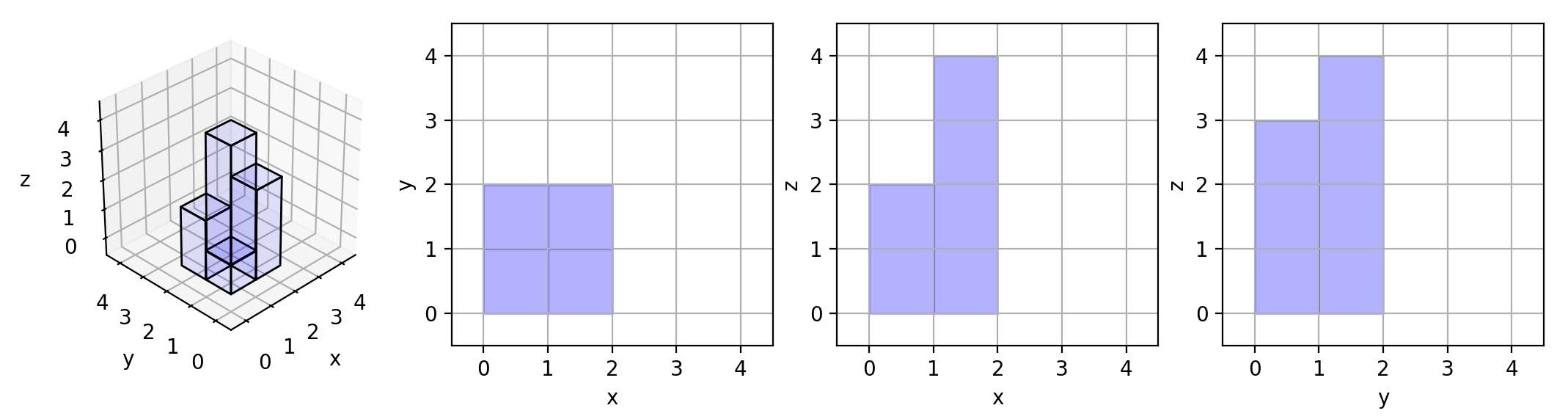
在 n x n 的网格 grid 中,我们放置了一些与 x,y,z 三轴对齐的 1 x 1 x 1 立方体。
每个值 v = grid[i][j] 表示 v 个正方体叠放在单元格 (i, j) 上。
现在,我们查看这些立方体在 xy 、yz 和 zx 平面上的投影。
投影 就像影子,将 三维 形体映射到一个 二维 平面上。从顶部、前面和侧面看立方体时,我们会看到“影子”。
返回 所有三个投影的总面积 。
示例 1:
输入:[[1,2],[3,4]] 输出:17 解释:这里有该形体在三个轴对齐平面上的三个投影(“阴影部分”)。
示例 2:
输入:grid = [[2]] 输出:5
示例 3:
输入:[[1,0],[0,2]] 输出:8
提示:
n == grid.length == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
根据题意:
- xy 表示 grid 中大于 0 的元素个数
- yz 表示 grid 每一行的最大值之和
- zx 表示 grid 每一列的最大值之和
遍历 grid,更新 xy, yz, zx。遍历结束返回 xy + yz + zx。
class Solution:
def projectionArea(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
xy = sum(v > 0 for row in grid for v in row)
yz = sum(max(row) for row in grid)
zx = sum(max(col) for col in zip(*grid))
return xy + yz + zxclass Solution {
public int projectionArea(int[][] grid) {
int xy = 0, yz = 0, zx = 0;
for (int i = 0, n = grid.length; i < n; ++i) {
int maxYz = 0;
int maxZx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (grid[i][j] > 0) {
++xy;
}
maxYz = Math.max(maxYz, grid[i][j]);
maxZx = Math.max(maxZx, grid[j][i]);
}
yz += maxYz;
zx += maxZx;
}
return xy + yz + zx;
}
}function projectionArea(grid: number[][]): number {
const n = grid.length;
let res = grid.reduce(
(r, v) => r + v.reduce((r, v) => r + (v === 0 ? 0 : 1), 0),
0,
);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let xMax = 0;
let yMax = 0;
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
xMax = Math.max(xMax, grid[i][j]);
yMax = Math.max(yMax, grid[j][i]);
}
res += xMax + yMax;
}
return res;
}impl Solution {
pub fn projection_area(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let n = grid.len();
let mut res = 0;
let mut x_max = vec![0; n];
let mut y_max = vec![0; n];
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
let val = grid[i][j];
if val == 0 {
continue;
}
res += 1;
x_max[i] = x_max[i].max(val);
y_max[j] = y_max[j].max(val);
}
}
res + y_max.iter().sum::<i32>() + x_max.iter().sum::<i32>()
}
}class Solution {
public:
int projectionArea(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int xy = 0, yz = 0, zx = 0;
for (int i = 0, n = grid.size(); i < n; ++i) {
int maxYz = 0, maxZx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
xy += grid[i][j] > 0;
maxYz = max(maxYz, grid[i][j]);
maxZx = max(maxZx, grid[j][i]);
}
yz += maxYz;
zx += maxZx;
}
return xy + yz + zx;
}
};func projectionArea(grid [][]int) int {
xy, yz, zx := 0, 0, 0
for i, row := range grid {
maxYz, maxZx := 0, 0
for j, v := range row {
if v > 0 {
xy++
}
maxYz = max(maxYz, v)
maxZx = max(maxZx, grid[j][i])
}
yz += maxYz
zx += maxZx
}
return xy + yz + zx
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}