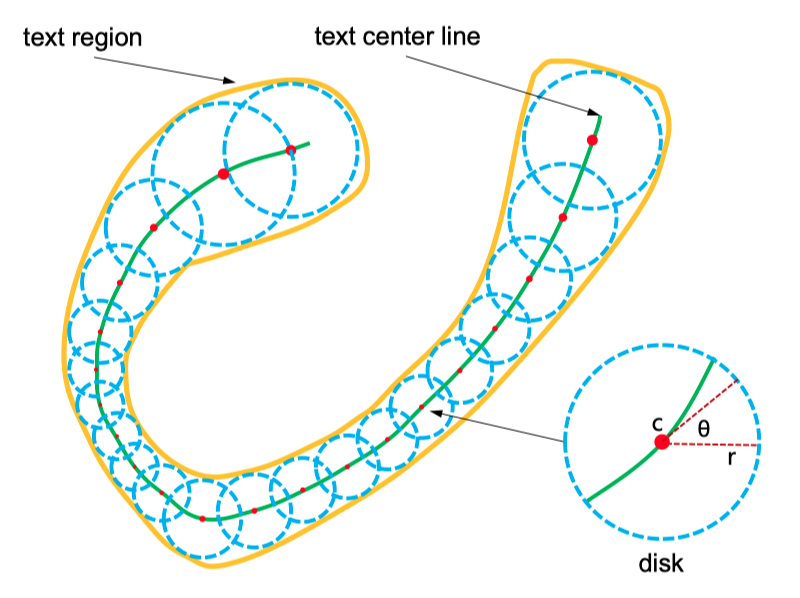
Textsnake elements:
- center point
- tangent line
- text region
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details
- This project is writen by Prince Wang, part of codes refer to songdejia/EAST
- Thanks techkang for your great help!