You have an undirected, connected graph of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given an array graph where graph[i] is a list of all the nodes connected with node i by an edge.
Return the length of the shortest path that visits every node. You may start and stop at any node, you may revisit nodes multiple times, and you may reuse edges.
Example 1:
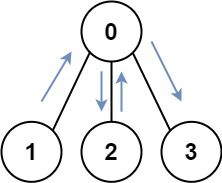
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0],[0],[0]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [1,0,2,0,3]
Example 2:
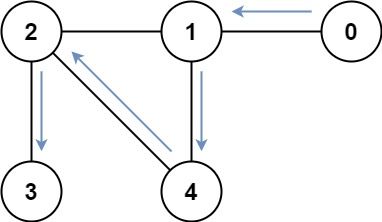
Input: graph = [[1],[0,2,4],[1,3,4],[2],[1,2]] Output: 4 Explanation: One possible path is [0,1,4,2,3]
Constraints:
n == graph.length1 <= n <= 120 <= graph[i].length < ngraph[i]does not containi.- If
graph[a]containsb, thengraph[b]containsa. - The input graph is always connected.
Because each edge has the same weight, the shortest path can be solution by using BFS, and the access of the point can be recorded by state compression.
class Solution:
def shortestPathLength(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(graph)
dst = -1 ^ (-1 << n)
q = deque()
vis = [[False] * (1 << n) for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
q.append((i, 1 << i, 0))
vis[i][1 << i] = True
while q:
u, state, dis = q.popleft()
for v in graph[u]:
nxt = state | (1 << v)
if nxt == dst:
return dis + 1
if not vis[v][nxt]:
q.append((v, nxt, dis + 1))
vis[v][nxt] = True
return 0A* search:
class Solution:
def shortestPathLength(self, graph: List[List[int]]) -> int:
n = len(graph)
def f(state):
return sum(((state >> i) & 1) == 0 for i in range(n))
q = []
dist = [[inf] * (1 << n) for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
heappush(q, (f(1 << i), i, 1 << i))
dist[i][1 << i] = 0
while q:
_, u, state = heappop(q)
if state == (1 << n) - 1:
return dist[u][state]
for v in graph[u]:
nxt = state | (1 << v)
if dist[v][nxt] > dist[u][state] + 1:
dist[v][nxt] = dist[u][state] + 1
heappush(q, (dist[v][nxt] + f(nxt), v, nxt))
return 0class Solution {
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
int n = graph.length;
int dst = -1 ^ (-1 << n);
Queue<Tuple> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
boolean[][] vis = new boolean[n][1 << n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
queue.offer(new Tuple(i, 1 << i, 0));
vis[i][1 << i] = true;
}
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Tuple t = queue.poll();
int u = t.u, state = t.state, dis = t.dis;
for (int v : graph[u]) {
int next = state | (1 << v);
if (next == dst) {
return dis + 1;
}
if (!vis[v][next]) {
queue.offer(new Tuple(v, next, dis + 1));
vis[v][next] = true;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private static class Tuple {
int u;
int state;
int dis;
public Tuple(int u, int state, int dis) {
this.u = u;
this.state = state;
this.dis = dis;
}
}
}A* search:
class Solution {
private int n;
public int shortestPathLength(int[][] graph) {
n = graph.length;
int[][] dist = new int[n][1 << n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
Arrays.fill(dist[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
PriorityQueue<int[]> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
q.offer(new int[] {f(1 << i), i, 1 << i});
dist[i][1 << i] = 0;
}
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int u = p[1], state = p[2];
if (state == (1 << n) - 1) {
return dist[u][state];
}
for (int v : graph[u]) {
int nxt = state | (1 << v);
if (dist[v][nxt] > dist[u][state] + 1) {
dist[v][nxt] = dist[u][state] + 1;
q.offer(new int[] {dist[v][nxt] + f(nxt), v, nxt});
}
}
}
return 0;
}
private int f(int state) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (((state >> i) & 1) == 0) {
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}type tuple struct {
u int
state int
dis int
}
func shortestPathLength(graph [][]int) int {
n := len(graph)
dst := -1 ^ (-1 << n)
q := make([]tuple, 0)
vis := make([][]bool, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
vis[i] = make([]bool, 1<<n)
q = append(q, tuple{i, 1 << i, 0})
vis[i][1<<i] = true
}
for len(q) > 0 {
t := q[0]
q = q[1:]
cur, state, dis := t.u, t.state, t.dis
for _, v := range graph[cur] {
next := state | (1 << v)
if next == dst {
return dis + 1
}
if !vis[v][next] {
q = append(q, tuple{v, next, dis + 1})
vis[v][next] = true
}
}
}
return 0
}class Solution {
public:
int shortestPathLength(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
int n = graph.size();
queue<tuple<int, int, int>> q;
vector<vector<bool>> vis(n, vector<bool>(1 << n));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
q.emplace(i, 1 << i, 0);
vis[i][1 << i] = true;
}
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [u, state, dist] = q.front();
q.pop();
if (state == (1 << n) - 1) return dist;
for (int& v : graph[u]) {
int nxt = state | (1 << v);
if (!vis[v][nxt]) {
q.emplace(v, nxt, dist + 1);
vis[v][nxt] = true;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
};A* search:
class Solution {
public:
int n;
int shortestPathLength(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
n = graph.size();
priority_queue<tuple<int, int, int>, vector<tuple<int, int, int>>, greater<tuple<int, int, int>>> q;
vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(1 << n, INT_MAX));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
q.push({f(1 << i), i, 1 << i});
dist[i][1 << i] = 0;
}
while (!q.empty())
{
auto [_, u, state] = q.top();
q.pop();
if (state == (1 << n) - 1) return dist[u][state];
for (int v : graph[u])
{
int nxt = state | (1 << v);
if (dist[v][nxt] > dist[u][state] + 1)
{
dist[v][nxt] = dist[u][state] + 1;
q.push({dist[v][nxt] + f(nxt), v, nxt});
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int f(int state) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (((state >> i) & 1) == 0)
++ans;
return ans;
}
};