| Capitolo precedente | Capitolo successivo |
|---|---|
| ◀︎ 05-mutations | 07-unexpected-errors ▶︎ |
È arrivato il momento che stavamo aspettando! Adesso aggiungerai l'autenticazione alla tua applicazione: grazie all'autenticazione riuscirai ad associare ogni twix all'utente che l'ha creato!
Da sapere per questa sezione è cosa sono i cookies HTTP e come funzionano sul web.
Ci sono tanti modi per aggiungere l'autenticazione ad un'app, ad esempio puoi utilizzare dei servizi tipo Auth0. Oggi però realizzerai la tua autenticazione da zero - non preoccuparti, non è così spaventoso come può sembrare.
Iniziamo andando ad aggiornare il file prisma/schema.prisma nel seguente modo:
// This is your Prisma schema file,
// learn more about it in the docs: https://pris.ly/d/prisma-schema
generator client {
provider = "prisma-client-js"
previewFeatures = ["mongoDb"]
}
datasource db {
provider = "mongodb"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
model User {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
createdAt DateTime @db.Date @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @db.Date @default(now())
username String @unique
passwordHash String
twixes Twix[]
}
model Twix {
id String @id @default(auto()) @map("_id") @db.ObjectId
twixesterId String @db.ObjectId
twixester User @relation(fields: [twixesterId], references: [id])
createdAt DateTime @db.Date @default(now())
updatedAt DateTime @db.Date @default(now())
title String
content String
}Prima di eseguire questo comando elimina la collezione che hai creato sul database di Mongo dato che abbiamo creato un nuovo tipo di dato. Ecco come fare:
Adesso che abbiamo aggiornato lo schema puoi eseguire il seguente comando:
npx prisma db pushQuesto comando ti darà questo output:
Environment variables loaded from .env
Prisma schema loaded from prisma/schema.prisma
Datasource "db"
🚀 Your database is now in sync with your schema. Done in 194ms
✔ Generated Prisma Client (3.10.0 | library) to ./node_modules/@prisma/client in 167msCon questo cambio, inizieremo a visualizzare alcuni errori di TypeScript nel progetto perchè non potrai più creare twix senza un valore per il twixsterId.
Prima di generare l'utente chiudi e riapri l'editor Visual Studio Code in modo che l'editor si accorga del cambiamento di Prisma.
💿 Cominciamo sistemando il nostro file prisma/seed.ts.
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
const db = new PrismaClient();
async function seed() {
const kody = await db.user.create({
data: {
username: "kody",
// this is a hashed version of "twixrox"
passwordHash:
"$2b$10$K7L1OJ45/4Y2nIvhRVpCe.FSmhDdWoXehVzJptJ/op0lSsvqNu/1u",
},
});
await Promise.all(
getTwixes().map((twix) => {
const data = { twixesterId: kody.id, ...twix };
return db.twix.create({ data });
})
);
}
seed();
function getTwixes() {
// shout-out to https://icanhazdadtwix.com/
return [
{
title: "Road worker",
content: `I never wanted to believe that my Dad was stealing from his job as a road worker. But when I got home, all the signs were there.`,
},
{
title: "Frisbee",
content: `I was wondering why the frisbee was getting bigger, then it hit me.`,
},
{
title: "Trees",
content: `Why do trees seem suspicious on sunny days? Dunno, they're just a bit shady.`,
},
{
title: "Skeletons",
content: `Why don't skeletons ride roller coasters? They don't have the stomach for it.`,
},
{
title: "Hippos",
content: `Why don't you find hippopotamuses hiding in trees? They're really good at it.`,
},
{
title: "Dinner",
content: `What did one plate say to the other plate? Dinner is on me!`,
},
{
title: "Elevator",
content: `My first time using an elevator was an uplifting experience. The second time let me down.`,
},
];
}💿 Ottimo, ora avvia di nuovo il comando per genearare dei twix di prova:
npx prisma db seedOttimo! Ora il database è pronto.
La nostra autenticazione sarà tradizionale, con username e password. Useremo la libreria bcryptjs per "mascherare" (in inglese to hash) le nostre password in modo tale che sia abbastanza difficile scoprire la password ed entrare nell'account.
💿 Ora procedi e installa la libreria con il seguente comando:
npm install bcryptjs💿 La libreria bcryptjs ha delle definizioni TypeScript presenti in DefinitelyTyped, installiamo anche quelle così il nostro editor non si lamenterà:
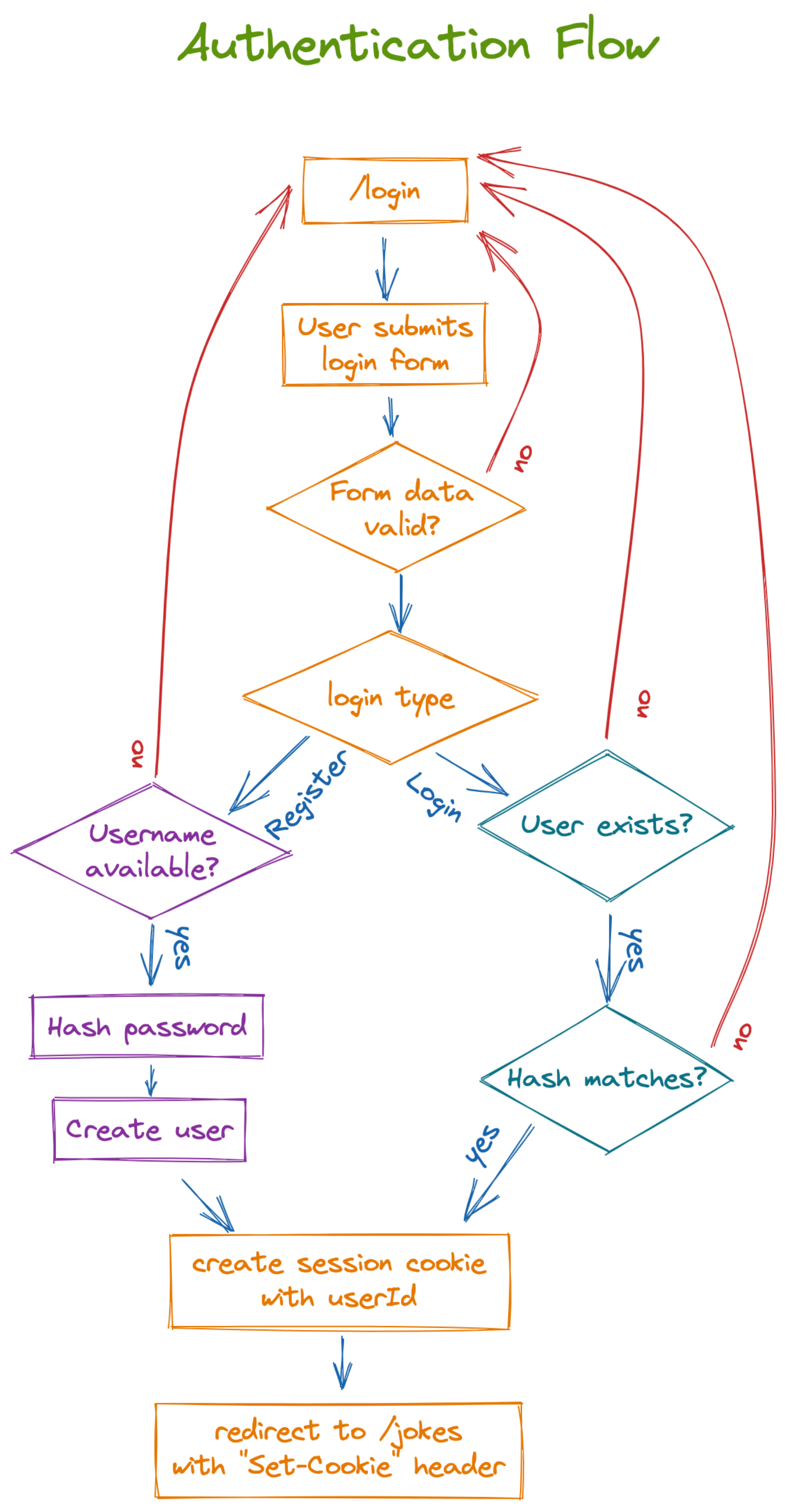
npm install --save-dev @types/bcryptjsQui puoi vedere un diagramma di come funzionerà l'autenticazione che implementerai:
Immagine tratta da Remix Run: Jokes App Tutorial
Ti lasciamo qui di seguito un piccolo riassunto di come funzionerà la nostra autenticazione:
- Alla pagina
/login- L'utente inserisce le proprie credenziali
- I dati vengono validati
- Se i dati non sono corretti viene mostrati all'utente un messaggio di errore
- Se l'utente si sta registrando
- Va controllato che non esistano utenti con lo stesso username
- Se lo username è già utilizzato viene mostrati all'utente un messaggio di errore.
- Viene fatto un hash della password
- Viene creato un nuovo utente
- Va controllato che non esistano utenti con lo stesso username
- Se l'utente è già registrato e sta accedendo
- Controllare che esista l'utente con quello username
- Se l'utente non esiste viene mostrato un messaggio di errore.
- Controllare che l'hashing delle password corrisponde
- Se gli hash delle password non corrispondono, viene mostrato un messaggio di errore
- Controllare che esista l'utente con quello username
- Viene creata una nuova sessione
- L'utente viene ridirezionato alla pagina
/twixescon un headerSet-Cookie.
Ottimo, ora che abbiamo parlato di un' po di concetti teorici, iniziamo a scrivere un po' di codice con Remix!
💿 Crea una pagina /login creando un file app/routes/login.tsx.
app/routes/login.tsx
import type { LinksFunction } from "remix";
import { Link, useSearchParams } from "remix";
export default function Login() {
const [searchParams] = useSearchParams();
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="content" data-light="">
<h1>Login</h1>
<form method="post">
<input
type="hidden"
name="redirectTo"
value={
searchParams.get("redirectTo") ?? undefined
}
/>
<fieldset>
<legend className="sr-only">
Login or Register?
</legend>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="login"
defaultChecked
/>{" "}
Login
</label>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="register"
/>{" "}
Register
</label>
</fieldset>
<div>
<label htmlFor="username-input">Username</label>
<input
type="text"
id="username-input"
name="username"
/>
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="password-input">Password</label>
<input
id="password-input"
name="password"
type="password"
/>
</div>
<button type="submit" className="button">
Submit
</button>
</form>
</div>
<div className="links">
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/twixes">Twixes</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
);
}Dovresti avere il seguente output:
Puoi notare che abbiamo usato useSearchParams per prendere il valore del parametro redirectTo e l'abbiamo messo in un input nascosto. In questo modo la nostra action saprà a quale pagina redirezionare l'utente. Questo sarà per noi molto utile quando nelle prossime sezioni redirezioneremo l'utente alla pagina di login.
Ottimo, adesso che abbiamo la struttura della schermata procediamo con l'aggiugere un po' di interazioni. Le seguenti operazioni saranno molto simili a quello che è stato fatto per la pagina /twixes/new.
💿 Implementa la validazione con una action nel file app/routes/login.tsx
app/routes/login.tsx
import type { ActionFunction, LinksFunction } from "remix";
import {
useActionData,
json,
Link,
useSearchParams,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "~/utils/db.server";
function validateUsername(username: unknown) {
if (typeof username !== "string" || username.length < 3) {
return `Usernames deve essere di almeno 3 caratteri`;
}
}
function validatePassword(password: unknown) {
if (typeof password !== "string" || password.length < 6) {
return `Passwords deve essere di almeno 6 caratteri`;
}
}
type ActionData = {
formError?: string;
fieldErrors?: {
username: string | undefined;
password: string | undefined;
};
fields?: {
loginType: string;
username: string;
password: string;
};
};
const badRequest = (data: ActionData) =>
json(data, { status: 400 });
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
const form = await request.formData();
const loginType = form.get("loginType");
const username = form.get("username");
const password = form.get("password");
const redirectTo = form.get("redirectTo") || "/twixes";
if (
typeof loginType !== "string" ||
typeof username !== "string" ||
typeof password !== "string" ||
typeof redirectTo !== "string"
) {
return badRequest({
formError: `Il form non è stato inviato con i dati corretti`,
});
}
const fields = { loginType, username, password };
const fieldErrors = {
username: validateUsername(username),
password: validatePassword(password),
};
if (Object.values(fieldErrors).some(Boolean))
return badRequest({ fieldErrors, fields });
switch (loginType) {
case "login": {
// login per prendere i dati dell'utente
// se non c'è un utente, ritorna i campi vuoti e il form error
// se l'utente esiste, crea la sessione e fai redirect alla pagina /twixes
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: "Non implementato",
});
}
case "register": {
const userExists = await db.user.findFirst({
where: { username },
});
if (userExists) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `L'utente con il nome utente ${username} esiste già`,
});
}
// create the user
// create their session and redirect to /twixes
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: "Non implementato",
});
}
default: {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `I dati forniti non sono validi`,
});
}
}
};
export default function Login() {
const actionData = useActionData<ActionData>();
const [searchParams] = useSearchParams();
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="content" data-light="">
<h1>Login</h1>
<form method="post">
<input
type="hidden"
name="redirectTo"
value={
searchParams.get("redirectTo") ?? undefined
}
/>
<fieldset>
<legend className="sr-only">
Login o Registrazione?
</legend>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="login"
defaultChecked={
!actionData?.fields?.loginType ||
actionData?.fields?.loginType === "login"
}
/>{" "}
Accedi
</label>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="register"
defaultChecked={
actionData?.fields?.loginType ===
"register"
}
/>{" "}
Iscriviti
</label>
</fieldset>
<div>
<label htmlFor="username-input">Username</label>
<input
type="text"
id="username-input"
name="username"
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.username}
aria-invalid={Boolean(
actionData?.fieldErrors?.username
)}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.username
? "username-error"
: undefined
}
/>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.username ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="username-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.username}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="password-input">Password</label>
<input
id="password-input"
name="password"
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.password}
type="password"
aria-invalid={
Boolean(
actionData?.fieldErrors?.password
) || undefined
}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.password
? "password-error"
: undefined
}
/>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.password ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="password-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.password}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div id="form-error-message">
{actionData?.formError ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
>
{actionData.formError}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<button type="submit" className="button">
Invia
</button>
</form>
</div>
<div className="links">
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Homepage</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/twixes">Twixes</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
);
}Ora dovresti avere una cosa simile a questo:
Bene! Adesso le cose si fanno più interessanti. Iniziamo con la parte legata al login. Abbiamo aggiunto in precedenza nel file di seed lo username "kody" e la password (hashed) è "twixrox". Ora vogliamo implementare la giusta quantità di logica in modo da fare login con solo queste credenziali. Metteremo questa logica in un nuovo file chiamato app/utils/session.server.ts.
Questo è il riassunto della logica che ci serve nel file:
- Esporta una funzione chiamata
loginche accettausernameepasswordcome parametri - Interroga Prisma per sapere se esiste quell'utente con quello
username - Se non c'è un utente, ritorna
null - Utilizza
bcrypt.compareper comparare lapasswordinserita dall'utente con lapasswordHashdell'utente - Se le password non corrispondono, ritorna
null - Se le password corrispondono, allora ritorna l'utente
💿 Crea un file app/utils/session.server.ts e implementiamo i requisiti dei punti appena scritti:
app/utils/session.server.ts
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import { db } from "./db.server";
type LoginForm = {
username: string;
password: string;
};
export async function login({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { username },
});
if (!user) return null;
const isCorrectPassword = await bcrypt.compare(
password,
user.passwordHash
);
if (!isCorrectPassword) return null;
return { id: user.id, username };
}Ottimo! Con questo adesso possiamo ritornare al nostro file app/routes/login.tsx e aggiornarlo con la funzione che hai appena creato:
app/routes/login.tsx
// ...
import { db } from "~/utils/db.server";
import { login } from "~/utils/session.server";
// ...
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
// ...
switch (loginType) {
case "login": {
const user = await login({ username, password });
console.log({ user });
if (!user) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `Username/Password combination is incorrect`,
});
}
// if there is a user, create their session and redirect to /twixes
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: "Not implemented",
});
}
// ...
}
};
export default function Login() {
// ...
}Per controllare abbiamo aggiunto un console.log al file app/routes/login.tsx dopo la chiamata login in modo da vedere le risposte nel terminale.
Ricorda che
actionseloadersvengono avviate sul server, quindi iconsole.lognon li vedrai nella console del browser, ma li vedrai nel terminale dove hai avviato il server
💿 Ora prova a fare login con username "kody" e password "twixrox" e controlla il terminale. Dovresti vedere una cosa simile a questa:
{
user: {
id: '1dc45f54-4061-4d9e-8a6d-28d6df6a8d7f',
username: 'kody'
}
}Se stai avendo alcuni problemi, esegui il comdando
npx prisma studioper vedere il database direttamente sul browser. È possibile che tu non abbia alcun dato perchè ti sia scordata di eseguirenpx prisma db seed(come noi quando abbiamo scritto questo tutorial 😅).
Ora abbiamo l'utente! Possiamo finalmente salvare l'id dell'utente nella sessione per accedere alle pagine che lo richiedono. Apri il file app/utils/session.server.ts. Remix è costruito in un modo astratto tale da permetterci di gestire diversi meccanismi di gestione delle sessioni (here are the docs). Noi useremo la funzione createCookieSessionStorage dato che è la più semplice e la più scalabile.
💿 Scrivi una funzione createUserSession nel file app/utils/session.server.ts che accetta un ID utente e una pagina a cui ridirezionare l'utente:
- Crea una nuova sessione (usando la funzione
getSessiondel cookie storage), - Imposta il campo
userIdnella sessione, - Ridireziona l'utente secondo le impostazioni date nell'header
Set-Cookieheader (usando la funzionecommitSessiondel cookie storage function)
app/utils/session.server.ts
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import {
createCookieSessionStorage,
redirect,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "./db.server";
type LoginForm = {
username: string;
password: string;
};
export async function login({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { username },
});
if (!user) return null;
const isCorrectPassword = await bcrypt.compare(
password,
user.passwordHash
);
if (!isCorrectPassword) return null;
return { id: user.id, username };
}
const sessionSecret = process.env.SESSION_SECRET;
if (!sessionSecret) {
throw new Error("SESSION_SECRET must be set");
}
const storage = createCookieSessionStorage({
cookie: {
name: "RJ_session",
// normally you want this to be `secure: true`
// but that doesn't work on localhost for Safari
// https://web.dev/when-to-use-local-https/
secure: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
secrets: [sessionSecret],
sameSite: "lax",
path: "/",
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 30,
httpOnly: true,
},
});
export async function createUserSession(
userId: string,
redirectTo: string
) {
const session = await storage.getSession();
session.set("userId", userId);
return redirect(redirectTo, {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.commitSession(session),
},
});
}Poi aggiorna il case "login" della funzione Switch nel file app/routes/login.tsx dopo aver aggiunto la createUserSession nell'import di ~/utils/session.server :
app/routes/login.tsx
// ...
import { createUserSession, login } from "~/utils/session.server";
// ...
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
// ...
switch (loginType) {
case "login": {
const user = await login({ username, password });
if (!user) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `Username/Password combination is incorrect`,
});
}
return createUserSession(user.id, redirectTo);
}
// ...
}
};
// ...Vogliamo farti notare la variabile d'ambiente SESSION_SECRET che stiamo usando. Il valore dell'opzione secrets non lo vogliamo visibile all'interno del codice perché potrebbe venir utilizzato per scopi malevoli. Quindi andremo a leggere il valore dal nostro environment, questo significa che quello che devi fare è creare e dare un valore alla variabile SESSION_SECRET nel tuo file .env. Prisma carica i dati del file automaticamente.
💿 Carichiamo nel file .env file la variabile SESSION_SECRET (con qualsiasi valore tu voglia). Dopo averla scritta chiudi e riapri il terminale per applicare le modifiche.
Adesso apri la Network tab sul browser (clicca tasto destro e poi Ispeziona e Newtork nel pannello che si apre), naviga alla pagina /login e inserisci kody and twixrox come password, poi clicca Accedi. Ora controlla gli header della risposta - dovrebbe essere simile a questo:
E se controlli la parte relativa ai cookie nella Application tab allora vedrai che anche i cookie sono settati.
E ora ogni richiesta che verrà fatta dal browser al server, includerà il cookie (non dobbiamo fare nulla sulla parte client, qui trovi una spiegazione su come funzionano i cookie):
Adesso che abbiamo impostato e salvato il cookie possiamo verificare se l'utente è autenticato leggendo l'header e ottenendo il valore dello userId che ci abbiamo inserito. Per testarne il funzionamento andiamo a modificare la pagina /twixes/new e aggiungiamo il campo twixsterId alla chiamata db.twix.create.
Puoi controllare la documentazione per scoprire nuove modalità su come ottenere le sessioni dalla richiesta
💿 Aggiorniamo quindi il file app/utils/session.server.ts per ottenere lo userId dalla sessione. Nella soluzione che ti proponiamo abbiamo creato 3 funzioni: getUserSession(request: Request), getUserId(request: Request) and requireUserId(request: Request, redirectTo: string).
app/utils/session.server.ts
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import {
createCookieSessionStorage,
redirect,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "./db.server";
type LoginForm = {
username: string;
password: string;
};
export async function login({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { username },
});
if (!user) return null;
const isCorrectPassword = await bcrypt.compare(
password,
user.passwordHash
);
if (!isCorrectPassword) return null;
return { id: user.id, username };
}
const sessionSecret = process.env.SESSION_SECRET;
if (!sessionSecret) {
throw new Error("SESSION_SECRET must be set");
}
const storage = createCookieSessionStorage({
cookie: {
name: "RJ_session",
// normally you want this to be `secure: true`
// but that doesn't work on localhost for Safari
// https://web.dev/when-to-use-local-https/
secure: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
secrets: [sessionSecret],
sameSite: "lax",
path: "/",
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 30,
httpOnly: true,
},
});
function getUserSession(request: Request) {
return storage.getSession(request.headers.get("Cookie"));
}
export async function getUserId(request: Request) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") return null;
return userId;
}
export async function requireUserId(
request: Request,
redirectTo: string = new URL(request.url).pathname
) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") {
const searchParams = new URLSearchParams([
["redirectTo", redirectTo],
]);
throw redirect(`/login?${searchParams}`);
}
return userId;
}
export async function createUserSession(
userId: string,
redirectTo: string
) {
const session = await storage.getSession();
session.set("userId", userId);
return redirect(redirectTo, {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.commitSession(session),
},
});
}Nell'esempio abbiamo creato una funzione requireUserId che, se non c'è uno userId, ritornerà in risposta un redirect. Ricorda che redirect è una funzione di Remix che ritorna un oggetto Response. Remix catturerà questa risposta e la manderà al client. Facendo fare all'utente un redirect ci assicuriamo e possiamo assumere che dalla funzione requireUserId verrà sempre dato in risposta uno userId e non dobbiamo preoccuparci di cosa succede se non c'è uno userId in risposta perché se non c'è uno userId l'esecuzione della funzione verrà fermata dal codice throw redirect(\/login?${searchParams});!`
Della gestione degli errori parleremo meglio nelle prossime sezioni.
💿 Adesso aggiorniamo il file app/routes/twixes/new.tsx in modo da usare la funzione creata e ottenere uno userId da usare e passare alla chiamata db.twix.create.
app/routes/twixes/new.tsx
import type { ActionFunction } from "remix";
import { useActionData, redirect, json } from "remix";
import { db } from "~/utils/db.server";
import { requireUserId } from "~/utils/session.server";
function validateTwixContent(content: string) {
if (content.length < 10) {
return `That twix is too short`;
}
}
function validateTwixTitle(title: string) {
if (title.length < 3) {
return `That twix's title is too short`;
}
}
type ActionData = {
formError?: string;
fieldErrors?: {
title: string | undefined;
content: string | undefined;
};
fields?: {
title: string;
content: string;
};
};
const badRequest = (data: ActionData) =>
json(data, { status: 400 });
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
const userId = await requireUserId(request);
const form = await request.formData();
const title = form.get("title");
const content = form.get("content");
if (
typeof title !== "string" ||
typeof content !== "string"
) {
return badRequest({
formError: `Form not submitted correctly.`,
});
}
const fieldErrors = {
title: validateTwixTitle(title),
content: validateTwixContent(content),
};
const fields = { title, content };
if (Object.values(fieldErrors).some(Boolean)) {
return badRequest({ fieldErrors, fields });
}
const twix = await db.twix.create({
data: { ...fields, twixesterId: userId },
});
return redirect(`/twixes/${twix.id}`);
};
export default function NewTwixRoute() {
const actionData = useActionData<ActionData>();
return (
<div>
<p>Add your own hilarious twix</p>
<form method="post">
<div>
<label>
Name:{" "}
<input
type="text"
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.title}
name="title"
aria-invalid={
Boolean(actionData?.fieldErrors?.title) ||
undefined
}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.title
? "name-error"
: undefined
}
/>
</label>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.title ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="name-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.title}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div>
<label>
Content:{" "}
<textarea
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.content}
name="content"
aria-invalid={
Boolean(actionData?.fieldErrors?.content) ||
undefined
}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.content
? "content-error"
: undefined
}
/>
</label>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.content ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="content-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.content}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div>
<button type="submit" className="button">
Add
</button>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
}Fantastico! Adesso se un utente prova a creare un nuovo twix, verrà ridirezionato alla pagina di login perché per creare di nuovi bisogna essere autenticati (e dev'esserci uno userId nella sessione).
Ora che abbiamo l'autenticazione dovremmo permettere alle persone di vedere se sono loggati oppure permettere di fare log out, no?
💿 Aggiorna il file app/utils/session.server.ts e aggiungi la funzione getUser che ci permette di ottenere l'utente da Prisma e passarlo alla funzione di logout che userà la funzione destroySession per fare il logout dell'utente.
app/utils/session.server.ts
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import {
createCookieSessionStorage,
redirect,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "./db.server";
type LoginForm = {
username: string;
password: string;
};
export async function login({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { username },
});
if (!user) return null;
const isCorrectPassword = await bcrypt.compare(
password,
user.passwordHash
);
if (!isCorrectPassword) return null;
return { id: user.id, username };
}
const sessionSecret = process.env.SESSION_SECRET;
if (!sessionSecret) {
throw new Error("SESSION_SECRET must be set");
}
const storage = createCookieSessionStorage({
cookie: {
name: "RJ_session",
// normally you want this to be `secure: true`
// but that doesn't work on localhost for Safari
// https://web.dev/when-to-use-local-https/
secure: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
secrets: [sessionSecret],
sameSite: "lax",
path: "/",
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 30,
httpOnly: true,
},
});
function getUserSession(request: Request) {
return storage.getSession(request.headers.get("Cookie"));
}
export async function getUserId(request: Request) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") return null;
return userId;
}
export async function requireUserId(
request: Request,
redirectTo: string = new URL(request.url).pathname
) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") {
const searchParams = new URLSearchParams([
["redirectTo", redirectTo],
]);
throw redirect(`/login?${searchParams}`);
}
return userId;
}
export async function getUser(request: Request) {
const userId = await getUserId(request);
if (typeof userId !== "string") {
return null;
}
try {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { id: userId },
select: { id: true, username: true },
});
return user;
} catch {
throw logout(request);
}
}
export async function logout(request: Request) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
return redirect("/login", {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.destroySession(session),
},
});
}
export async function createUserSession(
userId: string,
redirectTo: string
) {
const session = await storage.getSession();
session.set("userId", userId);
return redirect(redirectTo, {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.commitSession(session),
},
});
}💿 Ottimo, adesso andremo ad aggiornare il file app/routes/twixes.tsx così possiamo mostrare il link alla pagina di login se l'utente non è loggato. Se invece l'utente è loggato allora mostreremo il suo nome utente e un pulsante per fare il logout.
app/routes/twixes.tsx
import type { User } from "@prisma/client";
import type { LinksFunction, LoaderFunction } from "remix";
import { Link, Outlet, useLoaderData } from "remix";
import { db } from "~/utils/db.server";
import { getUser } from "~/utils/session.server";
type LoaderData = {
user: Awaited<ReturnType<typeof getUser>>;
twixListItems: Array<{ id: string; title: string }>;
};
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
const twixListItems = await db.twix.findMany({
take: 5,
orderBy: { createdAt: "desc" },
select: { id: true, title: true },
});
const user = await getUser(request);
const data: LoaderData = {
twixListItems,
user,
};
return data;
};
export default function TwixesRoute() {
const data = useLoaderData<LoaderData>();
return (
<div className="twixes-layout">
<header className="twixes-header">
<div className="container">
<h1 className="home-link">
<Link
to="/"
title="Remix Twixes"
aria-label="Remix Twixes"
>
<span className="logo">🤪</span>
<span className="logo-medium">J🤪KES</span>
</Link>
</h1>
{data.user ? (
<div className="user-info">
<span>{`Hi ${data.user.username}`}</span>
<form action="/logout" method="post">
<button type="submit" className="button">
Logout
</button>
</form>
</div>
) : (
<Link to="/login">Login</Link>
)}
</div>
</header>
<main className="twixes-main">
<div className="container">
<div className="twixes-list">
<Link to=".">Get a random twix</Link>
<p>Here are a few more twixes to check out:</p>
<ul>
{data.twixListItems.map((twix) => (
<li key={twix.id}>
<Link to={twix.id}>{twix.title}</Link>
</li>
))}
</ul>
<Link to="new" className="button">
Add your own
</Link>
</div>
<div className="twixes-outlet">
<Outlet />
</div>
</div>
</main>
</div>
);
}Creaiamo poi una pagina di logout che quando viene visualizzata riporta direttamente in homepage, creando un file app/routes/logout.tsx:
app/routes/logout.tsx
import type { ActionFunction, LoaderFunction } from "remix";
import { redirect } from "remix";
import { logout } from "~/utils/session.server";
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
return logout(request);
};
export const loader: LoaderFunction = async () => {
return redirect("/");
};La nuova pagina logout è stata creata per facilitarci il logout - il motivo per cui stiamo usando una action (invece che usare il loader) è perché vogliamo evitare problemi di CSRF che subentrano quando usiamo una richiesta POST invece di una GET. Questo è perché il bottone di logout è un form e non un link. In aggiunta Remix richiama i loader solo quando viene eseguita una action, quindi se avessimo usato un loader non saremmo riusciti ad invalidare la cache (rischiando di avere l'utente che sembra loggato ma invece non lo è più).
Il loader viene usato solamente se una persona arriva con un link diretto alla pagina di logout e allora solo in quel caso verrà ridirezionato alla home. Guardiamo un esempio come quello sotto:
<Link to="new" className="button">
Add your own
</Link>Nota come il valore di to è "new" senza avere /. Questo è possibile grazie al nested routing, ovvero a quella struttura a cartelle con cui stiamo gestendo le pagine. Non bisogna quindi ogni volta riscrivere l'intero URL, può essere relativo - in automatico se scrivo new remix Run capisce che deve partire dalla pagina che sta visualizzando e cercare <sito web>/<pagina visualizzata>/new. Lo stesso concetto è valido per il link <Link to=".">Get a random twix</Link> che avendo il valore di to settato a ., dirà a Remix di ricaricare la pagina.
Ora che abbiamo gestito logout e login, è ora di gestire anche la registrazione di nuovi utenti.
Fortunatamente tutto quello che dobbiamo fare per supportare la registrazione è aggiornare il file app/utils/session.server.ts con la funzione register che è molto simile alla funzione login. La differenza è che ora dobbiamo usare bcrypt.hash per fare un hash della password prima di salvarla nel nostro database. Poi va aggiornata la funzione register nel file app/routes/login.tsx per gestire la registrazione.
💿 Aggiorna sia app/utils/session.server.ts che app/routes/login.tsx per gestire la registrazione utente.
app/utils/session.server.ts
import bcrypt from "bcryptjs";
import {
createCookieSessionStorage,
redirect,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "./db.server";
type LoginForm = {
username: string;
password: string;
};
export async function register({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const passwordHash = await bcrypt.hash(password, 10);
const user = await db.user.create({
data: { username, passwordHash },
});
return { id: user.id, username };
}
export async function login({
username,
password,
}: LoginForm) {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { username },
});
if (!user) return null;
const isCorrectPassword = await bcrypt.compare(
password,
user.passwordHash
);
if (!isCorrectPassword) return null;
return { id: user.id, username };
}
const sessionSecret = process.env.SESSION_SECRET;
if (!sessionSecret) {
throw new Error("SESSION_SECRET must be set");
}
const storage = createCookieSessionStorage({
cookie: {
name: "RJ_session",
// normally you want this to be `secure: true`
// but that doesn't work on localhost for Safari
// https://web.dev/when-to-use-local-https/
secure: process.env.NODE_ENV === "production",
secrets: [sessionSecret],
sameSite: "lax",
path: "/",
maxAge: 60 * 60 * 24 * 30,
httpOnly: true,
},
});
function getUserSession(request: Request) {
return storage.getSession(request.headers.get("Cookie"));
}
export async function getUserId(request: Request) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") return null;
return userId;
}
export async function requireUserId(
request: Request,
redirectTo: string = new URL(request.url).pathname
) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
const userId = session.get("userId");
if (!userId || typeof userId !== "string") {
const searchParams = new URLSearchParams([
["redirectTo", redirectTo],
]);
throw redirect(`/login?${searchParams}`);
}
return userId;
}
export async function getUser(request: Request) {
const userId = await getUserId(request);
if (typeof userId !== "string") {
return null;
}
try {
const user = await db.user.findUnique({
where: { id: userId },
select: { id: true, username: true },
});
return user;
} catch {
throw logout(request);
}
}
export async function logout(request: Request) {
const session = await getUserSession(request);
return redirect("/login", {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.destroySession(session),
},
});
}
export async function createUserSession(
userId: string,
redirectTo: string
) {
const session = await storage.getSession();
session.set("userId", userId);
return redirect(redirectTo, {
headers: {
"Set-Cookie": await storage.commitSession(session),
},
});
}app/routes/login.tsx
import type { ActionFunction, LinksFunction } from "remix";
import {
useActionData,
json,
useSearchParams,
Link,
} from "remix";
import { db } from "~/utils/db.server";
import {
createUserSession,
login,
register,
} from "~/utils/session.server";
function validateUsername(username: unknown) {
if (typeof username !== "string" || username.length < 3) {
return `Usernames must be at least 3 characters long`;
}
}
function validatePassword(password: unknown) {
if (typeof password !== "string" || password.length < 6) {
return `Passwords must be at least 6 characters long`;
}
}
type ActionData = {
formError?: string;
fieldErrors?: {
username: string | undefined;
password: string | undefined;
};
fields?: {
loginType: string;
username: string;
password: string;
};
};
const badRequest = (data: ActionData) =>
json(data, { status: 400 });
export const action: ActionFunction = async ({
request,
}) => {
const form = await request.formData();
const loginType = form.get("loginType");
const username = form.get("username");
const password = form.get("password");
const redirectTo = form.get("redirectTo") || "/twixes";
if (
typeof loginType !== "string" ||
typeof username !== "string" ||
typeof password !== "string" ||
typeof redirectTo !== "string"
) {
return badRequest({
formError: `Form not submitted correctly.`,
});
}
const fields = { loginType, username, password };
const fieldErrors = {
username: validateUsername(username),
password: validatePassword(password),
};
if (Object.values(fieldErrors).some(Boolean))
return badRequest({ fieldErrors, fields });
switch (loginType) {
case "login": {
const user = await login({ username, password });
if (!user) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `Username/Password combination is incorrect`,
});
}
return createUserSession(user.id, redirectTo);
}
case "register": {
const userExists = await db.user.findFirst({
where: { username },
});
if (userExists) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `User with username ${username} already exists`,
});
}
const user = await register({ username, password });
if (!user) {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `Something went wrong trying to create a new user.`,
});
}
return createUserSession(user.id, redirectTo);
}
default: {
return badRequest({
fields,
formError: `Login type invalid`,
});
}
}
};
export default function Login() {
const actionData = useActionData<ActionData>();
const [searchParams] = useSearchParams();
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="content" data-light="">
<h1>Login</h1>
<form method="post">
<input
type="hidden"
name="redirectTo"
value={
searchParams.get("redirectTo") ?? undefined
}
/>
<fieldset>
<legend className="sr-only">
Login o Registrazione?
</legend>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="login"
defaultChecked={
!actionData?.fields?.loginType ||
actionData?.fields?.loginType === "login"
}
/>{" "}
Login
</label>
<label>
<input
type="radio"
name="loginType"
value="register"
defaultChecked={
actionData?.fields?.loginType ===
"register"
}
/>{" "}
Iscriviti
</label>
</fieldset>
<div>
<label htmlFor="username-input">Username</label>
<input
type="text"
id="username-input"
name="username"
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.username}
aria-invalid={Boolean(
actionData?.fieldErrors?.username
)}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.username
? "username-error"
: undefined
}
/>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.username ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="username-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.username}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div>
<label htmlFor="password-input">Password</label>
<input
id="password-input"
name="password"
defaultValue={actionData?.fields?.password}
type="password"
aria-invalid={
Boolean(
actionData?.fieldErrors?.password
) || undefined
}
aria-errormessage={
actionData?.fieldErrors?.password
? "password-error"
: undefined
}
/>
{actionData?.fieldErrors?.password ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
id="password-error"
>
{actionData.fieldErrors.password}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<div id="form-error-message">
{actionData?.formError ? (
<p
className="form-validation-error"
role="alert"
>
{actionData.formError}
</p>
) : null}
</div>
<button type="submit" className="button">
Iscriviti
</button>
</form>
</div>
<div className="links">
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Homepage</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/twixes">Twixes</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
);
}Ottimo, ci siamo - ora gli utenti potranno registrarsi e creare il loro account! Prova per credere 👀
| Capitolo precedente | Capitolo successivo |
|---|---|
| ◀︎ 05-mutations | 07-unexpected-errors ▶︎ |