Expand is a parallel file system based on standard servers. This section describes the work developed to convert Expand into an ad-hoc parallel file system.
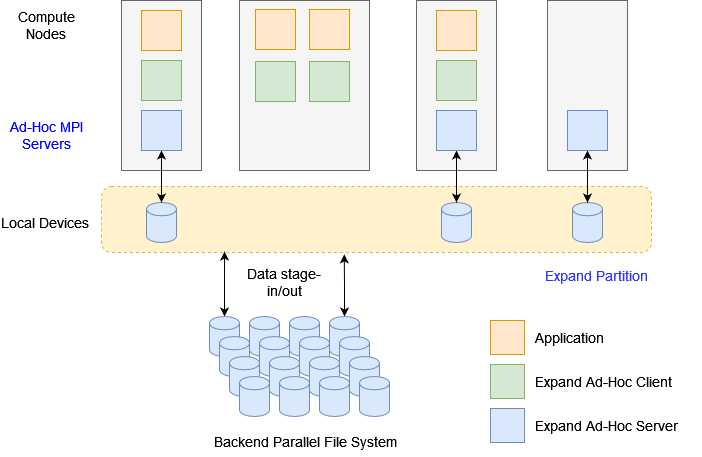
The next figure shows the structure of Expand as an ad-hoc parallel file system. This structure is based on a series of data servers running on the compute nodes that communicate with each other using MPI. The use of MPI facilitates the standardization of Expand and its use in HCP environments.
Parallel data partitions are created on the ad-hoc servers on the local storage devices (HDD or SSD) using the services provided by the local operating system. The applications are deployed on the compute nodes and communicate with the Expand servers also using MPI. As can be seen in the figure, applications can be deployed on nodes without ad-hoc servers and servers can be deployed on nodes where no applications are running.
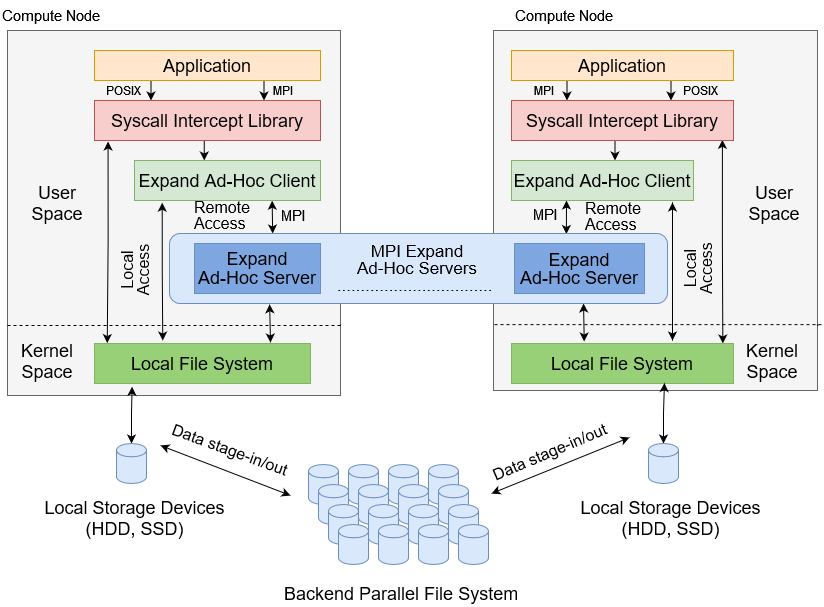
The next figure shows the internal details of the Expand as ad-hoc parallel file system. Next section describes some aspects of Expand design.
Expand combines several Expand MPI ad-hoc servers (see the previous figure) in order to provide a generic parallel partition. Each server provide one or more directories that are combined to build a distributed partition to use in compute nodes. All files in the system are striped across all ad-hoc servers to facilitate parallel access, with each server storing conceptually a subfile of the parallel file.
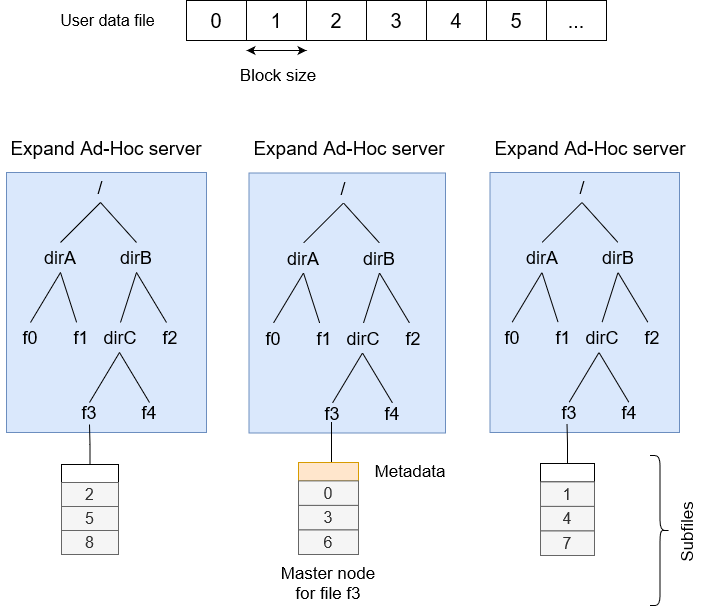
A file consists in several subfiles, one for each ad-hoc server. All subfiles are fully transparent to the Expand users. On a parallel partition, the user can create stripped files with cyclic layout. In these files, blocks are distributed across the partition following a round-robin pattern. This structure is shown in the next figure. In this figure the user data file is the file stored in Expand and the block size is the used in Expand for distributed the blocks among all servers. This block size is independent of the structure used in the backend parallel file system.
Partitions in Expand are defined using a small configuration file. For example, the following configuration file defines a partition with two ad-hoc servers and an block size of 512 KB. For each server, a directory must be specified. All files will be storage in this directory.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="ISO-8859-1"?>
<xpn_conf>
<partition name="xpn" type="NORMAL" bsize="512k" >
<data_node id="<node ID>" url="mpiServer://<server name or IP>/<storage path1>">
<data_node id="<node ID>" url="mpiServer://<server name or IP>/<storage path1>">
</partition>
</xpn_conf>Each subfile of a Expand file (see the previous figure) has a small header at the beginning of the subfile. This header stores the file’s metadata. This metadata includes the following information: stride size, base node, that identifies the ad-hoc server where the first block of the file resides and the file distribution pattern used. By the moment, we only use files with cyclic layout.
All subfiles have a header for metadata, although only one node, called master node (described below) stores the current metadata. The master node can be different from the base node. To simplify the naming process and reduce potential bottlenecks, Expand does not use any metadata manager. The previous figure shows how directory mapping is made in Expand.
The metadata of a file resides in the header of a subfile stored in an ad-hoc server. This server is the master node of the file. To obtain this node the file name is hashed into the number of node.
Because the determination of the master node is based on the file name, when a user renames a file, the master node for that file changes. The algorithm used in Expand to rename a file is as follows:
rename(oldname, newname) {
oldmaster = hash(oldname)
newmaster = hash(newname)
move the metadata from oldmaster to newmaster
}All file operations in Expand use a virtual filehandle. This virtual filehandle is the reference used in Expand to reference all operations. When Expand needs to access to a subfile, it uses the appropriated filehandle. To enhance I/O, user requests are split by the Expand library into parallel subrequests sent to the involved servers. When a request involves k ad-hoc servers, Expand issues k requests in parallel to the servers, using threads to parallelize the operations. The same criteria is used in all Expand operations. A parallel operation to k servers is divided in k individual operations that are provided by ad-hoc servers.
Data stage-in operations are perfomed in parallel from the backend parallel file system to the ad-hoc servers without the intervention of any client application. Each server builds the corresponding subfile in its local storage space, reading the data from the file stored on the backend file system. This operation is performed in parallel in all ad-hoc servers.
In the same way, data stage-out are performed in parallel. Each server writes the blocks stored in his local subfile to the final file of the backend parallel file system.
Although these operations could be performed using a normal POSIX application, we have developed two new system calls that allow these operations to be performed directly from the servers with improved performance. This system calls are:
- Preload. Copy a file from the backend file system to the Expand partition.
- Flush. Write a file from the Expand partition to the final backend file system.
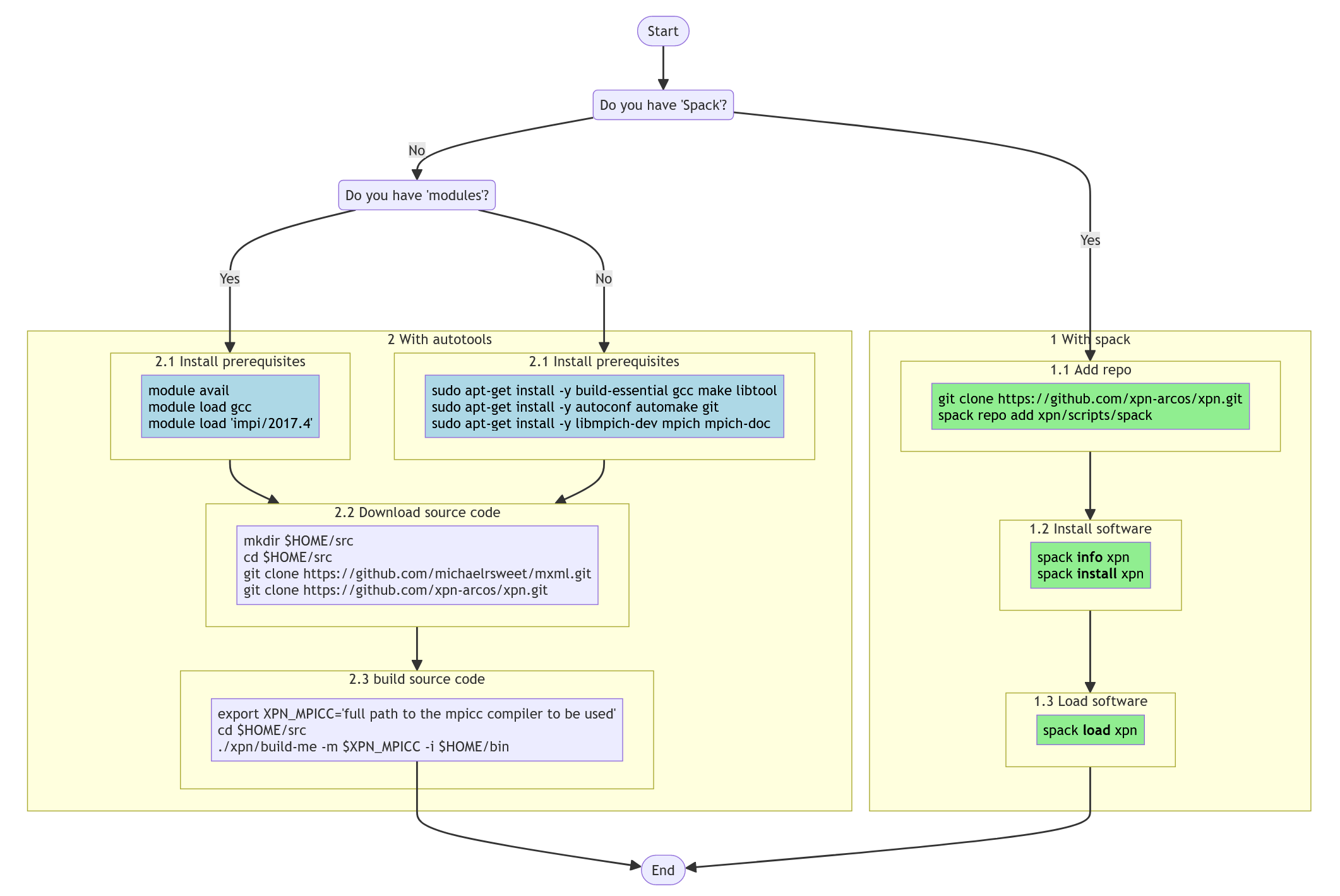
The typical executions has 3 main steps:
- First, launch the Expand MPI server (xpn_mpi_server):
./xpn -v \ -n <number of processes> -l <full path to the hostfile> \ -w <shared directory among hostfile computers, $HOME for example> \ -x <local directory on each node to be used, /tmp for example> \ start - Then, launch the program that will use Expand (XPN client):
2.1. Example for the app1 MPI application:2.2. Example for the app2 program (a NON-MPI application):mpiexec -np <number of processes> \ -hostfile <full path to the hostfile> \ -genv XPN_DNS <nameserver file> \ -genv XPN_CONF <XPN configuration file> \ -genv LD_LIBRARY_PATH <INSTALL_PATH>/mxml/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH \ -genv LD_PRELOAD <INSTALL_PATH>/xpn/lib/xpn_bypass.so:$LD_PRELOAD \ <full path to app1>/app1
2.3. Example for the app3 Python program:export XPN_DNS=<full path to the nameserver file> export XPN_CONF=<full path to the XPN configuration file> LD_PRELOAD=<INSTALL_PATH>/xpn/lib/xpn_bypass.so <full path to app2>/app2
export XPN_DNS=<full path to the nameserver file> export XPN_CONF=<full path to the XPN configuration file> LD_PRELOAD=<INSTALL_PATH>/xpn/lib/xpn_bypass.so python3 <full path to app3>/app3
- At the end of your working session, you need to stop the MPI server (xpn_mpi_server):
./xpn -v -l <full path to the hostfile> stop
- Q: Where is the source code of Expand?
- A: https://github.com/xpn-arcos/xpn
- Q: under what license is it released?
- A: GPLv3.0
-
A new Ad-Hoc parallel file system for HPC environments based on the Expand parallel file system DOI
In 22nd International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Computing (ISPDC) 2023,
Authors: Diego Camarmas-Alonso, Félix García-Carballeira, Alejandro Calderón-Mateos, Jesús Carretero Pérez -
Evaluación de rendimiento del sistema de ficheros paralelo Expand Ad-Hoc en MareNostrum 4 DOI
Jornadas Sarteco 2023,
Authors: Diego Camarmas-Alonso, Félix García-Carballeira, Alejandro Calderón-Mateos, Jesús Carretero Pérez -
Sistema de almacenamiento Ad-Hoc para entornos HPC basado en el sistema de ficheros paralelo Expand DOI
Jornadas Sarteco 2022,
Authors: Diego Camarmas-Alonso, Félix García-Carballeira, Alejandro Calderón-Mateos, Jesús Carretero Pérez -
The design of the Expand parallel file system DOI
The International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications 2003,
Authors: Felix Garcia-Carballeira, Alejandro Calderon-Mateos, Jesus Carretero, Javier Fernandez, Jose M Perez -
An implementation of MPI-IO on Expand: A parallel file system based on NFS servers DOI
In European Parallel Virtual Machine/Message Passing Interface Users’ Group Meeting 2002,
Authors: Alejandro Calderon-Mateos, Felix Garcia-Carballeira, Jesus Carretero, Jose M Perez, Javier Fernandez
The following list includes the updates and progress for ad-hoc Expand version:
- New version of the system call interception library.
- New ad-hoc Expand server developed.
- New ad-hoc Expand client developed.
- New installation manual.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Félix García Carballeira | Alejandro Calderón Mateos | Diego Camarmas Alonso | Luis Miguel Sánchez García | Borja Bergua Guerra | Jesús Carretero Pérez |